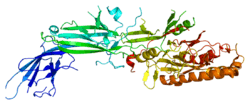PADI4
Peptidyl arginine deiminase, type IV, also known as PADI4, is a human protein which in humans is encoded by the PADI4 gene.[5][6]
Molecular biology
The human gene is found on the short arm of Chromosome 1 near the telomere (1p36.13). It is located on the Watson (plus) strand and is 55,806 bases long. The protein is 663 amino acids long with a molecular weight of 74,095 Da.[5]
Function
This gene is a member of a gene family which encodes enzymes responsible for the conversion of arginine to citrulline residues. This gene may play a role in granulocyte and macrophage development leading to inflammation and immune response.[6] PADI4 plays a role in the epigenetics, the deimination of arginines on histones 3 and 4 can act antagonistically to arginine methylation (Chromatin modifications and their function, Kouzarides 2007, Cell, review)
The protein may be found in oligomers and binds 5 calcium ions per subunit. It catalyses the reaction:
- Protein L-arginine + H2O = protein L-citrulline + NH3
Subcellular and tissue distribution
It is normally found in the cytoplasm, nucleus and in cytoplasmic granules of eosinophils and neutrophils. It is not expressed in peripheral monocytes or lymphocytes. It is also expressed in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissues.
References
- 1 2 3 ENSG00000159339 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000280908, ENSG00000159339 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000025330 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- 1 2 Nakashima K, Hagiwara T, Ishigami A, Nagata S, Asaga H, Kuramoto M, Senshu T, Yamada M (September 1999). "Molecular characterization of peptidylarginine deiminase in HL-60 cells induced by retinoic acid and 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3)". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (39): 27786–92. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.39.27786. PMID 10488123.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: PADI4 peptidyl arginine deiminase, type IV".
Further reading
- Nakashima K, Hagiwara T, Ishigami A, et al. (1999). "Molecular characterization of peptidylarginine deiminase in HL-60 cells induced by retinoic acid and 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3)". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (39): 27786–92. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.39.27786. PMID 10488123.
- Zhang QH, Ye M, Wu XY, et al. (2001). "Cloning and functional analysis of cDNAs with open reading frames for 300 previously undefined genes expressed in CD34+ hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells". Genome Res. 10 (10): 1546–60. doi:10.1101/gr.140200. PMC 310934. PMID 11042152.
- Asaga H, Nakashima K, Senshu T, et al. (2001). "Immunocytochemical localization of peptidylarginine deiminase in human eosinophils and neutrophils". J. Leukoc. Biol. 70 (1): 46–51. PMID 11435484.
- Nakashima K, Hagiwara T, Yamada M (2003). "Nuclear localization of peptidylarginine deiminase V and histone deimination in granulocytes". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (51): 49562–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208795200. PMID 12393868.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Suzuki A, Yamada R, Chang X, et al. (2003). "Functional haplotypes of PADI4, encoding citrullinating enzyme peptidylarginine deiminase 4, are associated with rheumatoid arthritis". Nat. Genet. 34 (4): 395–402. doi:10.1038/ng1206. PMID 12833157.
- Barton A, Bowes J, Eyre S, et al. (2004). "A functional haplotype of the PADI4 gene associated with rheumatoid arthritis in a Japanese population is not associated in a United Kingdom population". Arthritis Rheum. 50 (4): 1117–21. doi:10.1002/art.20169. PMID 15077293.
- Chavanas S, Méchin MC, Takahara H, et al. (2004). "Comparative analysis of the mouse and human peptidylarginine deiminase gene clusters reveals highly conserved non-coding segments and a new human gene, PADI6". Gene. 330: 19–27. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2003.12.038. PMID 15087120.
- Arita K, Hashimoto H, Shimizu T, et al. (2004). "Structural basis for Ca(2+)-induced activation of human PAD4". Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 11 (8): 777–83. doi:10.1038/nsmb799. PMID 15247907.
- Hoppe B, Heymann GA, Tolou F, et al. (2005). "High variability of peptidylarginine deiminase 4 (PADI4) in a healthy white population: characterization of six new variants of PADI4 exons 2-4 by a novel haplotype-specific sequencing-based approach". J. Mol. Med. 82 (11): 762–7. doi:10.1007/s00109-004-0584-6. PMID 15338034.
- Cuthbert GL, Daujat S, Snowden AW, et al. (2004). "Histone deimination antagonizes arginine methylation". Cell. 118 (5): 545–53. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.08.020. PMID 15339660.
- Wang Y, Wysocka J, Sayegh J, et al. (2004). "Human PAD4 regulates histone arginine methylation levels via demethylimination". Science. 306 (5694): 279–83. doi:10.1126/science.1101400. PMID 15345777.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Nakayama-Hamada M, Suzuki A, Kubota K, et al. (2005). "Comparison of enzymatic properties between hPADI2 and hPADI4". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 327 (1): 192–200. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.11.152. PMID 15629448.
- Lee YH, Coonrod SA, Kraus WL, et al. (2005). "Regulation of coactivator complex assembly and function by protein arginine methylation and demethylimination". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102 (10): 3611–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.0407159102. PMC 553305. PMID 15731352.
- Kearney PL, Bhatia M, Jones NG, et al. (2005). "Kinetic characterization of protein arginine deiminase 4: a transcriptional corepressor implicated in the onset and progression of rheumatoid arthritis". Biochemistry. 44 (31): 10570–82. doi:10.1021/bi050292m. PMID 16060666.
- Ikari K, Kuwahara M, Nakamura T, et al. (2005). "Association between PADI4 and rheumatoid arthritis: a replication study". Arthritis Rheum. 52 (10): 3054–7. doi:10.1002/art.21309. PMID 16200584.
- Chang X, Han J (2006). "Expression of peptidylarginine deiminase type 4 (PAD4) in various tumors". Mol. Carcinog. 45 (3): 183–96. doi:10.1002/mc.20169. PMID 16355400.
- Plenge RM, Padyukov L, Remmers EF, et al. (2006). "Replication of putative candidate-gene associations with rheumatoid arthritis in >4,000 samples from North America and Sweden: association of susceptibility with PTPN22, CTLA4, and PADI4". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 77 (6): 1044–60. doi:10.1086/498651. PMC 1285162. PMID 16380915.
- Hoppe B, Häupl T, Gruber R, et al. (2006). "Detailed analysis of the variability of peptidylarginine deiminase type 4 in German patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a case-control study". Arthritis Research & Therapy. 8 (2): R34. doi:10.1186/ar1889. PMC 1526594. PMID 16469113.