Petroglyph
_Petroglyphs_Wadi_Methkandoush_Luca_Galuzzi_2007.jpg)

Petroglyphs are images created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other descriptions of the technique to refer to such images. Petroglyphs are found worldwide, and are often associated with prehistoric peoples. The word comes from the Greek prefix petro-, from πέτρα petra meaning "stone", and γλύφω glýphō meaning "to carve", and was originally coined in French as pétroglyphe.
The term petroglyph should not be confused with petrograph, which is an image drawn or painted on a rock face. Both types of image belong to the wider and more general category of rock art or parietal art. Petroforms, or patterns and shapes made by many large rocks and boulders over the ground, are also quite different. Inuksuit are also unique, and found only in the Arctic (except for reproductions and imitations built in more southerly latitudes).
Another form of petroglyph, normally found in literate cultures, a rock relief or rock-cut relief is a relief sculpture carved on "living rock" such as a cliff, rather than a detached piece of stone. While these relief carvings are a category of rock art, sometimes found in conjunction with rock-cut architecture,[1] they tend to be omitted in most works on rock art, which concentrate on engravings and paintings by prehistoric or nonliterate cultures. Some of these reliefs exploit the rock's natural properties to define an image. Rock reliefs have been made in many cultures, especially in the Ancient Near East.[2] Rock reliefs are generally fairly large, as they need to be to make an impact in the open air. Most have figures that are larger than life-size.
Stylistically, a culture's rock relief carvings relate to other types of sculpture from period concerned. Except for Hittite and Persian examples, they are generally discussed as part of the culture's sculptural practice.[3] The vertical relief is most common, but reliefs on essentially horizontal surfaces are also found. The term relief typically excludes relief carvings inside natural or human-made caves, that are common in India. Natural rock formations made into statues or other sculpture in the round, most famously at the Great Sphinx of Giza, are also usually excluded. Reliefs on large boulders left in their natural location, like the Hittite İmamkullu relief, are likely to be included, but smaller boulders described as stele or carved orthostats.
History


Some petroglyphs might be as old as 40,000 years, and petroglyph sites in Australia are estimated to date back 27,000 years. Many petroglyphs are dated to approximately the Neolithic and late Upper Paleolithic boundary, about 10,000 to 12,000 years ago, if not earlier, such as Kamyana Mohyla. Around 7,000 to 9,000 years ago, other precursors of writing systems, such as pictographs and ideograms, began to appear. Petroglyphs were still common though, and some cultures continued using them much longer, even until contact with Western culture was made in the 19th and 20th centuries. Petroglyphs have been found in all parts of the globe except Antarctica, with highest concentrations in parts of Africa, Scandinavia, Siberia, southwestern North America, and Australia.
Interpretation
Many hypotheses explain the purpose of petroglyphs, depending on their location, age, and subject matter. Some many be astronomical markers, maps, and other forms of symbolic communication, including a form of proto-writing. Petroglyph maps may show trails, symbols communicating time and distances traveled, as well as the local terrain in the form of rivers, landforms, and other geographic features. A petroglyph that represents a landform or the surrounding terrain is known as a geocontourglyph. They might also have been a by-product of other rituals: sites in India, for example, have been identified as musical instruments or "rock gongs".[4]
Some petroglyph images probably have deep cultural and religious significance for the societies that created them; in many cases this significance remains for their descendants. Many petroglyphs are thought to represent some kind of not-yet-fully understood symbolic or ritual language. Later glyphs from the Nordic Bronze Age in Scandinavia seem to refer to some form of territorial boundary between tribes, in addition to possible religious meanings. Petroglyph styles has local or regional "dialects" from similar or neighboring peoples. Siberian inscriptions loosely resemble an early form of runes, although no direct relationship has been established. They are not yet well understood.
Petrogylphs from different continents show similarities. While people would be inspired by their direct surroundings, it is harder to explain the common styles. This could be mere coincidence, an indication that certain groups of people migrated widely from some initial common area, or indication of a common origin. In 1853, George Tate presented a paper to the Berwick Naturalists' Club, at which a John Collingwood Bruce agreed that the carvings had "... a common origin, and indicate a symbolic meaning, representing some popular thought."[5] In his cataloguing of Scottish rock art, Ronald Morris summarized 104 different theories on their interpretation.[6]
More controversial explanations of similarities are grounded in Jungian psychology and the views of Mircea Eliade. According to these theories it is possible that the similarity of petroglyphs (and other atavistic or archetypal symbols) from different cultures and continents is a result of the genetically inherited structure of the human brain.
Other theories suggest that petroglyphs were carved by spiritual leaders, such as shamans, in an altered state of consciousness,[7] perhaps induced by the use of natural hallucinogens. Many of the geometric patterns (known as form constants) which recur in petroglyphs and cave paintings have been shown by David Lewis-Williams to be hardwired into the human brain. They frequently occur in visual disturbances and hallucinations brought on by drugs, migraine, and other stimuli.
Recent analysis of surveyed and GPS-logged petroglyphs around the world has identified commonalities indicating pre-historic (7,000–3,000 BCE) intense auroras, or natural light display in the sky, observable across the continents.[8][9]
The Rock Art Research Institute (RARI) of the University of the Witwatersrand studies present-day links between religion and rock art among the San people of the Kalahari Desert.[10] Though the San people's artworks are predominantly paintings, the beliefs behind them can perhaps be used as a basis for understanding other types of rock art, including petroglyphs. To quote from the RARI website:
Using knowledge of San beliefs, researchers have shown that the art played a fundamental part in the religious lives of its San painters. The art captured things from the San's world behind the rock-face: the other world inhabited by spirit creatures, to which dancers could travel in animal form, and where people of ecstasy could draw power and bring it back for healing, rain-making and capturing the game.[11]
List of petroglyph sites
Africa


