Pendentive

A pendentive is a constructive device permitting the placing of a circular dome over a square room or an elliptical dome over a rectangular room.[1] The pendentives, which are triangular segments of a sphere, taper to points at the bottom and spread at the top to establish the continuous circular or elliptical base needed for the dome.[2] In masonry the pendentives thus receive the weight of the dome, concentrating it at the four corners where it can be received by the piers beneath.
Prior to the pendentive's development, the device of corbelling or the use of the squinch in the corners of a room had been employed. Pendentives were commonly used in Orthodox, Renaissance, and Baroque churches, with a drum with windows often inserted between the pendentives and the dome. The first experimentation with pendentives was made in Roman dome construction beginning in the 2nd–3rd century AD,[3] while full development of the form was achieved in the 6th-century Eastern Roman Hagia Sophia at Constantinople.[4]
Gallery
 Arches (left and right), dome (top) and pendentive (centre) in Moscow Cathedral
Arches (left and right), dome (top) and pendentive (centre) in Moscow Cathedral_%E2%80%93_frs-002.jpg)
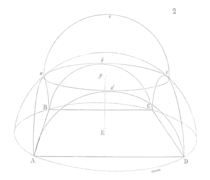 Formation of a pendentive. Eugène Viollet-le-Duc, 1856
Formation of a pendentive. Eugène Viollet-le-Duc, 1856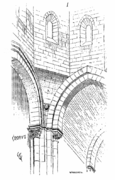 A pendentive, labelled A. Illustration of a church in Nantua.
A pendentive, labelled A. Illustration of a church in Nantua. Pendentive structure
Pendentive structure One pendentive of the Hagia Sophia main dome
One pendentive of the Hagia Sophia main dome
See also
References
- ↑ The Columbia Encyclopedia, sixth edition
- ↑ "pendentive (architecture) - Britannica Online Encyclopedia". Britannica.com. Retrieved 2012-08-15.
- ↑ Rasch 1985, pp. 129f.
- ↑ Heinle & Schlaich 1996, pp. 30–32
Sources
- Heinle, Erwin; Schlaich, Jörg (1996), Kuppeln aller Zeiten, aller Kulturen, Stuttgart, ISBN 3-421-03062-6
- Rasch, Jürgen (1985), "Die Kuppel in der römischen Architektur. Entwicklung, Formgebung, Konstruktion", Architectura, 15, pp. 117–139
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pendentives. |