Machine code
| Program execution |
|---|
| General concepts |
| Types of code |
| Compilation strategies |
| Notable runtimes |
|
| Notable compilers & toolchains |
|
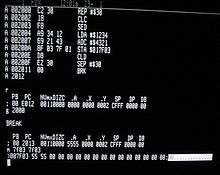
Machine code is a computer program written in machine language instructions that can be executed directly by a computer's central processing unit (CPU). Each instruction causes the CPU to perform a very specific task, such as a load, a jump, or an ALU operation on a unit of data in a CPU register or memory.
Machine code is a strictly numerical language which is intended to run as fast as possible, and may be regarded as the lowest-level representation of a compiled or assembled computer program or as a primitive and hardware-dependent programming language. While it is possible to write programs directly in machine code, it is tedious and error prone to manage individual bits and calculate numerical addresses and constants manually. For this reason, programs are very rarely written directly in machine code in modern contexts, but may be done for low level debugging, program patching, and assembly language disassembly.
The overwhelming majority of practical programs today are written in higher-level languages or assembly language. The source code is then translated to executable machine code by utilities such as compilers, assemblers, and linkers, with the important exception of interpreted programs,[1] which are not translated into machine code. However, the interpreter itself, which may be seen as an executor or processor, performing the instructions of the source code, typically consists of directly executable machine code (generated from assembly or high-level language source code).
Machine code is by definition the lowest level of programming detail visible to the programmer, but internally many processors use microcode or optimise and transform machine code instructions into sequences of micro-ops, this is not generally considered to be a machine code per se.
Instruction set
Every processor or processor family has its own instruction set. Instructions are patterns of bits that by physical design correspond to different commands to the machine. Thus, the instruction set is specific to a class of processors using (mostly) the same architecture. Successor or derivative processor designs often include all the instructions of a predecessor and may add additional instructions. Occasionally, a successor design will discontinue or alter the meaning of some instruction code (typically because it is needed for new purposes), affecting code compatibility to some extent; even nearly completely compatible processors may show slightly different behavior for some instructions, but this is rarely a problem. Systems may also differ in other details, such as memory arrangement, operating systems, or peripheral devices. Because a program normally relies on such factors, different systems will typically not run the same machine code, even when the same type of processor is used.
A processor's instruction set may have all instructions of the same length, or it may have variable-length instructions. How the patterns are organized varies strongly with the particular architecture and often also with the type of instruction. Most instructions have one or more opcode fields which specifies the basic instruction type (such as arithmetic, logical, jump, etc.) and the actual operation (such as add or compare) and other fields that may give the type of the operand(s), the addressing mode(s), the addressing offset(s) or index, or the actual value itself (such constant operands contained in an instruction are called immediates).[2]
Not all machines or individual instructions have explicit operands. An accumulator machine has a combined left operand and result in an implicit accumulator for most arithmetic instructions. Other architectures (such as 8086 and the x86-family) have accumulator versions of common instructions, with the accumulator regarded as one of the general registers by longer instructions. A stack machine has most or all of its operands on an implicit stack. Special purpose instructions also often lack explicit operands (CPUID in the x86 architecture writes values into four implicit destination registers, for instance). This distinction between explicit and implicit operands is important in code generators, especially in the register allocation and live range tracking parts. A good code optimizer can track implicit as well as explicit operands which may allow more frequent constant propagation, constant folding of registers (a register assigned the result of a constant expression freed up by replacing it by that constant) and other code enhancements.
Programs
A computer program is a list of instructions that can be executed by a central processing unit. A program's execution is done in order for the CPU that is executing it to solve a specific problem and thus accomplish a specific result. While simple processors are able to execute instructions one after another, superscalar processors are capable of executing a variety of different instructions at once.
Program flow may be influenced by special 'jump' instructions that transfer execution to an instruction other than the numerically following one. Conditional jumps are taken (execution continues at another address) or not (execution continues at the next instruction) depending on some condition.
Assembly languages
A much more readable rendition of machine language, called assembly language, uses mnemonic codes to refer to machine code instructions, rather than using the instructions' numeric values directly. For example, on the Zilog Z80 processor, the machine code 00000101, which causes the CPU to decrement the B processor register, would be represented in assembly language as DEC B.