- Bambari, Lengo and Bangassou in the south; Bwale in the west
- Toulou
- Djebel Mela
- Koumbala

- Niola Doa

- The Niari Valley, 250 km south west of Brazzaville

- Wadi Hammamat in Qift, many carvings and inscriptions dating from before the earliest Egyptian Dynasties to the modern era, including the only painted petroglyph known from the Eastern Desert and drawings of Egyptian reed boats dated to 4000 BCE
- Inscription Rock in South Sinai, is a large rock with carvings and writings ranging from Nabatean to Latin, Ancient Greek and Crusder eras located a few miles from the Ain Hudra Oasis. A second rock sites approximately 1 km from the main rock near the Nabatean tombs of Nawamis with carvings of animals including Camels, Gazelles and others. The original archaeologists who investigated these in the 1800s have also left their names carved on this rock.
- Giraffe petroglyphs found in the region of Gebel el-Silsila. The rock faces have been used for extensive quarrying of materials for temple building especially during the period specified as the New Kingdom. The Giraffe depictions are located near a stela of the king Amenhotep IV. The images are not dated, but they are probably dated from the Predynastic periods.


- Ogooue River Valley
- Epona
- Elarmekora
- Kongo Boumba
- Lindili
- Kaya Kaya


- The Draa River valley
.jpg)


- Life-size giraffe carvings on Dabous Rock, Aïr Mountains

- Driekops Eiland near Kimberley[12]
- ǀXam and ǂKhomani heartland in the Karoo, Northern Cape
- Wildebeest Kuil Rock Art Centre near Kimberley, Northern Cape
- Keiskie near Calvinia, Northern Cape

- Nyambwezi Falls in the north-west province.
Asia




- Yin Mountains in Inner Mongolia
- Petroglyphs in Zhuhai
- Hua'an Engravings
- Lianyungan Rock Engravings

Eight sites in Hong Kong:
- Tung Lung Island
- Kau Sai Chau
- Po Toi Island
- Cheung Chau
- Shek Pik on Lantau Island
- Wong Chuk Hang and Big Wave Bay on Hong Kong Island
- Lung Ha Wan in Sai Kung

