Mantharta language
| Mantharta | |
|---|---|
| Region | Western Australia |
Native speakers |
2 Dhargari (2005)[1] (1 cited 2007)[2] |
|
Pama–Nyungan
| |
| Dialects |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 |
Variously:dhr – Dhargariwri – Warriyanggaiin – Thiindze – Djiwarli |
| Glottolog |
mant1266[3] |
| AIATSIS[1] |
W21 Tharrkari, W22 Warriyangka, W25 Thiin, W28 Jiwarli |
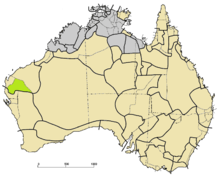 Mantharta languages (green) among other Pama–Nyungan (tan). | |
Mantharta is a possibly extinct dialect cluster spoken in the southern Pilbara region of Western Australia. There were four varieties, which were distinct but largely mutually intelligible. The four were:[4][5]
- Tharrgari (Tharrkari, Dhargari), still spoken c. 2005
- Warriyangka (Wadiwangga), still spoken c. 1973
- Thiin, extinct by 2004
- Jiwarli (Tjiwarli), extinct by 2004
The name mantharta comes from the word for "man" in all four varieties.
For details, see Jiwarli dialect.
References
- 1 2 Tharrkari at the Australian Indigenous Languages Database, Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies (see the info box for additional links)
- ↑ Dhargari at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Mantharta". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Dixon, R. M. W. (2002). Australian Languages: Their Nature and Development. Cambridge University Press. p. xxxviii.
- ↑ Bowern & Koch (2004) Australian Languages: Classification and the Comparative Method
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.