Sardine
.jpg)
"Sardine" and "pilchard" are common names used to refer to various small, oily fish in the herring family Clupeidae.[2] The term "sardine" was first used in English during the early 15th century and may come from the Mediterranean island of Sardinia, around which sardines were once abundant.[3][4]
The terms "sardine" and "pilchard” are not precise, and what is meant depends on the region. The United Kingdom's Sea Fish Industry Authority, for example, classifies sardines as young pilchards.[5] One criterion suggests fish shorter in length than 15 cm (6 in) are sardines, and larger fish are pilchards.[6] The FAO/WHO Codex standard for canned sardines cites 21 species that may be classed as sardines;[7] FishBase, a comprehensive database of information about fish, calls at least six species "pilchard", over a dozen just "sardine", and many more with the two basic names qualified by various adjectives.
Etymology
'Sardine' first appeared in English in the 15th century, a loanword from French sardine; derived from Latin sardina, from Ancient Greek σαρδίνη (sardínē) or σαρδῖνος (sardínos),[8] said to be from the Greek "Sardò" (Σαρδώ), indicating the island of Sardinia. Athenaios quotes a passage from Aristotle mentioning the fish sardinos, referring to the sardine or pilchard.[9] However, Sardinia is around 800 miles (1300 km) distant from Athens: Ernest Klein in his Etymological Dictionary of the English Language (1971) says: "It is hardly probable that the Greeks would have obtained fish from so far as Sardinia at a time relatively so early as that of Aristotle".[10]
The flesh of some sardines or pilchards is a reddish-brown colour similar to some varieties of red sardonyx or sardine stone: this word derives from σαρδῖον (sardion), from a root meaning 'red', apparently cognate with Sardis, the capital of ancient Lydia (now western Turkey) where it was obtained.[11]
The phrase "packed like sardines" (in a tin) is recorded from 1911.[10]
Genera
| This article is part of a series on |
| Commercial fish |
|---|
| Large pelagic |
| Forage |
| Demersal |
| Mixed |
Sardines occur in several genera
- Genus Dussumieria
- Rainbow sardine (Dussumieria acuta)
- Slender rainbow sardine (Dussumieria elopsoides)
- Genus Escualosa
- Slender white sardine (Escualosa elongata)
- White sardine (Escualosa thoracata)
- Genus Sardina
- European pilchard (true sardine) (Sardina pilchardus)
- Genus Sardinella
- Goldstripe sardinella (Sardinella gibbosa)
- Indian oil sardine (Sardinella longiceps)
- Round sardinella (Sardinella aurita)
- Genus Sardinops
- South American pilchard (Sardinops sagax)
Species
| Commercially significant species | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Common name | Scientific name | Max. length | Common length | Max. mass | Max. age years |
Trophic level |
Fish Base |
FAO | ITIS | IUCN status | |||
| cm | in | cm | in | g | oz | |||||||||
| Sardina | European pilchard* | Sardina pilchardus (Walbaum, 1792) | 27.5 | 10.8 | 20.0 | 7.9 | 15 | 3.05 | [12] | [13] | [14] | |||
| Sardinops | South American pilchard | Sardinops sagax (Jenyns, 1842) | 39.5 | 15.6 | 20.0 | 7.9 | 490 | 17 | 25 | 2.43 | [15] | [16] | [17] | |
| Japanese pilchard[note 1] | Sardinops melanostictus (Schlegel, 1846) | [19] | [20] | [21] | ||||||||||
| Californian pilchard[note 1] | Sardinops caeruleus (Girard, 1854) | [22] | [23] | [24] | ||||||||||
| southern African pilchard[note 1] | Sardinops ocellatus (Pappe, 1854) | [25] | [26] | [27] | ||||||||||
