List of exceptional asteroids


The following is a collection of lists of exceptional asteroids in the Solar System. For the purposes of this article "asteroid" means minor planet up to the orbit of Jupiter, which includes the dwarf planet Ceres. For a complete list of minor planets in numerical order, see List of minor planets.
Asteroids are given a unique sequential identifying number once their orbit is precisely determined. Prior to this, they are known only by their systematic name or provisional designation, such as 1950 DA.
Physical characteristics
Largest by diameter
Estimating the sizes of asteroids from observations is difficult due to their irregular shapes, varying albedo, and small angular diameter. For example, pure C-type asteroids are much darker than most. Asteroids with only one or two axes measured may have a falsely inflated geometric mean diameter if the unknown second or third axis is significantly smaller than the primary axis. Asteroid 16 Psyche has an IRAS diameter of 253 km, yet has a more recent and accurate geometric mean of only 186 km.
| Name | Diameter (km) (geometric mean) | Dimensions (km) | Mean distance from Sun (in AU) | Date discovered | Discoverer | Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Ceres | 946±2 | 965×962×891 | 2.766 | January 1, 1801 | Piazzi, G. | G |
| 4 Vesta | 525.4±0.2 | 572.6 × 557.2 × 446.4 ± 0.2 | 2.362 | March 29, 1807 | Olbers, H. W. | V |
| 2 Pallas | 512±3 | 550±4 × 516±3 × 476±3 km[2] | 2.773 | March 28, 1802 | Olbers, H. W. | B |
| 10 Hygiea | 431±7 | 530×407×370 | 3.139 | April 12, 1849 | de Gasparis, A. | C |
| 704 Interamnia | 326 | 350×304 | 3.062 | October 2, 1910 | Cerulli, V. | F |
| 52 Europa | 315 | 380×330×250 | 3.095 | February 4, 1858 | Goldschmidt, H. | C |
| 511 Davida | 289 | 357×294×231 | 3.168 | May 30, 1903 | Dugan, R. S. | C |
| 87 Sylvia | 286 | 385×265×230 | 3.485 | May 16, 1866 | Pogson, N. R. | X |
| 65 Cybele | 273 | 302×290×232 | 3.439 | March 8, 1861 | Tempel, E. W. | C |
| 15 Eunomia | 268 | 357×255×212 | 2.643 | July 29, 1851 | de Gasparis, A. | S |
| 3 Juno | 258 | 320×267×200 | 2.672 | September 1, 1804 | Harding, K. L. | S |
| 31 Euphrosyne | 256 | 255.9 ± 5.8 km | 3.149 | September 1, 1854 | Ferguson, J. | C |
| 624 Hektor | 241 | 370×195(×195) | 5.235 | February 10, 1907 | Kopff, A. | D |
| 88 Thisbe | 232 | 221×201×168 | 2.769 | June 15, 1866 | Peters, C. H. F. | B |
| 324 Bamberga | 229 | 229×235×229 | 2.684 | February 25, 1892 | Palisa, J. | C |
| 451 Patientia | 225 | 225×234 | 3.059 | December 4, 1899 | Charlois, A. | |
| 532 Herculina | 222 | 260×220×215 | 2.772 | April 20, 1904 | Wolf, M. | S |
| 48 Doris | 222 | 278×142 | 3.108 | September 19, 1857 | Goldschmidt, H. | C |
| 375 Ursula | 216 | 189×192×194 | 3.126 | September 18, 1893 | Charlois, A. | |
| 107 Camilla | 215 | 285×205×170 | 3.476 | November 17, 1868 | Pogson, N. R. | C |
| 45 Eugenia | 213 | 305×220×145 | 2.720 | June 27, 1857 | Goldschmidt, H. | F |
| 7 Iris | 213 | 240×200×200 | 2.386 | August 13, 1847 | Hind, J. R. | S |
| 29 Amphitrite | 212 | 233×212×193 | 2.554 | March 1, 1854 | Marth, A. | S |
| 423 Diotima | 209 | 171×138 | 3.065 | December 7, 1896 | Charlois, A. | C |
| 19 Fortuna | 208 | 225×205×195 | 2.442 | August 22, 1852 | Hind, J. R. | G |
| 13 Egeria | 206 | 217×196 | 2.576 | November 2, 1850 | de Gasparis, A. | G |
| 24 Themis | 198 | spheroid 198 | 3.136 | April 5, 1853 | de Gasparis, A. | C |
| 94 Aurora | 197 | 225×173 | 3.160 | September 6, 1867 | Watson, J. C. | C |
| 702 Alauda | 195 | 97.365±1.6 km | 3.195 | July 16, 1910 | Helffrich, J. | C/B |
| 121 Hermione | 190 | 268×186×183 | 3.457 | May 12, 1872 | Watson, J. C. | C |
| 259 Aletheia | 190 | 178×190 | 3.135 | June 28, 1886 | Peters, C. H. F. | C/P/X |
| 372 Palma | 189 | 188 | 3.149 | August 19, 1893 | Charlois, A. | B |
| 128 Nemesis | 188 | 188 | 2.751 | November 25, 1872 | Watson, J. C. | C |
| 6 Hebe | 186 | 205x185x170 | 2.426 | July 1, 1847 | Hencke, K. L. | S |
| 16 Psyche | 186 | 240×185×145 | 2.924 | March 17, 1852 | de Gasparis, A. | M |
| 120 Lachesis | 174 | 184x144 | 3.301 | April 10, 1872 | Borrelly, A. | C |
| 41 Daphne | 174 | 213x160 | 2.765 | May 22, 1856 | Goldschmidt, H. | C |
| 9 Metis | 174 | 222x182x130 | 2.385 | April 25, 1848 | Graham, A. | S |
The number of bodies grows rapidly as the size decreases. Based on IRAS data there are about 140 main-belt asteroids with a diameter greater than 120 km.[3] For a more complete list, see List of Solar System objects by size.