- Bhimbetka rock shelters, Raisen District, Madhya Pradesh, India.
- Kupgal petroglyphs on Dolerite Dyke, near Bellary, Karnataka, India.
- Kudopi, Sindhudurg District, Maharashtra, India.
- Hiwale, Sindhudurg District, Maharashtra, India.
- Barsu, Ratnagiri District, Maharashtra, India.
- Devihasol, Ratnagiri District, Maharashtra, India
- Edakkal Caves, Wayanad District, Kerala, India.
- Perumukkal, Tindivanam District, Tamil Nadu, India.
- Kollur, Villupuram, Tamil Nadu.
- Unakoti near Kailashahar in North Tripura District, Tripura, India.
- Usgalimal rock engravings, Kushavati river banks, in Goa[14]
- Ladakh, NW Indian Himalaya.[15]
Recently petroglyphs were found at Kollur village in Tamil Nadu. A large dolmen with four petroglyphs that portray men with trident and a wheel with spokes has been found at Kollur near Triukoilur 35 km from Villupuram. The discovery was made by K.T. Gandhirajan. This is the second instance when a dolmen with petrographs has been found in Tamil Nadu, India.[16] In October 2018, petroglyphs were discovered in the Ratnagiri and Rajapur areas in the Konkan region of western Maharashtra. Those rock carvings which might date back to 10,000 BC, depict animals like hippopotamuses and rhinoceroses which aren't found in that region of India.[17]

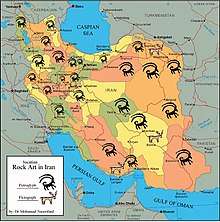
Iran Petroglyphs

During recent years a large number of rock carvings has been identified in different parts of Iran. The vast majority depict the ibex.[18][19] Rock drawings were found in December 2016 near Khomeyn, Iran, which may be the oldest drawings discovered, with one cluster possibly 40,000 years old. Accurate estimations were unavailable due to US sanctions.[20]
Petroglyphs are the most ancient works of art left by humankind that secretly provide an opening to the past eras of life and help us to discover different aspects of prehistoric lives. Tools to create petroglyphs can be classified by the age and the historical era; they could be flint, thighbone of hunted quarries, or metallic tools. The oldest pictographs in Iran are seen in Yafteh cave in Lorestan that date back 40,000 and the oldest petroglyph discovered belongs to Timareh dating back to 40,800 years ago.
Iran provides exclusive demonstrations of script formation from pictogram, ideogram, linear (2300 BC) or proto Elamite, geometric old Elamite script, Pahlevi script, Arabic script (906 years ago), Kufi script, and Farsi script back to at least 250 years ago. More than 50000 petroglyphs have been discovered, extended over all Iran's states.[21]

One of the characteristics of Iran’s petroglyphs is the continuity of existence of prehistoric marks on the ancient pottery and bronze sculptures that reveal the impressiveness of petroglyphs of the facades of caves and rocks reflected on ancient work of arts.
This continuity can be traced from eighth millennium BCE by the potteries in Ganj Darreh near Harseen in Kermanshah state, to third and first millennium BCE, considering the bronze period in Lorestan. There is a unique similarity between petroglyph marks and prehistoric potteries as if all these works are done by a sole artist.

- Kibbutz Ginosar
- Har Karkom
- Negev
- Awashima shrine (Kitakyūshū city)[22]
- Hikoshima (Shimonoseki city)[22]
- Miyajima[22]
- Temiya cave (Otaru city)[23]


- Koksu River, in Almaty Province
- Chumysh River basin,
- Tamgaly Tas on the Ili River
- Tamgaly – a World Heritage Site nearly of Almaty



- Several sites in the Tien Shan mountains: Cholpon-Ata, the Talas valley, Saimaluu Tash, and on the rock outcrop called Suleiman's Throne in Osh in the Fergana valley




- "Graffiti Rocks", about 110 km SW of Riyadh off the Mecca highway
- Arwa, west of Riyadh
- al Jawf, near al Jawf
- Jubbah, Umm Samnan, north of Hail
- Janin Cave, south of Hail
- Yatib, south of Hail
- Milihiya, south of Hail
- Jebel al Lawz, north of Tabuk
- Wadi Damm, near Tabuk
- Wadi Abu Oud, near al Ula
- Shuwaymis, north of Madina
- Jebel al Manjour & Ratt, north of Madina
- Hanakiya, north of Madina
- Shimli
- Bir Hima, north of Najran
- Tathleeth, north of Najran
- Al-Magar, in Najd
- The Wanshan Rock Carvings Archeological Site near Maolin District, Kaohsiung, were discovered between 1978 and 2002.