| Sardinella | Bali sardinella | Sardinella lemuru (Bleeker, 1853) | 23 | 9.1 | 20 | 7.9 | [28] | [29] | [30] | |||||
| Brazilian sardinella | Sardinella brasiliensis (Steindachner, 1879) | 3.10 | [31] | [32] | [33] | |||||||||
| Japanese sardinella | Sardinella zunasi (Bleeker, 1854) | 3.12 | [34] | [35] | [36] | |||||||||
| Indian oil sardine | Sardinella longiceps (Valenciennes, 1847) | 2.41 | [37] | [38] | [39] | [40] | ||||||||
| Goldstripe sardinella | Sardinella gibbosa (Bleeker, 1849) | 2.85 | [41] | [42] | [43] | |||||||||
| Round sardinella | Sardinella aurita (Valenciennes, 1847) | 3.40 | [44] | [45] | [46] | |||||||||
| Madeiran sardinella | Sardinella maderensis (Lowe, 1839) | 3.20 | [47] | [48] | [49] | |||||||||
| Dussumieria | Rainbow sardine | Dussumieria acuta (Valenciennes, 1847) | 20 | 7.9 | 3.40 | [50] | [51] | [52] | ||||||
 The European pilchard, Sardina pilchardus
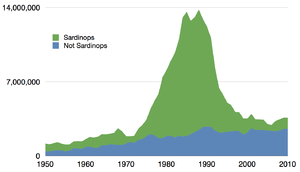
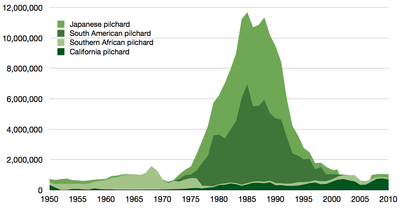
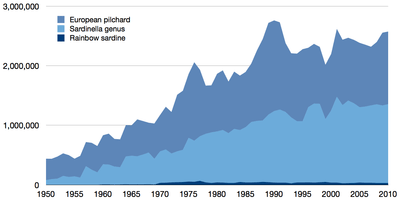
The European pilchard, Sardina pilchardus In the 1980s the South American pilchard, Sardinops sagax, was the most intensively fished species of sardine. Some major stocks declined precipitously in the 1990s (see chart below).
In the 1980s the South American pilchard, Sardinops sagax, was the most intensively fished species of sardine. Some major stocks declined precipitously in the 1990s (see chart below). The Pacific sardine, Sardinops sagax caerulea
The Pacific sardine, Sardinops sagax caerulea
Feeding
Sardines feed almost exclusively on zooplankton, "animal plankton", and congregate wherever this is abundant.
Fisheries
Typically, sardines are caught with encircling nets, particularly purse seines. Many modifications of encircling nets are used, including traps or weirs. The latter are stationary enclosures composed of stakes into which schools of sardines are diverted as they swim along the coast. The fish are caught mainly at night, when they approach the surface to feed on plankton. After harvesting, the fish are submerged in brine while they are transported to shore.
Sardines are commercially fished for a variety of uses: for bait; for immediate consumption; for drying, salting, or smoking; and for reduction into fish meal or oil. The chief use of sardines is for human consumption, but fish meal is used as animal feed, while sardine oil has many uses, including the manufacture of paint, varnish, and linoleum.
As food
Sardines are commonly consumed by human beings. Fresh sardines are often grilled, pickled, or smoked, or preserved in cans.
Sardines are rich in vitamins and minerals.[53] A small serving of sardines once a day can provide 13% of vitamin B2; roughly one-quarter of niacin; and about 150% of the recommended daily value of vitamin B12. All B vitamins help to support proper nervous system function and are used for energy metabolism, or converting food into energy.[54] Also, sardines are high in the major minerals such as phosphorus, calcium, and potassium, and some trace minerals including iron and selenium. Sardines are also a natural source of marine omega-3 fatty acids, which may reduce the occurrence of cardiovascular disease.[55] Regular consumption of omega-3 fatty acids may reduce the likelihood of developing Alzheimer's disease.[56] These fatty acids can also lower blood sugar levels.[57] They are also a good source of vitamin D,[58] calcium, vitamin B12,[59][60] and protein.