The inner asteroid belt (defined as the region interior to the 3:1 Kirkwood gap at 2.50 AU) has few large asteroids. Of those in the above list, only 4 Vesta, 19 Fortuna, 6 Hebe, 7 Iris and 9 Metis orbit there.
Most massive
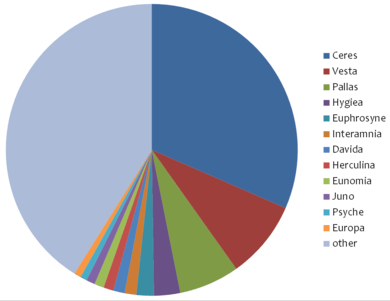
Below are the nineteen most massive measured asteroids.[4] The masses of asteroids are calculated from perturbations they induce on the orbits of other asteroids, except for asteroids that have been visited by spacecraft or have an observable moon, where a direct mass determination is possible. Different sets of astrometric observations lead to different mass determinations; the biggest problem is accounting for the aggregate perturbations caused by all of the smaller asteroids.[5]
| Name | Mass (×1018 kg) |
Precision | Approx. prop'n all asteroids |
Diameter ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Ceres | 939.3 | 0.05% (939–940) | 31% | 1 |
| 4 Vesta | 259.076 | 0.0004% (259.075–259.077) | 8.6% | 2 |
| 2 Pallas | 201 | 6.4% (188–214) | 6.7% | 3 |
| 10 Hygiea | 86.7 | 1.7% (85.2–88.4) | 2.9% | 4 |
| 31 Euphrosyne | 58.1 | 34% (38.4–77.8) | 1.9% | 12 |
| 704 Interamnia | 38.8 | 4.6% (37.0–40.6) | 1.3% | 5 |
| 511 Davida | 37.7 | 5.2% (35.7–39.7) | 1.3% | 7 |
| 532 Herculina | 33 | 17% (27–39) | 1.1% | 17 |
| 15 Eunomia | 31.8 | 0.9% (31.5–32.1) | 1.1% | 10 |
| 3 Juno | 28.6 | 16% (24.0–33.2) | 0.95% | 11 |
| 16 Psyche | 22.7 | 3.7% (21.9–23.5) | 0.76% | 35 |
| 52 Europa | 22.7 | 7% (21.1–24.3) | 0.76% | 6 |
| 88 Thisbe | 18.3 | 6% (17.2–19.4) | 0.61% | 14 |
| 7 Iris | 16.2 | 5.6% (15.3–17.1) | 0.54% | 21 |
| 13 Egeria | 16 | 27% (12–20) | 0.53% | 26 |
| 423 Diotima | 16 | Unknown | 0.53% | 24 |
| 29 Amphitrite | 15.2 | 4% (14.8–15.6) | 0.51% | 23 |
| 87 Sylvia | 14.78 | 0.4% (14.72–14.84) | 0.49% | 8 |
| 48 Doris | 12 | 50% (6–18) | 0.4% | 18 |
| Total | 1868.0 | NA | 62.0% | NA |
(All the data above are from Baer et al. 2011, apart from 48 Doris and 532 Herculina, which are Kochetova, 2004. The proportions assume that the total mass is 3.0×1021 kg, or (15.0±1.0)×10−10 M☉.[6]
Significant uncertainties remain. For example, the uncertainty in the estimate of 31 Euphrosyne is enough for its low end to overlap with both 704 Interamnia and 511 Davida, which overlap each other and also with 532 Herculina, which overlaps with 15 Eunomia and 3 Juno. Juno barely overlaps 52 Europa, which in turn overlaps with 16 Psyche. That is, outside the top four, the order of all the asteroids is uncertain. However, none of the lesser asteroids, of which the most massive are thought to be 88 Thisbe (at 17–19×1018 kg), 7 Iris, 29 Amphitrite and 48 Doris (all in the range of ≈15×1018 kg), overlap with Europa or Psyche, so the first 12 asteroids in the chart above are likely to be the top dozen unless a hitherto unmeasured asteroid proves to be unexpectedly massive.
