''N''-Oxoammonium salt
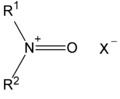
The structure of a typical N-oxoammonium salt.
N-Oxoammonium salts in organic chemistry are a class of organic compounds sharing a functional group with the general structure R1R2N+=O X− where X− is the counterion. They are isoelectronic with carbonyls and structurally related to aldoximes (hydroxylamines) and aminoxyl (nitroxide) radicals, with which they can interconvert via a series of redox steps.
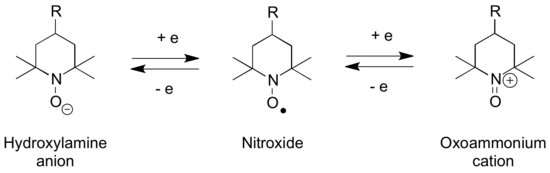
The N-oxoammonium salts are used for oxidation of alcohols to carbonyl groups,[1] as well as other forms of oxoammonium-catalyzed oxidations. The stable radical TEMPO reacts via its N-oxoammonium salt.
See also
- Nitrone – structurally related, the N-oxide of an imine
References
- ↑ Bobbitt, James M.; Brückner, Christian; Merbouh, Nabyl (2010). "Oxoammonium- and Nitroxide-Catalyzed Oxidations of Alcohols". Organic Reactions: 103–424. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or074.02.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.