- Rock engravings in Sapa, Sa Pa District, Lào Cai Province
- Rock engravings in Namdan, Xín Mần District, Hà Giang Province
 Rock carving on Cheung Chau Island, Hong Kong. This 3000-year-old rock carving was reported by geologists in 1970
Rock carving on Cheung Chau Island, Hong Kong. This 3000-year-old rock carving was reported by geologists in 1970 Petroglyphs at Cholpon-Ata in Kyrgyzstan
Petroglyphs at Cholpon-Ata in Kyrgyzstan Tamgaly petroglyphs in Kazakhstan
Tamgaly petroglyphs in Kazakhstan

- Petroglyph found in Awashima shrine (Japan)
Europe
 Petroglyph from Foppe of Nadro, Val Camonica, Italy
Petroglyph from Foppe of Nadro, Val Camonica, Italy.jpg) Duel in Foppe of Nadro, Val Camonica, Italy
Duel in Foppe of Nadro, Val Camonica, Italy
 Engravers from Val Camonica, Italy
Engravers from Val Camonica, Italy Rock Carving in Tanum, Sweden
Rock Carving in Tanum, Sweden Carving "The Shoemaker", Brastad, Sweden
Carving "The Shoemaker", Brastad, Sweden Petroglyph in Roque Bentayga, Gran Canaria (Canary Islands).
Petroglyph in Roque Bentayga, Gran Canaria (Canary Islands). Petroglyph at Dalgarven Mill, Ayrshire, Scotland.
Petroglyph at Dalgarven Mill, Ayrshire, Scotland. Bronze Age petroglyphs depicting weapons, Castriño de Conxo, Santiago de Compostela, Galicia.
Bronze Age petroglyphs depicting weapons, Castriño de Conxo, Santiago de Compostela, Galicia.- Labyrinth, Meis, Galicia.
 Cup-and-ring mark, Louro, Muros, Galicia.
Cup-and-ring mark, Louro, Muros, Galicia.- Deer and cup-and-ring motifs, Tourón, Ponte Caldelas, Galicia.
 Petroglyphs in Zalavruga, Belomorsk, Karelia, Russia
Petroglyphs in Zalavruga, Belomorsk, Karelia, Russia "oranti saltici" of the Rupe Magna in Grosio, Italy
"oranti saltici" of the Rupe Magna in Grosio, Italy


- Hauensuoli, Hanko, Finland
 The sorcerer, Vallée des Merveilles, France
The sorcerer, Vallée des Merveilles, France The tribe master, Vallée des Merveilles, France
The tribe master, Vallée des Merveilles, France


- Rock Drawings in Valcamonica – World Heritage Site, Italy (biggest European site, over 350,000)
- Bagnolo stele, Valcamonica, Italy
- Grotta del Genovese, Sicily, Italy
- Grotta dell'Addaura, Sicily, Italy
- Rock Engravings in Grosio (in Valtellina), Italy
 Grosio - Rupe Magna
Grosio - Rupe Magna Grosio - Rupe Magna
Grosio - Rupe Magna Grosio - Rupe Magna
Grosio - Rupe Magna
Northern Ireland
- Knockmany
 Leftmost of three central stones, Knockmany Chambered Tomb, Co. Tyrone, Northern Ireland
Leftmost of three central stones, Knockmany Chambered Tomb, Co. Tyrone, Northern Ireland Central of three central stones, Knockmany Chambered Tomb, Co. Tyrone, Northern Ireland
Central of three central stones, Knockmany Chambered Tomb, Co. Tyrone, Northern Ireland- A stone on the right of the passage, Knockmany Chambered Tomb, Co. Tyrone, Northern Ireland
- Sess Kilgreen
 Sess Kilgreen Chambered Tomb, Co. Tyrone, Northern Ireland
Sess Kilgreen Chambered Tomb, Co. Tyrone, Northern Ireland Sess Kilgreen Chambered Tomb, Co. Tyrone, Northern Ireland
Sess Kilgreen Chambered Tomb, Co. Tyrone, Northern Ireland
- Rock carvings at Alta, World Heritage Site (1985)
- Rock carvings in Central Norway
- Rock carvings at Møllerstufossen
- Rock carvings at Tennes

