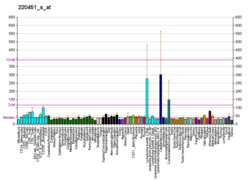
BIRC7
Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BIRC7 gene.[5][6][7]
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the family of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAP) and contains a single copy of a baculovirus IAP repeat (BIR) as well as a RING-type zinc finger domain. The BIR domain is essential for inhibitory activity and interacts with caspases, while the RING finger domain sometimes enhances antiapoptotic activity but does not inhibit apoptosis alone. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. The two isoforms have different antiapoptotic properties, with isoform alpha protecting cells from apoptosis induced by staurosporine and isoform b protecting cells from apoptosis induced by etoposide.[7] In melanoma, BIRC7 gene expression is regulated by the Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor.[8][9]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000101197 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000038840 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Kasof GM, Gomes BC (May 2001). "Livin, a novel inhibitor of apoptosis protein family member". J Biol Chem. 276 (5): 3238–46. doi:10.1074/jbc.M003670200. PMID 11024045.
- ↑ Lin JH, Deng G, Huang Q, Morser J (Feb 2001). "KIAP, a novel member of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein family". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 279 (3): 820–31. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.4027. PMID 11162435.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: BIRC7 baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 7 (livin)".
- ↑ Dynek JN, Chan SM, Liu J, et al. (2008). "Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor is a critical transcriptional regulator of melanoma inhibitor of apoptosis in melanomas". Cancer Res. 68 (9): 3124–32. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6622. PMID 18451137.
- ↑ Hoek KS, Schlegel NC, Eichhoff OM, et al. (2008). "Novel MITF targets identified using a two-step DNA microarray strategy". Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 21 (6): 665–76. doi:10.1111/j.1755-148X.2008.00505.x. PMID 19067971.
External links
- Human BIRC7 genome location and BIRC7 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Bavykin AS, Korotaeva AA, Poyarkov SV, et al. (2013). "Double siRNA-targeting of cIAP2 and LIVIN results in synergetic sensitization of HCT-116 cells to oxaliplatin treatment". Onco Targets Ther 0. 6 (6): 1333–40. doi:10.2147/OTT.S44893. PMC 3789649. PMID 24098083.
- Vucic D, Stennicke HR, Pisabarro MT, et al. (2001). "ML-IAP, a novel inhibitor of apoptosis that is preferentially expressed in human melanomas". Curr. Biol. 10 (21): 1359–66. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(00)00781-8. PMID 11084335.
- Ashhab Y, Alian A, Polliack A, et al. (2001). "Two splicing variants of a new inhibitor of apoptosis gene with different biological properties and tissue distribution pattern". FEBS Lett. 495 (1–2): 56–60. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(01)02366-3. PMID 11322947.
- Deloukas P, Matthews LH, Ashurst J, et al. (2002). "The DNA sequence and comparative analysis of human chromosome 20". Nature. 414 (6866): 865–71. doi:10.1038/414865a. PMID 11780052.
- Vucic D, Deshayes K, Ackerly H, et al. (2002). "SMAC negatively regulates the anti-apoptotic activity of melanoma inhibitor of apoptosis (ML-IAP)". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (14): 12275–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112045200. PMID 11801603.
- Sanna MG, da Silva Correia J, Ducrey O, et al. (2002). "IAP suppression of apoptosis involves distinct mechanisms: the TAK1/JNK1 signaling cascade and caspase inhibition". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (6): 1754–66. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.6.1754-1766.2002. PMC 135597. PMID 11865055.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Gazzaniga P, Gradilone A, Giuliani L, et al. (2003). "Expression and prognostic significance of LIVIN, SURVIVIN and other apoptosis-related genes in the progression of superficial bladder cancer". Ann. Oncol. 14 (1): 85–90. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdg002. PMID 12488298.
- Clark HF, Gurney AL, Abaya E, et al. (2003). "The secreted protein discovery initiative (SPDI), a large-scale effort to identify novel human secreted and transmembrane proteins: a bioinformatics assessment". Genome Res. 13 (10): 2265–70. doi:10.1101/gr.1293003. PMC 403697. PMID 12975309.
- Crnkovic-Mertens I, Hoppe-Seyler F, Butz K (2004). "Induction of apoptosis in tumor cells by siRNA-mediated silencing of the livin/ML-IAP/KIAP gene". Oncogene. 22 (51): 8330–6. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206973. PMID 14614456.
- Andersen MH, Reker S, Becker JC, thor Straten P (2004). "The melanoma inhibitor of apoptosis protein: a target for spontaneous cytotoxic T cell responses". J. Invest. Dermatol. 122 (2): 392–9. doi:10.1046/j.0022-202X.2004.22242.x. PMID 15009721.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Tanabe H, Yagihashi A, Tsuji N, et al. (2005). "Expression of survivin mRNA and livin mRNA in non-small-cell lung cancer". Lung Cancer. 46 (3): 299–304. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2004.05.002. PMID 15541814.
- Yagihashi A, Ohmura T, Asanuma K, et al. (2006). "Detection of autoantibodies to survivin and livin in sera from patients with breast cancer". Clin. Chim. Acta. 362 (1–2): 125–30. doi:10.1016/j.cccn.2005.06.009. PMID 16026775.
- Crnković-Mertens I, Semzow J, Hoppe-Seyler F, Butz K (2006). "Isoform-specific silencing of the Livin gene by RNA interference defines Livin beta as key mediator of apoptosis inhibition in HeLa cells". J. Mol. Med. 84 (3): 232–40. doi:10.1007/s00109-005-0021-5. PMID 16437214.
- Ma L, Huang Y, Song Z, et al. (2007). "Livin promotes Smac/DIABLO degradation by ubiquitin-proteasome pathway". Cell Death Differ. 13 (12): 2079–88. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401959. PMID 16729033.
- Yan H, Brouha B, Liu T, et al. (2006). "Proteolytic cleavage of Livin (ML-IAP) in apoptotic melanoma cells potentially mediated by a non-canonical caspase". J. Dermatol. Sci. 43 (3): 189–200. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2006.05.007. PMC 2292408. PMID 16806840.
- Wu H, Ma Y, Zhu Y, et al. (2007). "Expression of BIRC7 protein and mRNA in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma". Leuk. Lymphoma. 47 (6): 1110–6. doi:10.1080/10428190500472271. PMID 16840203.
- Crnković-Mertens I, Muley T, Meister M, et al. (2007). "The anti-apoptotic livin gene is an important determinant for the apoptotic resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells". Lung Cancer. 54 (2): 135–42. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2006.07.018. PMID 16965834.