Example
The MIPS architecture provides a specific example for a machine code whose instructions are always 32 bits long. The general type of instruction is given by the op (operation) field, the highest 6 bits. J-type (jump) and I-type (immediate) instructions are fully specified by op. R-type (register) instructions include an additional field funct to determine the exact operation. The fields used in these types are:
6 5 5 5 5 6 bits [ op | rs | rt | rd |shamt| funct] R-type [ op | rs | rt | address/immediate] I-type [ op | target address ] J-type
rs, rt, and rd indicate register operands; shamt gives a shift amount; and the address or immediate fields contain an operand directly.
For example, adding the registers 1 and 2 and placing the result in register 6 is encoded:
[ op | rs | rt | rd |shamt| funct]
0 1 2 6 0 32 decimal
000000 00001 00010 00110 00000 100000 binary
Load a value into register 8, taken from the memory cell 68 cells after the location listed in register 3:
[ op | rs | rt | address/immediate] 35 3 8 68 decimal 100011 00011 01000 00000 00001 000100 binary
Jumping to the address 1024:
[ op | target address ]
2 1024 decimal
000010 00000 00000 00000 10000 000000 binary
Relationship to microcode
In some computer architectures, the machine code is implemented by an even more fundamental underlying layer called microcode, providing a common machine language interface across a line or family of different models of computer with widely different underlying dataflows. This is done to facilitate porting of machine language programs between different models. An example of this use is the IBM System/360 family of computers and their successors. With dataflow path widths of 8 bits to 64 bits and beyond, they nevertheless present a common architecture at the machine language level across the entire line.
Using microcode to implement an emulator enables the computer to present the architecture of an entirely different computer. The System/360 line used this to allow porting programs from earlier IBM machines to the new family of computers, e.g. an IBM 1401/1440/1460 emulator on the IBM S/360 model 40.
Relationship to bytecode
Machine code is generally different from bytecode (also known as p-code), which is either executed by an interpreter or itself compiled into machine code for faster (direct) execution. An exception is when a processor is designed to use a particular bytecode directly as its machine code, such as is the case with Java processors.
Machine code and assembly code are sometimes called native code when referring to platform-dependent parts of language features or libraries.[3]
Storing in memory
The Harvard architecture is a computer architecture with physically separate storage and signal pathways for the code (instructions) and data. Today, most processors implement such separate signal pathways for performance reasons but actually implement a Modified Harvard architecture, so they can support tasks like loading an executable program from disk storage as data and then executing it. Harvard architecture is contrasted to the Von Neumann architecture, where data and code are stored in the same memory which is read by the processor allowing the computer to execute commands.
From the point of view of a process, the code space is the part of its address space where the code in execution is stored. In multitasking systems this comprises the program's code segment and usually shared libraries. In multi-threading environment, different threads of one process share code space along with data space, which reduces the overhead of context switching considerably as compared to process switching.
Readability by humans
Pamela Samuelson wrote that machine code is so unreadable that the United States Copyright Office cannot identify whether a particular encoded program is an original work of authorship;[4] however, the US Copyright Office does allow for copyright registration of computer programs[5] and a program's machine code can sometimes be decompiled in order to make its functioning more easily understandable to humans.[6]
Cognitive science professor Douglas Hofstadter has compared machine code to genetic code, saying that "Looking at a program written in machine language is vaguely comparable to looking at a DNA molecule atom by atom."[7]
See also
| Look up machine code in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Notes and references
- ↑ Such as many versions of BASIC, especially early ones, as well as Smalltalk, MATLAB, Perl, Python, Ruby and other special purpose or scripting languages.
- ↑ Bradley Kjell; kjell at ieee dot org. "Immediate Operand".
- ↑ "Managed, Unmanaged, Native: What Kind of Code Is This?". developer.com. Retrieved 2008-09-02.
- ↑ Pamela Samuelson (Sep 1984). "CONTU Revisited: The Case against Copyright Protection for Computer Programs in Machine-Readable Form". 1984 (4). Duke Law Journal: 663–769. JSTOR 1372418.
- ↑ "Copyright Registration for Computer Programs" (PDF). US Copyright Office. August 2008. Retrieved February 23, 2014.
- ↑ "What is decompile? - Definition from WhatIs.com". WhatIs.com. Retrieved 2016-12-26.
- ↑ D. Hofstadter (1980). "Gödel, Escher, Bach: An Eternal Golden Braid": 290.
Further reading
- Hennessy, John L.; Patterson, David A. Computer Organization and Design. The Hardware/Software Interface. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers. ISBN 1-55860-281-X.
- Tanenbaum, Andrew S. Structured Computer Organization. Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-020435-8.
- Brookshear, J. Glenn. Computer Science: An Overview. Addison Wesley. ISBN 0-321-38701-5.