Because they are low in the food chain, sardines are very low in contaminants, such as mercury, relative to other fish commonly eaten by humans.[61]
History
History of sardine fishing in the UK
Pilchard fishing and processing became a thriving industry in Cornwall (UK) from around 1750 to around 1880, after which it went into decline. Catches varied from year to year, and in 1871, the catch was 47,000 hogsheads, while in 1877, only 9,477 hogsheads. A hogshead contained 2,300 to 4,000 pilchards, and when filled with pressed pilchards, weighed 476 lbs. The pilchards were mostly exported to Roman Catholic countries such as Italy and Spain, where they are known as fermades. The chief market for the oil was Bristol, where it is used on machinery.[62] Since 1997, sardines from Cornwall have been sold as "Cornish sardines", and since March 2010, under EU law, Cornish sardines have Protected Geographical Status.[63] The industry has featured in numerous works of art, particularly by Stanhope Forbes and other Newlyn School artists.
The traditional "Toast to Pilchards" refers to the lucrative export of the fish to Catholic Europe:
History of sardine fishing in the United States
In the United States, the sardine canning industry peaked in the 1950s. Since then, the industry has been on the decline. The canneries in Monterey Bay, in what was known as Cannery Row (where John Steinbeck's novel of the same name was set), failed in the mid-1950s. The last large sardine cannery in the United States, the Stinson Seafood plant in Prospect Harbor, Maine, closed its doors on 15 April 2010 after 135 years in operation.[65]
In April 2015 the Pacific Fishery Management Council voted to direct NOAA Fisheries Service to halt the current commercial season in Oregon, Washington and California, because of a dramatic collapse in Pacific sardine stocks. The ban affected about 100 fishing boats with sardine permits, although far fewer were actively fishing at the time. The season normally would end June 30.[66] The ban was expected to last for more than a year, and was still in place in March 2018.[67]
In popular culture
The manner in which sardines can be packed in a can has led to the popular English language saying "packed like sardines", which is used to metaphorically describe situations where people or objects are crowded closely together.[68] The British poet and comic Spike Milligan satirises this in his poem "Sardine Submarine", where a sardine's mother describes the unfamiliar sight of a submarine to its offspring as "a tin full of people".[69]
Sardines is also the name of a children's game, where one person hides and each successive person who finds the hidden one packs into the same space until only one is left out, who becomes the next one to hide.[70]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 "FAO Fisheries & Aquaculture - FI fact sheet search". www.fao.org. Archived from the original on 8 May 2009. Retrieved 2018-08-10.
- ↑ "What's an oily fish?". Food Standards Agency. 24 June 2004. Archived from the original on 10 December 2010.
- ↑ "Sardine | Origin and meaning of sardine by Online Etymology Dictionary". www.etymonline.com. Retrieved 2018-08-10. Archived 22 August 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Sardine". The Good Food Glossary. BBC Worldwide. 2009. Archived from the original on 12 October 2008. Retrieved 1 November 2009.
- ↑ "FAQs". Seafish. Archived from the original on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 22 February 2010.
- ↑ Stummer, Robin (17 August 2003). "Who are you calling pilchard? It's 'Cornish sardine' to you..." The Independent. Archived from the original on 12 September 2010. Retrieved 1 November 2009.
- ↑ "Codex standard for canned sardines and sardine-type products codex stan 94 –1981 REV. 1–1995" (PDF). Codex Alimentarius. FAO/WHO Codex Alimentarius Commission. pp. 1–7. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 March 2007. Retrieved 18 January 2007.
- ↑ "sardine". Wiktionary. Retrieved 28 March 2018.
- ↑ "σαρδίνη". The Online Liddell-Scott-Jones Greek-English Lexicon. Retrieved 28 March 2018.
- 1 2 "sardine (n.)". Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 28 March 2018.
- ↑ "Sardius, Sardine". Vine's Expository Dictionary of NT Words (1940), hosted at StudyLight.org. Retrieved 28 March 2018.
- ↑ Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2012). "Sardina pilchardus" in FishBase. April 2012 version.
- ↑ "Sardina pilchardus". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2018-08-10. Walbaum, 1792) Archived 25 July 2012 at the Wayback Machine. FAO, Species Fact Sheet. Retrieved April 2012.
