''meta''-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Chlorobenzene-1-carboperoxoic acid | |||
| Other names
3-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid 3-Chloroperbenzoic acid 3-Chlorobenzoperoxoic acid meta-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid m-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid meta-Chloroperbenzoic acid mCPBA m-CPBA | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.111 | ||
| EC Number | 213-322-3 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number | SD9470000 | ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 3106 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C7H5ClO3 | |||
| Molar mass | 172.56 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White powder | ||
| Melting point | 92 to 94 °C (198 to 201 °F; 365 to 367 K) decomposes | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 7.57 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Oxidizing, corrosive, explosive | ||
| GHS pictograms |    | ||
| GHS signal word | Danger | ||
| H226, H314, H318, H335 | |||
| P210, P220, P233, P234, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P271, P272, P280, P301+330+331, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P321, P332+313, P333+313, P337+313 | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
peroxyacetic acid; peroxybenzoic acid | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
meta-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid (mCPBA) is a peroxycarboxylic acid used widely as an oxidant in organic synthesis. mCPBA is often preferred to other peroxy acids because of its relative ease of handling. The main areas of use are the conversion of ketones to esters (Baeyer-Villiger oxidation), epoxidation of alkenes (Prilezhaev reaction), conversion of silyl enol ethers to silyl α-hydroxy ketones (Rubottom oxidation), oxidation of sulfides to sulfoxides and sulfones, and oxidation of amines to produce amine oxides.[1] mCPBA is a strong oxidizing agent that may cause fire upon contact with flammable material.
Preparation
mCPBA can be prepared by reacting m-chlorobenzoyl chloride with hydrogen peroxide in the presence of magnesium sulfate, aqueous sodium hydroxide, and dioxane, followed by acidification.[2]
Availability and purity
As a pure substance, mCPBA can be detonated by shock or by sparks. It is therefore sold commercially as a much more stable mixture that is less than 72% mCPBA, with the balance made up of m-chlorobenzoic acid (10%) and water.[1] The peroxyacid can be purified by washing the commercial material with a slightly basic buffer solution and then drying.[3] Peroxyacids are generally slightly less acidic than their carboxylic acid counterparts, so one can extract the acid impurity by careful control of pH. The purified material is reasonably stable against decomposition if stored at low temperatures in a plastic container.
In reactions where the exact amount of mCPBA must be controlled, a sample can be titrated to determine the exact amount of active oxidant.
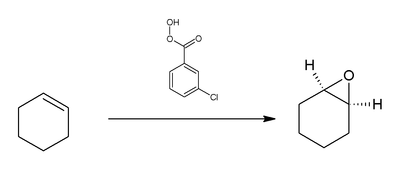
Epoxidation example
The following scheme shows the reaction of cyclohexene with mCPBA to give an epoxide.
The epoxidation mechanism is concerted: the cis or trans geometry of the alkene starting material is retained in the epoxide ring of the product.
m-CPBA does also react with carbonyl group,for instance aldehyde or ketone, to yield carboxylic acids or esters respectively.
References
- 1 2 "3-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid". Organic Chemistry Portal.
- ↑ Richard N. McDonald; Richard N. Steppel; James E. Dorsey (1988). "m-Chloroperbenzoic Acid". Organic Syntheses. ; Collective Volume, 6, p. 276
- ↑ Armarego, W. L. F.; Perrin, D. D. (1996). Purification of Laboratory Chemicals (4th ed.). Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 145. ISBN 0-7506-3761-7.