The largest asteroids with an accurately measured mass, due to the fact that they have been (and are being) studied by the probe Dawn, are 1 Ceres with a mass of 939.3±0.5×1018 kg, and 4 Vesta at 259.076±0.001×1018 kg. The third-largest asteroid with an accurately measured mass, due to the fact that it has moons, is 87 Sylvia at 14.78±0.06×1018 kg.
For a more complete list, see List of Solar System objects by size. Other large asteroids such as 423 Diotima currently only have estimated masses.[8][9]
Brightest from Earth
Only Vesta regularly attains a brightness sufficient to be visible to the naked eye. The following asteroids can all reach an apparent magnitude brighter than or equal to the +8.3 attained by Saturn's moon Titan at its brightest, which was discovered 145 years before the first asteroid was found owing to its closeness to the easily observed Saturn.
None of the asteroids in the outer part of the asteroid belt can ever attain this brightness. Even Hygiea and Interamnia rarely reach magnitudes of above 10.0. This is due to the different distribution of spectral types within different sections of the asteroid belt being such that the highest-albedo asteroids are all concentrated closer to Mars, and much lower albedo C and D types being common in the outer belt.
Those asteroids with very high eccentricities will only reach their maximum magnitude on unusual occasions when their perihelion is very close to a heliocentric conjunction with Earth, or (in the case of 99942 Apophis) when the asteroid passes very close to Earth.
| Asteroid | Magnitude when brightest | Semi-major axis (AU) | Eccentricity of orbit | Diameter (km) | Year of discovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 99942 Apophis | 3.4* | 0.922 | 0.191 | 0.32 | 2004 |
| 4 Vesta | 5.20 | 2.361 | 0.089172 | 529 | 1807 |
| 2 Pallas | 6.49 | 2.773 | 0.230725 | 544 | 1802 |
| 1 Ceres | 6.65 | 2.766 | 0.079905 | 952 | 1801 |
| 7 Iris | 6.73 | 2.385 | 0.231422 | 200 | 1847 |
| 433 Eros | 6.8 | 1.458 | 0.222725 | 34 × 11 × 11 | 1898 |
| 6 Hebe | 7.5 | 2.425 | 0.201726 | 186 | 1847 |
| 3 Juno | 7.5 | 2.668 | 0.258194 | 233 | 1804 |
| 18 Melpomene | 7.5 | 2.296 | 0.218708 | 141 | 1852 |
| 15 Eunomia | 7.9 | 2.643 | 0.187181 | 268 | 1851 |
| 8 Flora | 7.9 | 2.202 | 0.156207 | 128 | 1847 |
| 324 Bamberga | 8.0 | 2.682 | 0.338252 | 229 | 1892 |
| 1036 Ganymed | 8.1 | 2.6657 | 0.533710 | 32 | 1924 |
| 9 Metis | 8.1 | 2.387 | 0.121441 | 190 | 1848 |
| 192 Nausikaa | 8.2 | 2.404 | 0.246216 | 103 | 1879 |
| 20 Massalia | 8.3 | 2.409 | 0.142880 | 145 | 1852 |
* Apophis will only achieve that brightness on April 13, 2029.[10][11] It typically has an apparent magnitude of 20–22.