- Côa Valley Paleolithic Art, Portugal


| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Petroglyphs in Galicia. |

- Petroglyph Park near Petrozavodsk–Lake Onega, Russia
- Tomskaya Pisanitsa
- Kanozero Petroglyphs
- Sikachi-Alyan, Khabarovsk Krai
- Kapova cave, Bashkortostan

- Tanumshede (Bohuslän); World Heritage Site (1994)
- Himmelstalund (by Norrköping in Östergötland)
- Enköping (Uppland)
- Southwest Skåne (Götaland)
- Alvhem (Västra Götaland)
- Torhamn (Blekinge)
- Nämforsen (Ångermanland)
- Häljesta (Västmanland)
- Slagsta (Södermanland)
- Glösa (Jämtland)
- The King's Grave at Kivik
- Rock carvings at Norrfors, Umeå[29]


.svg.png)
- Garn Turne, Pembrokeshire
Central and South America and the Caribbean

- Cueva de las Manos, Santa Cruz
- Talampaya National Park, La Rioja
- Lihué Calel National Park, La Pampa
.jpg)
 Petroglyph on Tunduqueral hill at Uspallata, Argentina
Petroglyph on Tunduqueral hill at Uspallata, Argentina
- Arikok National Park
- Quadiriki Caves
- Ayo and Casabari Rock Formations

The oldest reliably dated rock art in the Americas is known as the "Horny Little Man." It is petroglyph depicting a stick figure with an oversized phallus and carved in Lapa do Santo, a cave in central-eastern Brazil and dates from 12,000 to 9,000 years ago.[30]
- Serra da Capivara National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, Piauí
- Vale do Catimbau National Park, Pernambuco
- Ingá Stone, Paraíba
- Costao do Santinho, Santa Catarina
- Lagoa Santa (Holy Lake), Minas Gerais
- Ivolandia, Goiás
- Capivara National Park, Piauí, Brazil
- Ivolandia, Goiás, Brazil
- Costao do Santinho, SC, Brazil

- Rincón las Chilcas, Combarbalá
- Easter Island petroglyphs

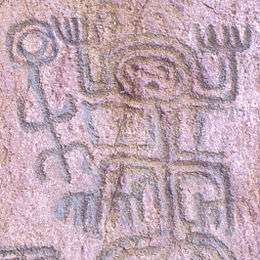 El Abra archaeological site, Cundinamarca
El Abra archaeological site, Cundinamarca Petroglyph in the Chiribiquete Natural National Park. (Possible equine)
Petroglyph in the Chiribiquete Natural National Park. (Possible equine) Petroglyph in the Chiribiquete Natural National Park. Aboriginal
Petroglyph in the Chiribiquete Natural National Park. Aboriginal Petroglyph in the Chiribiquete Natural National Park. (Possible mammal).
Petroglyph in the Chiribiquete Natural National Park. (Possible mammal).- Petroglyphs in the Chiribiquete Natural National Park.


- Cueva de las Maravillas, San Pedro de Macorís
- Las Caritas, near Lake Enriquillo
- Los Tres Ojos, Santo Domingo




- Cumbe Mayo, Cajamarca
- Petroglyphs of Pusharo, Manú National Park, Madre de Dios region
- Petroglyphs of Quiaca, Puno Region
- Petroglyphs of Jinkiori, Cusco Region

- La Piedra Escrita (The Written Rock), Jayuya
- Caguana Indian Park, Utuado
- Tibes Indian Park, Ponce
- La Cueva del Indio (Indians Cave), Arecibo

- Carib Petroglyphs, Wingfield Manor Estate, Saint Kitts


- Caurita
 The only known Amerindian petroglyph in Trinidad
The only known Amerindian petroglyph in Trinidad

North America
 Petroglyphs on a Bishop Tuff tableland, eastern California
Petroglyphs on a Bishop Tuff tableland, eastern California Southern Utah
Southern Utah Southern Utah
Southern Utah

- Animal print carvings outside of Barnesville, Ohio


 Upside-down man in Western Colorado
Upside-down man in Western Colorado Web-like petroglyph on the White Tank Mountain Regional Park Waterfall Trail, Arizona
Web-like petroglyph on the White Tank Mountain Regional Park Waterfall Trail, Arizona Chipping petroglyph on the White Tank Mountain Regional Park Waterfall Trail, Arizona
Chipping petroglyph on the White Tank Mountain Regional Park Waterfall Trail, Arizona- Sample of petroglyphs at Painted Rock near Gila Bend, Arizona off Interstate 8.



