Patent Law Treaty
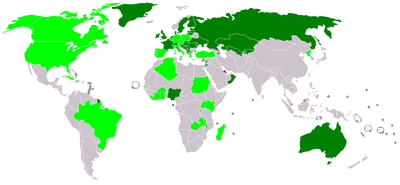
The Patent Law Treaty (PLT) is a patent law multilateral treaty concluded on 1 June 2000 in Geneva, Switzerland, by 53 States and the European Patent Organisation (an intergovernmental organization). Its aim is to harmonize formal procedures such as the requirements to obtain a filing date for a patent application, the form and content of a patent application, and representation.
As of November 2017, the PLT had 39 contracting states, while 59 states and the European Patent Organisation have signed the treaty.[1]
History
| Date | State |
|---|---|
| 28 April 2005 | Republic of Moldova, Kyrgyz Republic, Republic of Slovenia, Slovak Republic, Federal Republic of Nigeria, Ukraine, Republic of Estonia, Kingdom of Denmark, Republic of Croatia, Romania |
| 15 December 2005 | Bahrain |
| 6 March 2006 | Finland |
| 22 March 2006 | United Kingdom |
| 19 July 2006 | Uzbekistan |
| 16 October 2007 | Oman |
| 27 December 2007 | Sweden |
| 12 March 2008 | Hungary |
| 1 July 2008 | Switzerland |
| 16 March 2009 | Australia |
| 12 August 2009 | Russia |
| 18 December 2009 | Liechtenstein |
| 5 January 2010 | France |
| 22 April 2010 | The Republic of Macedonia |
| 17 May 2010 | Albania |
| 12 June 2010 | Latvia |
| 20 August 2010 | Serbia |
| 27 December 2010 | Netherlands |
| 19 October 2011 | Kazakhstan |
| 3 February 2012 | Lithuania |
| 9 March 2012 | Montenegro |
| 9 May 2012 | Bosnia and Herzegovina |
| 27 May 2012 | Ireland |
| 3 August 2013 | Saudi Arabia |
| 17 September 2013 | Armenia |
| 18 December 2013 | United States |
| 11 June 2016 | Japan |
| 21 October 2016 | Belarus |
| 4 January 2017 | Liberia |
Canada
The Canadian government tabled 5 treaties in the House of Commons on 27 January 2014.[2] Among the treaties is the PLT. However, the government has not yet tabled legislation to incorporate the treaties in Canadian law, but the tabling of the treaties is a strong signal that the government is moving ahead with harmonization of its IP laws.
France
Prior to the entry into force of the treaty in France, a bill was submitted on 14 January 2009 at the French Senate proposing the ratification of the PLT by France.[3][4] In March 2009, a report from French Senator Rachel Mazuir recommended the ratification of the PLT, as soon as possible, by France.[5][6] On 24 July 2009, the government was authorized to ratify the PLT.[7] The PLT then entered into force for France on 5 January 2010.[1]
United States of America
The Treaty was ratified by the United States on 18 September 2013. Parts of the PLT were applied to U.S. patent law with the passage of the Patent Law Treaties Implementation Act of 2012.[8]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 "Patent Law Treaty (Total Contracting Parties : 39)". WIPO. Retrieved 24 November 2017.
- ↑ http://www.parl.gc.ca/HousePublications/Publication.aspx?Language=E&Mode=1&Parl=41&Ses=2&DocId=6388324
- ↑ (in French) French Senate web site, Sénat, Session Ordinaire de 2008-2009, Annexe au procès-verbal de la séance du 14 janvier 2009, Projet de Loi autorisant la ratification du traité sur le droit des brevets, 14 January 2009. Consulted on 22 January 2009
- ↑ (in French) Laurent Teyssedre, Ratification du PLT, Le blog du droit européen des brevets, 20 January 2009. Consulted on 22 January 2009
- ↑ (in French) French Senate web site, Annexe au procès-verbal de la séance du 17 mars 2009, Rapport fait au nom de la commission des Affaires étrangères, de la défense et des forces armées sur le projet de loi autorisant la ratification du traité sur le droit des brevets, Par M. Rachel Mazuir, Sénateur
- ↑ (in French) Laurent Teyssedre, Ratification du PLT (suite), Le blog du droit européen des brevets, 25 March 2009. Consulted on 29 March 2009
- ↑ (in French) JORF n°0170 du 25 juillet 2009 page 12409, texte n° 3, LOI n° 2009-892 du 24 juillet 2009 autorisant la ratification du traité sur le droit des brevets, NOR: MAEJ0815903L
- ↑ Patent Law Treaties Implementation Act of 2012, Pub. Law 112-211
External links
- Patent Law Treaty in the WIPO Lex database — official website of WIPO.
- The full text of the Patent Law Treaty (in English)