Slowest rotators
This list contains the slowest-rotating known minor planets with a period of at least 1000 hours, or 412⁄3 days, while most bodies have rotation periods between 2 and 20 hours. Also see Potentially slow rotators for minor planets with an insufficiently accurate period (U < 2).
| # | Minor planet designation | Rotation period (hours) |
Δmag | Quality (U) |
Orbit or family | Spectral type | Diameter (km) |
Abs. mag (H) |
Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | (300163) 2006 VW139 | 3240 | ? | ? | MBA (outer) | C | 3.20 | 16.2 | LCDB · List |
| 2. | (11474) 1982 SM2 | 1917.221 | 0.04 | 1 | Baptistina | C | 5.71 | 14.94 | LCDB · List |
| 3. | (162058) 1997 AE12 | 1880 | 0.6 | 2 | NEO | S | 0.782 | 17.9 | LCDB · List |
| 4. | 846 Lipperta | 1641 | 0.30 | 2 | Themis | CBU: | 52.41 | 10.26 | LCDB · List |
| 5. | 2440 Educatio | 1561 | 0.80 | 2 | Flora | S | 6.51 | 13.1 | LCDB · List |
| 6. | 912 Maritima | 1332 | 0.18 | 3- | MBA (outer) | C | 82.14 | 9.30 | LCDB · List |
| 7. | 9165 Raup | 1320 | 1.34 | 3- | Hungaria | S | 4.62 | 13.60 | LCDB · List |
| 8. | 1235 Schorria | 1265 | 1.40 | 3 | Hungaria | CX: | 5.04 | 13.10 | LCDB · List |
| 9. | (50719) 2000 EG140 | 1256 | 0.42 | 2 | Eunomia | S | 3.40 | 14.65 | LCDB · List |
| 10. | (75482) 1999 XC173 | 1234.2 | 0.69 | 2 | Vestian | S | 2.96 | 15.01 | LCDB · List |
| 11. | 288 Glauke | 1170 | 0.90 | 3 | MBA (outer) | S | 32.24 | 10.00 | LCDB · List |
| 12. | (39546) 1992 DT5 | 1167.4 | 0.80 | 2 | MBA (outer) | C | 5.34 | 15.09 | LCDB · List |
| 13. | (145727) 1994 PL29 | 1084.883 | 0.06 | 1 | Nysa-Polana | S | 1.43 | 16.54 | LCDB · List |
| 14. | 496 Gryphia | 1072 | 1.25 | 3 | Flora | S | 15.47 | 11.61 | LCDB · List |
| 15. | 4524 Barklajdetolli | 1069 | 1.26 | 2 | Flora | S | 7.14 | 12.90 | LCDB · List |
| 16. | 5316 Filatov | 1061.376 | 0.07 | 1 | MBA (outer) | C | 22.95 | 11.92 | LCDB · List |
| 17. | 2675 Tolkien | 1060 | 0.75 | 2+ | Flora | S | 9.85 | 12.20 | LCDB · List |
| 18. | (219774) 2001 YY145 | 1007.7 | 0.86 | 2 | MBA (inner) | S | 1.54 | 16.43 | LCDB · List |
Fastest rotators
This list contains the fastest-rotating minor planets with a period of less than 100 seconds, or 0.027 hours. Bodies with a highly uncertain period, having a quality of less than 2, are highlighted in dark-grey. The fastest rotating bodies are all unnumbered near-Earth objects (NEOs) with a diameter of less than 100 meters (see table).
Among the numbered minor planets with an unambiguous period solution are (459872) 2014 EK24, a 60-meter sized stony NEO with a period of 352 seconds, as well as (335433) 2005 UW163 and (60716) 2000 GD65, two main-belt asteroids, with a diameter of 0.86 and 2.25 kilometers and a period of 1.29 and 1.95 hours, respectively (see full list).
| # | Minor planet designation | Rotation period | Δmag | Quality (U) |
Orbit or family | Spectral type | Diameter (km) |
Abs. mag (H) |
Refs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (seconds) | (hours) | |||||||||
| 1. | 2014 RC | 16 | 0.004389 | 0.10 | n.a. | NEO | S | 0.012 | 26.80 | LCDB · MPC |
| 2. | 2015 SV6 | 18 | 0.00490 | 0.74 | 2 | NEO | S | 0.009 | 27.70 | LCDB · MPC |
| 3. | 2010 JL88 | 25 | 0.0068295 | 0.52 | 3 | NEO | S | 0.013 | 26.80 | LCDB · MPC |
| 4. | 2017 EK | 30 | 0.0083 | 0.30 | 2 | NEO | S | 0.045 | 24.10 | LCDB · MPC |