- Kejimkujik National Park, Nova Scotia
- Petroglyph Provincial Park, Nanaimo, British Columbia[35]
- Petroglyphs Provincial Park, north of Peterborough, Ontario
- Agnes Lake, Quetico Provincial Park, Ontario
- Sproat Lake Provincial Park, near Port Alberni, British Columbia
- Stuart Lake, British Columbia
- St. Victor Provincial Park, Saskatchewan
- Writing-on-Stone Provincial Park, east of Milk River, Alberta
- Gabriola Island, British Columbia[36]
- East Sooke Regional Park, British Columbia

- Boca de Potrerillos, Mina, Nuevo León
- Chiquihuitillos, Mina, Nuevo León
- Cuenca del Río Victoria, near Xichú, Guanajuato
- Coahuiltecan Cueva Ahumada, Nuevo León
- La Proveedora, Caborca, Sonora
- Samalayuca, Juarez, Chihuahua
- Las Labradas, near Mazatlán, Sinaloa


- Arches National Park, Utah
- Bandelier National Monument Near Santa Fe, New Mexico
- Barnesville Petroglyph, Ohio
- California Petroglyphs & Pictographs[37]
- Capitol Reef National Park, Utah
- Columbia Hills State Park, Washington[38]
- Corn Springs, Colorado Desert, California
- Coso Rock Art District, Coso Range, northern Mojave Desert, California[39]
- Death Valley National Park, California
- Dinosaur National Monument, Colorado and Utah
- Dighton Rock, Massachusetts
- Dominguez Canyon Wilderness, Colorado
- Fremont Indian State Park Utah
- Great Basin National Park Nevada
- Grimes Point, Nevada[40]
- Independence Slab, Ohio
- Inscription Rock (Kelleys Island, Ohio), Ohio
- Jeffers Petroglyphs, Minnesota
- Judaculla Rock, North Carolina
- Kanopolis State Park, Kansas
- Lava Beds National Monument, Tule Lake, California
- Legend Rock Petroglyph Site, Thermopolis, Wyoming
- Lemonweir Glyphs, Wisconsin
- Leo Petroglyph, Leo, Ohio[41]
- Mesa Verde National Park, Colorado
- Newspaper Rock State Historic Monument, Utah
- Olympic National Park, Washington
- Paintlick Mountain, Tazewell, Virginia[42]
- Petit Jean State Park, Arkansas
- Petrified Forest National Park Arizona
- Petroglyphs National Monument of New Mexico, in Albuquerque, New Mexico.[43]
- Picture Canyon, Flagstaff, Arizona
- Puye Cliff Dwellings, New Mexico
- Red Rock Canyon National Conservation Area, Nevada
- Rochester Rock Art Panel, Utah
- Ring Mountain, Marin County, California
- Saint John, U.S. Virgin Islands
- Sanilac Petroglyphs Historic State Park, Michigan
- Sedona, Arizona
- Seminole Canyon, Texas
- Sloan Canyon National Conservation Area, Nevada
- South Mountain Park, Arizona
- The Cove Palisades State Park, Oregon
- Three Rivers Petroglyphs, New Mexico[44]
- Valley of Fire State Park, Nevada
- Washington State Park, Washington County, Missouri
- West Virginia glyphs
- White Mountain (Wyoming), Rock Springs, Wyoming
- White Tank Mountain Regional Park, Waddell, Arizona
- Winnemucca Lake, Nevada
- Writing Rock State Historical Site, North Dakota
- Monolyth at Caguas & El Yunque, Puerto Rico
- Track Rock, Georgia
- Forsyth Petroglyph Originally discovered, locates and documented near Cumming, Georgia in Forsyth County but has been relocated to the campus of the University of Georgia in Athens, Georgia
Oceania
- Arnhem Land / Kakadu National Park, Northern Australia
- Murujuga, Western Australia – world heritage assessed
- Sydney Rock Engravings, New South Wales
 Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park, New South Wales
Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park, New South Wales- Part of a 20-metre-long petroglyph at Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park, New South Wales
- Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park, New South Wales
- Mutawintji National Park, New South Wales
- Burrup Peninsula, Western Australia
See also
Notes
- ↑ Harmanşah (2014), 5–6.
- ↑ Harmanşah (2014), 5–6; Canepa, 53.
- ↑ See: Rawson and Sickman & Soper
- ↑ Ancient Indians made 'rock music'. BBC News (2004-03-19). Retrieved on 2013-02-12.
- ↑ J. Collingwood Bruce (1868; cited in Beckensall, S., Northumberland's Prehistoric Rock Carvings: A Mystery Explained. Pendulum Publications, Rothbury, Northumberland. 1983:19)
- ↑ Morris, Ronald (1979) The Prehistoric Rock Art of Galloway and The Isle of Man, Blandford Press, ISBN 978-0-7137-0974-2.
- ↑ [See: D. Lewis-Williams, A Cosmos in Stone: Interpreting Religion and Society through Rock Art (Walnut Creek, CA: Altamira Press, 2002).]
- ↑ Peratt, A.L. (2003). "Characteristics for the occurrence of a high-current, Z-pinch aurora as recorded in antiquity". IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science. 31 (6): 1192. doi:10.1109/TPS.2003.820956.
- ↑ Peratt, Anthony L.; McGovern, John; Qoyawayma, Alfred H.; Van Der Sluijs, Marinus Anthony; Peratt, Mathias G. (2007). "Characteristics for the Occurrence of a High-Current Z-Pinch Aurora as Recorded in Antiquity Part II: Directionality and Source". IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science. 35 (4): 778. doi:10.1109/TPS.2007.902630.
- ↑ Rockart.wits.ac.za Retrieved on 2013-02-12.
- ↑ "Rock Art Research Institute (RARI)". University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg. Retrieved 9 September 2017.
- ↑ Parkington, J. Morris, D. & Rusch, N. 2008. Karoo rock engravings. Clanwilliam: Krakadouw Trust; Morris, D. & Beaumont, P. 2004. Archaeology in the Northern Cape: some key sites. Kimberley: McGregor Museum.
- ↑ Khechoyan, Anna. "The Rock Art of the Mt. Aragats System | Anna Khechoyan". Academia.edu. Retrieved 2013-08-18.
- ↑ Kamat, Nandkumar. "Petroglyphs on the banks of Kushvati". Prehistoric Goan Shamanism. the Navhind times. Archived from the original on 7 August 2011. Retrieved 30 March 2011.
- ↑ Petroglyphs of Ladakh: The Withering Monuments. tibetheritagefund.org
- ↑ Dolmen with petroglyphs found near Villupuram. Beta.thehindu.com (2009-09-19). Retrieved on 2013-02-12.
- ↑ "Prehistoric art hints at lost Indian civilisation". BBC. 1 October 2018.
- ↑ "Iran Petroglyphs – سنگ نگاره های ایران Iran Petroglyphs". iranrockart.com. Archived from the original on 2014-07-19.
- ↑ Foundation, Bradshaw. "Middle East Rock Art Archive – Iran Rock Art Gallery". bradshawfoundation.com.
- ↑ "Archaeologist uncovers 'the world's oldest drawings'". independent.co.uk. 12 December 2016.
- ↑ Iran Petroglyphs, Universal Common language (book); Iran Petrogylphs, Ideogram Symbols (book); Rock Museums Rock Arts (Iran Petroglyphs) (book); For more information : http://iranrockart.com ; http://www.bradshawfoundation.com/middle_east/iran_rock_art/index.php ; https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/middle-east/world-oldest-rock-drawings-archaeologist-iran-khomeyn-mohammed-naserifard-a7470321.html ; http://www.hurriyetdailynews.com/deciphering-irans-ancient-rock-art-.aspx?pageID=238&nID=107184&NewsCatID=375 ; http://theiranproject.com/blog/tag/dr-mohammed-naserifard/