- ↑ "Sardina pilchardus". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved April 11, 2012.
- ↑ Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2012). "Sardinops sagax" in FishBase. April 2012 version.
- ↑ "Sardinops sagax". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2018-08-10. (Jenyns, 1842) Archived 29 July 2012 at the Wayback Machine. FAO, Species Fact Sheet. Retrieved April 2012.
- ↑ "Sardinops sagax". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved April 11, 2012.
- ↑ Grant, W. S.; et al. (1998). "Why restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of mitochondrial DNA failed to resolve sardine (Sardinops) biogeography: insights from mitochondrial DNA cytochrome b sequences". Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences. 55 (12): 2539–47. doi:10.1139/f98-127.
- ↑ Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2012). "Sardinops melanostictus" in FishBase. April 2012 version.
- ↑ Schlegel (1846). "Sardinops melanostictus". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2018-08-10. Archived 24 September 2015 at the Wayback Machine. FAO, Species Fact Sheet. Retrieved April 2012.
- ↑ "Sardinops melanostictus". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved April 11, 2012.
- ↑ Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2012). "Sardinops caeruleus" in FishBase. April 2012 version.
- ↑ "Sardinops caeruleus". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2018-08-10. (Girard, 1854) Archived 14 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine. FAO, Species Fact Sheet. Retrieved April 2012.
- ↑ "Sardinops caeruleus". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved April 11, 2012.
- ↑ Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2012). "Sardinops ocellatus" in FishBase. April 2012 version.
- ↑ "Sardinops ocellatus". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2018-08-10. (Pappe, 1854) Archived 2012-12-13 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Sardinops ocellatus". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved April 11, 2012.
- ↑ Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2012). "Sardinella lemuru" in FishBase. April 2012 version.
- ↑ "Sardinella lemuru". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2018-08-10. Archived 13 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Sardinella lemuru". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved April 11, 2012.
- ↑ Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2012). "Sardinella brasiliensis" in FishBase. April 2012 version.
- ↑ "Sardinella brasiliensis". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2018-08-10. (Steindachner, 1879) Archived 7 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Sardinella brasiliensis". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved April 11, 2012.
- ↑ Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2012). "Sardinella zunasi" in FishBase. April 2012 version.
- ↑ "Sardinella zunasi". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2018-08-10. (Bleeker, 1854) Archived 13 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine. FAO, Species Fact Sheet. Retrieved April 2012.
- ↑ "Sardinella zunasi". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved April 11, 2012.
- ↑ Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2012). "Sardinella longiceps" in FishBase. April 2012 version.
- ↑ "Sardinella longiceps". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2018-08-10. (Valenciennes, 1847) Archived 8 May 2012 at the Wayback Machine. FAO, Species Fact Sheet. Retrieved April 2012.
- ↑ "Sardinella longiceps". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved April 11, 2012.
- ↑ Munroe TA & Priede IG (2010). "Sardinella longiceps". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. IUCN. 2010: e.T154989A115258997. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2010-4.RLTS.T154989A4684198.en. Archived from the original on 9 June 2017. Retrieved 25 December 2017.
- ↑ Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2012). "Sardinella gibbosa" in FishBase. April 2012 version.
- ↑ "Sardinella gibbosa". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2018-08-10. (Bleeker, 1849) Archived 1 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine. FAO, Species Fact Sheet. Retrieved April 2012.
- ↑ "Sardinella gibbosa". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved April 11, 2012.
- ↑ Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2012). "Sardinella aurita" in FishBase. April 2012 version.
- ↑ "Sardinella aurita". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2018-08-10. (Valenciennes, 1847) Archived 7 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine. FAO, Species Fact Sheet. Retrieved April 2012.
- ↑ "Sardinella aurita". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved April 11, 2012.
- ↑ Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2012). "Sardinella maderensis" in FishBase. April 2012 version.
- ↑ "Sardinella maderensis". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2018-08-10. (Lowe, 1839) Archived 14 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine. FAO, Species Fact Sheet. Retrieved April 2012.
- ↑ "Sardinella maderensis". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved April 11, 2012.