| 5. | 2010 WA | 31 | 0.0085799 | 0.22 | 3 | NEO | S | 0.003 | 30.00 | LCDB · MPC |
| 6. | 2017 UK8 | 31 | 0.0086309 | 1.30 | 3 | NEO | S | 0.007 | 28.20 | LCDB · MPC |
| 7. | 2016 GE1 | 34 | 0.009438 | 0.13 | 2 | NEO | S | 0.014 | 26.60 | LCDB · MPC |
| 8. | 2008 HJ | 43 | 0.01185 | 0.80 | 3- | NEO | S | 0.021 | 25.80 | LCDB · MPC |
| 9. | 2009 TM8 | 43 | 0.012 | – | n.a. | NEO | S | 0.006 | 28.40 | LCDB · MPC |
| 10. | 2015 SU | 46 | 0.0127 | 0.20 | 2- | NEO | S | 0.025 | 25.40 | LCDB · MPC |
| 11. | 2010 SK13 | 52 | 0.0144 | – | n.a. | NEO | S | 0.01 | 27.40 | LCDB · MPC |
| 12. | 2009 BF2 | 57 | 0.01593 | 0.80 | 3 | NEO | S | 0.02 | 25.90 | LCDB · MPC |
| 13. | 2016 GS2 | 66 | 0.0182725 | 0.06 | 1 | NEO | S | 0.075 | 23.00 | LCDB · MPC |
| 14. | 2010 TG19 | 70 | 0.0193935 | 1.10 | 3 | NEO | S | 0.049 | 23.90 | LCDB · MPC |
| 15. | 2008 WA14 | 70 | 0.0195 | – | n.a. | NEO | S | 0.075 | 23.00 | LCDB · MPC |
| 16. | 2007 KE4 | 77 | 0.021408 | 0.38 | 3- | NEO | S | 0.027 | 25.20 | LCDB · MPC |
| 17. | 2000 DO8 | 78 | 0.0217 | 1.39 | 3 | NEO | S | 0.037 | 24.54 | LCDB · MPC |
| 18. | 2014 GQ17 | 78 | 0.0217 | 0.08 | 2- | NEO | S | 0.011 | 27.10 | LCDB · MPC |
| 19. | 2014 TV | 79 | 0.02190 | 0.32 | 2 | NEO | S | 0.039 | 24.40 | LCDB · MPC |
| 20. | 2000 WH10 | 80 | 0.02221 | 0.66 | 3- | NEO | S | 0.094 | 22.50 | LCDB · MPC |
| 21. | 2012 HG2 | 82 | 0.0227 | – | n.a. | NEO | S | 0.012 | 27.00 | LCDB · MPC |
| 22. | 2010 TD54 | 83 | 0.0229317 | 0.92 | 3 | NEO | S | 0.005 | 28.90 | LCDB · MPC |
| 23. | 2010 TS19 | 83 | 0.023 | – | n.a. | NEO | S | 0.022 | 25.70 | LCDB · MPC |
| 24. | 2009 UD | 84 | 0.023246 | 0.66 | 2+ | NEO | S | 0.011 | 27.20 | LCDB · MPC |
| 25. | 2014 WB366 | 86 | 0.0238 | 0.46 | 2+ | NEO | S | 0.033 | 24.80 | LCDB · MPC |
| 26. | 2015 RF36 | 90 | 0.025 | 0.15 | 2 | NEO | S | 0.062 | 23.40 | LCDB · MPC |
| 27. | 2015 AK45 | 93 | 0.0258 | 0.24 | 2 | NEO | S | 0.016 | 26.40 | LCDB · MPC |
| 28. | 2010 XE11 | 96 | 0.0265846 | 0.50 | 3 | NEO | S | 0.075 | 23.00 | LCDB · MPC |
| 29. | 2000 UK11 | 96 | 0.026599 | 0.28 | 2 | NEO | S | 0.026 | 25.30 | LCDB · MPC |
| 30. | 2016 RB1 | 96 | 0.02674 | 0.18 | 2+ | NEO | S | 0.007 | 28.30 | LCDB · MPC |
| 31. | 2015 CM | 96 | 0.0268 | 0.53 | 3- | NEO | S | 0.018 | 26.10 | LCDB · MPC |
| 32. | 2008 TC3 | 97 | 0.0269409 | 1.02 | 3 | NEO | F | 0.004 | 30.90 | LCDB · MPC |
Orbital characteristics
Retrograde
Minor planets with orbital inclinations greater than 90° (the greatest possible is 180°) orbit in a retrograde direction. As of September 2016, of the more than 700,000 minor planets known, there are only 95 known retrograde minor planets.[12] In comparison, there are over 1920 comets with retrograde orbits. This makes retrograde minor planets the rarest group of all. High-inclination asteroids are either Mars-crossers (possibly in the process of being ejected from the Solar System) or damocloids. Some of these are temporarily captured in retrograde resonance with the gas giants.[13]
| Minor planet designation | Inclination (°) | First observed/ Discovery date |
Condition code | Obs. × arc | Comment | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 TN178 | 90.937° | October 8, 2015 | 4 | 2542 | — | MPC |
| 2005 SB223 | 91.419° | September 30, 2005 | 1 | 12200 | Has a well-determined orbit | MPC |
