Succinyl-CoA:3-oxoacid CoA transferase deficiency
| Succinyl-CoA:3-oxoacid CoA transferase deficiency | |
|---|---|
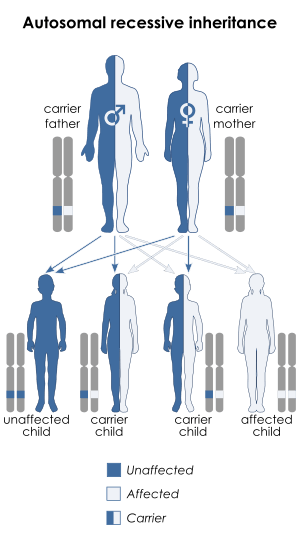 | |
| Succinyl-CoA:3-oxoacid CoA transferase deficiency is inherited via autosomal recessive manner |
Succinyl-CoA:3-oxoacid CoA transferase deficiency (SCOT deficiency) is an inborn error of ketone body utilization. Succinyl-CoA:3-oxoacid CoA transferase catalyzes the transfer of coenzyme A from succinyl-coenzyme A to acetoacetate. It can be caused by mutation in the OXCT1 gene.
First described in 1972, more than 30 people have been reported in the medical literature with this inborn error of metabolism. They experience attacks of ketoacidosis during illness, and even when unwell may have elevated levels of ketone bodies in blood and urine (ketonemia and ketonuria, respectively). Not all people with SCOT deficiency have persistent ketonemia and ketonuria, particularly those with milder defects of enzyme activity.[1]
References
- ↑ Fukao, Toshiyuki; Mitchell, Grant; Sass, Jörn Oliver; Hori, Tomohiro; Orii, Kenji; Aoyama, Yuka (8 April 2014). "Ketone body metabolism and its defects". Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease. 37 (4): 541–551. doi:10.1007/s10545-014-9704-9. PMID 24706027.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.