- ↑ Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2012). "Dussumieria acuta" in FishBase. April 2012 version.
- ↑ "Dussumieria acuta". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2018-08-10. (Valenciennes, 1847) Archived 13 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine. FAO, Species Fact Sheet. Retrieved April 2012.
- ↑ "Dussumieria acuta". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved April 11, 2012.
- ↑ "Fish, sardine, Pacific, canned in tomato sauce, drained solids with bone". USDA Food Composition Databases. May 2016. Archived from the original on 28 March 2017. Retrieved 27 March 2017.
- ↑ Campbell, Meg. "Are Sardines a Good Source of Calcium?". LIVESTRONG.COM. Retrieved 2018-08-10. Archived 18 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Kris-Etherton; Harris, WS; Appel, LJ; American Heart Association. Nutrition Committee; et al. (November 2002). "Fish Consumption, Fish Oil, Omega-3 Fatty Acids, and Cardiovascular Disease". Circulation. 106 (21): 2747–2757. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000038493.65177.94. PMID 12438303.
- ↑ Johnson, Sharon (6 November 2007). "Oily brain food ... Yum". The Mail Tribune. Archived from the original on 8 August 2010. Retrieved 1 November 2009.
- ↑ "Omega-3 fatty acids, fish oil, alpha-linolenic acid: MedlinePlus Supplements". Archived from the original on 8 February 2006. Retrieved January 22, 2010.
Fish oil supplements may lower blood sugar levels a small amount. Caution is advised when using herbs or supplements that may also lower blood sugar. Blood glucose levels may require monitoring, and doses may need adjustment.
- ↑ "Vitamin D and Healthy Bones". New York State Health Department. November 2003. Archived from the original on 18 August 2010. Retrieved 1 November 2009.
- ↑ "Vitamin B12". George Mateljan Foundation. Archived from the original on 19 April 2012. Retrieved 11 April 2012.
- ↑ "Vitamin B12". EatingWell. Archived from the original on 12 April 2012. Retrieved 11 April 2012.
- ↑ "Mercury Levels in Commercial Fish and Shellfish". U S Food and Drug Administration. 5 July 2009. Archived from the original on 24 October 2011. Retrieved 1 November 2009.
- ↑ Buckland, Frank (26 February 1880). "Our Fisheries". The Cornishman (85). p. 6.
- ↑ "EU Directory of PGI/PDO/TSG – Cornish Sardines profile". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 2018-08-10. Archived 4 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine. (accessed 1/11/2010)
- ↑ Traditional Cornish Stories and Rhymes, 1992 edition, Lodenek Press
- ↑ Canfield, Clarke (15 April 2010). "Last sardine plant in U.S. shuts its doors". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 17 April 2010. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- ↑ "Feds Cancel Commercial Sardine Fishing After Stocks Crash". North Country Public Radio, St. Lawrence University, Canton, New York. April 16, 2015. Retrieved 28 March 2018.
- ↑ "Pacific Sardine". NOAA Fisheries. Retrieved 28 March 2018.
- ↑ "packed like sardines | Definition of packed like sardines in English by Oxford Dictionaries". Oxford Dictionaries | English. Retrieved 2018-08-10. Archived 11 October 2017 at the Wayback Machine., Oxford English Dictionary. Accessed 11 October 2017.
- ↑ "Even More Spike Milligan Side Splitters". tostevin.net. 2012-07-13. Retrieved 2018-08-10. </Archived 23 February 2014 at the Wayback Machine. Tostevin.net (2012-07-13). Retrieved 2014-02-12.
- ↑ "Stinky Sardine Club – ITPedia". Itpedia.nyu.edu. 9 April 2010. Archived from the original on 29 November 2014. Retrieved 21 June 2012.
Further reading
- Parrish, R. H.; et al. (1989). "The monotypic sardines, Sardina and Sardinops: Their taxonomy, distribution, stock structure, and zoogeography" (PDF). Can.J.Fish.Aquar.Sci. 46 (11): 2019–36. doi:10.1139/f89-251.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sardines. |

.png)