| 2014 MH55 | 91.478° | June 29, 2014 | 9 | 96 | — | MPC |
| 2015 RK245 | 91.597° | September 12, 2015 | 2 | 182880 | — | MPC |
| 2010 EQ169 | 91.606° | March 8, 2010 | 9 | 32 | — | MPC |
| 2016 TK2 | 92.343° | July 13, 2016 | 5 | 3486 | — | MPC |
| 2016 FH13 | 93.486° | March 29, 2016 | 6 | 1638 | — | MPC |
| 2014 PP69 | 93.627° | August 5, 2014 | 5 | 4816 | — | MPC |
| 2015 BH311 | 95.575° | January 20, 2015 | 9 | 39 | — | MPC |
| 2014 JJ57 | 95.958° | May 9, 2014 | 3 | 61802 | — | MPC |
| 2014 HS150 | 96.456° | April 16, 2014 | 8 | 200 | — | MPC |
| 2013 BL76 | 98.607° | January 20, 2013 | 1 | 46716 | Has a semi-major axis of 1254 AU, giving it the third largest semi-major axis of any known minor planet | MPC |
| 2010 GW147 | 99.623° | April 14, 2010 | 3 | 93632 | — | MPC |
| 2011 MM4 | 100.446° | June 24, 2011 | 4 | 36036 | — | MPC |
| 2014 XS3 | 100.934° | December 8, 2014 | 9 | 55 | — | MPC |
| 2013 BN27 | 101.780° | January 17, 2013 | 7 | 1425 | — | MPC |
| 2008 KV42 | 103.483° | May 31, 2008 | 5 | 10449 | — | MPC |
| (342842) 2008 YB3 | 105.031° | December 18, 2008 | 1 | 864896 | — | MPC |
| 2016 PN66 | 105.111° | August 14, 2016 | 4 | 15219 | — | MPC |
| 2010 GW64 | 105.273° | April 6, 2010 | 4 | 9576 | — | MPC |
| 2012 YO6 | 106.914° | December 22, 2012 | 4 | 6674 | — | MPC |
| 2009 DD47 | 107.431° | February 27, 2009 | 7 | 1584 | — | MPC |
| 2007 VW266 | 108.345° | November 12, 2007 | 7 | 2280 | — | MPC |
| 2015 MJ116 | 108.876° | June 27, 2015 | 9 | — | MPC | |
| 2011 SP25 | 108.987° | September 20, 2011 | 5 | 3712 | — | MPC |
| (471325) 2011 KT19 | 110.154° | May 21, 2011 | 2 | 350463 | — | MPC |
| 2011 OR17 | 110.345° | May 21, 2010 | 1 | 75548 | — | MPC |
| 2005 TJ50 | 110.368° | October 3, 2005 | 7 | 1488 | — | MPC |
| 2005 VX3 | 112.459° | November 1, 2005 | 4 | 4050 | Semi-major axis of 837AU, but has a somewhat short 81-day observation arc for such a large orbit | MPC |
| 2016 LS | 114.360° | June 27, 2015 | 4 | 16800 | — | MPC |
| 2015 YY18 | 118.232° | December 29, 2015 | 4 | 6901 | — | MPC |
| 2010 OM1 | 118.689° | July 28, 2010 | 5 | 3232 | — | MPC |
| (65407) 2002 RP120 | 119.106° | September 4, 2002 | 2 | 660275 | This outer-planet crosser is a damocloid and SDO). | MPC |
| 2010 PO58 | 121.229° | August 5, 2010 | 9 | 168 | — | MPC |
| 2010 LG61 | 123.732° | June 2, 2010 | 9 | 770 | — | MPC |
| (468861) 2013 LU28 | 125.414° | June 8, 2013 | 5 | 21560 | — | MPC |
| 2014 SQ339 | 128.499° | September 9, 2014 | 7 | 1276 | — | MPC |
| 2000 DG8 | 129.478° | February 25, 2000 | 3 | 44460 | A damocloid and SDO. Crosses all the outer planets except Neptune. Came within 0.03 AU of Ceres in 1930.[14] | MPC |
| 2016 CO264 | 129.852° | February 14, 2016 | 4 | 8820 | — | MPC |
| 2013 NS11 | 130.340° | July 5, 2013 | 2 | 71929 | — | MPC |
| 2005 NP82 | 130.549° | July 6, 2005 | 6 | 8769 | — | MPC |
| 2006 RG1 | 133.195° | September 1, 2006 | 6 | 750 | Has an orbit with a data arc of 25 days (Uncertainty Parameter=4) | MPC |
| 2012 YE8 | 136.136° | December 21, 2012 | 7 | 1189 | — | MPC |
| 2009 QY6 | 137.654° | August 17, 2009 | 4 | 43560 | — | MPC |
| 2016 TP93 | 138.324° | October 9, 2016 | 7 | 704 | — | MPC |
| 2015 AO44 | 139.974° | November 27, 2014 | 2 | 102600 | — | MPC |