- 1 2 3 Nobuhiro, Yoshida (1994) The Handbook For Petrograph Fieldwork, Chou Art Publishing, ISBN 4-88639-699-2, p. 57
- ↑ Nobuhiro, Yoshida (1994) The Handbook For Petrograph Fieldwork, Chou Art Publishing, ISBN 4-88639-699-2, p. 54
- ↑ Petroglyphic Complexes of the Mongolian Altai – UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Whc.unesco.org (2011-06-28). Retrieved on 2013-02-12.
- ↑ Fitzhugh, William W. and Kortum, Richard (2012) Rock Art and Archaeology: Investigating Ritual Landscape in the Mongolian Altai. Field Report 2011. The Arctic Studies Center, National Museum of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D.C.
- ↑ http://www.giuseppetilli.com, Giuseppe Tilli. "The National Park of Rock Engravings in Capo di Ponte". www.vallecamonicaunesco.it. Retrieved 14 April 2018.
- ↑ "British Rock Art Blog | A Forum about Prehistoric Rock Art in the British Islands". Rockartuk.wordpress.com. Retrieved 2013-08-18.
- ↑ Photos. Celticland.com. (2007-08-13). Retrieved on 2013-02-12.
- ↑ "Umeå, Norrfors". Europreart.net. Retrieved 2013-08-18.
- ↑ Choi, Charles. "Call this ancient rock carving 'little horny man'." Science on MSNBC. 22 Feb 2012. Retrieved 9 April 2012.
- ↑ "Settlers at La Silla". www.eso.org. Retrieved 6 June 2017.
- ↑ "The Ascent of Man". Retrieved 28 December 2015.
- ↑ "Llamas at La Silla". ESO Picture of the Week. Retrieved 29 April 2014.
- 1 2 "Ometepe Island Info – El Ceibo". ometepeislandinfo.com. Retrieved 2017-03-05.
- ↑ Petroglyph Provincial Park, Nanaimo, Vancouver Island BC. Britishcolumbia.com. Retrieved on 2013-02-12.
- ↑ "Petroglyph Park - Gabriola Museum". gabriolamuseum.org. Retrieved 14 April 2018.
- ↑ Petroglyphs.us. Retrieved on 2013-02-12.
- ↑ Keyser, James D. (July 1992). Indian Rock Art of the Columbia Plateau. University of Washington Press. ISBN 978-0-295-97160-5.
- ↑ Moore, Donald W. Petroglyph Canyon Tours. Desertusa.com. Retrieved on 2013-02-12.
- ↑ Grimes Point National Recreation Trail, Nevada BLM Archaeological Site. Americantrails.org (2012-01-13). Retrieved on 2013-02-12.
- ↑ Museums & Historic Sites Archived 2007-07-05 at the Wayback Machine.. ohiohistory.org. Retrieved on 2013-02-12.
- ↑ "Paint Lick". Craborchardmuseum.com. Archived from the original on 2007-12-26. Retrieved 2013-08-18.
- ↑ "Petroglyph National Monument (U.S. National Park Service)". nps.gov.
- ↑ Three Rivers Petroglyph Site Archived 2007-06-18 at the Wayback Machine.. Nm.blm.gov (2012-09-13). Retrieved on 2013-02-12.
References
- Harmanşah, Ömür (ed) (2014), Of Rocks and Water: An Archaeology of Place, 2014, Oxbow Books, ISBN 1-78297-674-4, 9781782976745
- Rawson, Jessica (ed). The British Museum Book of Chinese Art, 2007 (2nd edn), British Museum Press, ISBN 978-0-7141-2446-9
- Sickman, Laurence, in: Sickman L. & Soper A., The Art and Architecture of China, Pelican History of Art, 3rd ed 1971, Penguin (now Yale History of Art), LOC 70-125675
Further reading
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Petroglyphs. |
- Rock Art Studies: A Bibliographic Database Bancroft Library's citations to rock art literature.