| (336756) 2010 NV1 | 140.818° | July 2, 2010 | 1 | 266805 | Perihelion at 9.4 AU, only 2008 KV42 has perihelion further out (154-day data arc) | MPC |
| 2011 WS41 | 141.645° | November 24, 2011 | 8 | 108 | — | MPC |
| 2010 OR1 | 143.861° | January 25, 2010 | 4 | 35416 | — | MPC |
| 2010 BK118 | 143.910° | January 30, 2010 | 1 | 385148 | Semi-major axis of 408 AU with perihelion at 6.1 AU in April 2012 (1 year data arc) | MPC |
| 2016 NM56 | 144.045° | July 14, 2016 | 3 | 39960 | — | MPC |
| 2010 CG55 | 146.246° | February 15, 2010 | 2 | 124816 | — | MPC |
| 2012 HD2 | 146.897° | April 18, 2012 | 2 | 32314 | — | MPC |
| 2009 YS6 | 147.797° | December 17, 2009 | 1 | 199547 | — | MPC |
| 2006 EX52 | 150.240° | March 5, 2006 | 2 | 62930 | q=2.58 AU and period=274 yr | MPC |
| 1999 LE31 | 151.807° | June 12, 1999 | 3 | 51943 | A damocloid, Jupiter- and Saturn-crossing minor planet.[15] | MPC |
| 2016 JK24 | 152.313° | March 3, 2016 | 7 | 2448 | — | MPC |
| 2017 CW32 | 152.436° | June 9, 2016 | 2 | 46500 | — | MPC |
| (343158) 2009 HC82 | 154.496° | April 29, 2009 | 0 | 385700 | NEO that sometimes has the highest relative velocity to Earth (79 km/s) of known objects that come within 0.5 AU of Earth. However, the relative velocity at 1 AU from the sun is less than 72 km/s. | MPC |
| 2013 LD16 | 154.748° | June 6, 2013 | 3 | 14148 | — | MPC |
| 2015 FK37 | 155.971° | March 20, 2015 | 7 | 748 | — | MPC |
| 2010 EB46 | 156.531° | March 12, 2010 | 7 | 2610 | — | MPC |
| 2015 XR384 | 157.532° | December 9, 2015 | 4 | 5580 | — | MPC |
| 2000 HE46 | 158.448° | April 29, 2000 | 4 | 26400 | — | MPC |
| 2015 XX351 | 159.106° | December 9, 2015 | 3 | 20790 | — | MPC |
| 2012 TL139 | 160.036° | October 8, 2012 | 6 | 900 | — | MPC |
| 20461 Dioretsa | 160.404° | June 8, 1999 | 2 | 256779 | most highly inclined known minor planet from 1999/06/08-2004/07/13 | MPC |
| (514107) 2015 BZ509 | 163.001° | November 26, 2014 | 2 | 72846 | A Jupiter co-orbital. First known example of a retrograde co-orbital asteroid with any of the planets. Might have an interstellar origin. | MPC Src |
| 2006 RJ2 | 164.582° | September 14, 2006 | 7 | 2812 | — | MPC |
| 2006 BZ8 | 165.315° | January 23, 2006 | 2 | 214312 | — | MPC |
| 2004 NN8 | 165.466° | July 13, 2004 | 2 | 23944 | Came within 0.80 AU of Saturn on 2007-Jun-05, most highly inclined known minor planet from 2004/07/13-2005/11/01 | MPC |
| 2014 AT8 | 165.554° | January 3, 2014 | 3 | 42517 | — | MPC |
| 2016 DF2 | 167.030° | February 28, 2016 | 9 | 26 | — | MPC |
| (330759) 2008 SO218 | 170.318° | September 30, 2008 | 1 | 733950 | — | MPC |
| 2014 UV114 | 170.510° | October 26, 2014 | 9 | 34 | — | MPC |
| 2014 CW14 | 170.747° | February 10, 2014 | 7 | 1938 | MPC | |
| 2016 EJ203 | 170.911° | March 11, 2016 | 7 | 1740 | — | MPC |
| 2006 LM1 | 172.138° | June 3, 2006 | 9 | 48 | Has a data arc of only 2 days (Uncertainty Parameter=E), but has a very high inclination | MPC |
| (434620) 2005 VD | 172.866° | November 1, 2005 | 2 | 130989 | most highly inclined known minor planet from 2005/11/01-2013/06/01 | MPC |
| 2013 LA2 | 175.189° | June 1, 2013 | 8 | 1075 | Has the highest inclination of any known minor planet | MPC |
^ the value given when the number of observations is multiplied by the observation arc; larger values are generally better than smaller values depending on residuals.
Highly inclined
| Minor planet designation | Inclination | Discovery date | Comment | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Ceres | 10.593° | January 1, 1801 | most highly inclined known minor planet from 1801/01/01-1802/03/28 | MPC |
| 2 Pallas | 34.841° | March 28, 1802 | most highly inclined known minor planet from 1802/03/28-1920/10/31 | MPC |
| 944 Hidalgo | 42.525° | October 31, 1920 | most highly inclined known minor planet from 1920/10/31-1950/05/22 | MPC |
| 1373 Cincinnati | 38.949° | August 30, 1935 | First main-belt asteroid discovered to have an inclination greater than 2 Pallas. Most highly inclined known main-belt asteroid from 1935/08/30-1980/06/14 | MPC |
| 1580 Betulia | 52.083° | May 22, 1950 | most highly inclined known minor planet from 1950/05/22-1973/07/04 | MPC |
| 2938 Hopi | 41.436° | June 14, 1980 | Most highly inclined known main-belt asteroid from 1980/06/14-2000/09/20 | MPC |
| (5496) 1973 NA | 67.999° | July 4, 1973 | An Apollo asteroid, Mars-crosser and +1 km NEO; most highly inclined known minor planet from 4 July 1973 to 8 August 1999. | MPC |
| (22653) 1998 QW2 | 45.794° | August 17, 1998 | Most highly inclined known main-belt asteroid from 1998/08/17-1998/10/19 | MPC |
| (88043) 2000 UE110 | 51.998° | October 29, 2000 | First main-belt asteroid discovered and numbered to have an inclination greater than 50°. | MPC |
| (138925) 2001 AU43 | 72.132° | January 4, 2001 | A Mars-crosser and near-Earth object. | MPC |
| (127546) 2002 XU93 | 77.904° | December 4, 2002 | A damocloid and SDO. It is almost a Uranus outer-grazer. | MPC |
| (196256) 2003 EH1 | 70.790° | March 6, 2003 | A Mars-crosser, near-Earth object and Jupiter inner-grazer. | MPC |
| 1998 UQ1 | 64.281° | October 19, 1998 | Most highly inclined known main-belt asteroid from 1998/10/19-2007/11/01 | MPC |
| (467372) 2004 LG | 70.725° | June 9, 2004 | A Mercury- through Mars-crosser and near-Earth object. | MPC |
| 2007 VR6 | 68.659° | November 1, 2007 | Most highly inclined known main-belt asteroid from 2007/11/01-2008/09/26 | MPC |
| 2008 SB85 | 74.247° | September 26, 2008 | Most highly inclined known main-belt asteroid from 2008/09/26-2010/03/08(?) | MPC |
| 2010 EQ169 | 91.606° | March 8, 2010 | Most highly inclined known main-belt asteroid(?) (orbit is not well-known) | MPC |
Trojans
- Earth trojans: 2010 TK7.
- Mars trojans: (121514) 1999 UJ7, 5261 Eureka, (101429) 1998 VF31, (311999) 2007 NS2, (385250) 2001 DH47, 2011 SC191, 2011 UN63, and the candidate 2011 SL25.
- Jupiter trojans: the first one was discovered in 1906, 588 Achilles, and the current total is over 6,000.
Record-setting close approaches to Earth
Timeline
Landmark asteroids
| Name | Diameter (km) | Discovered | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 Astraea | 117 | December 8, 1845 | First asteroid discovered after original four (38 years later) |
| 87 Sylvia | 261 | May 16, 1866 | First asteroid known to have more than one moon (determined in 2005) |
| 90 Antiope | 80×80 | October 1, 1866 | Double asteroid with two nearly equal components; its double nature was discovered using adaptive optics in 2000 |
| 92 Undina | 126 | 1867 July 7 | Created in one of the largest asteroid-on-asteroid collisions of the past 100 million years |
| 216 Kleopatra | 217×94 | April 10, 1880 | Metallic asteroid with "ham-bone" shape and 2 satellites |
| 243 Ida | 56×24×21 | September 29, 1884 | First asteroid known to have a moon (determined in 1993) |
| 243 Ida I Dactyl | 1.4 | February 17, 1994 | Moon of 243 Ida, first confirmed satellite of an asteroid |
| 279 Thule | 127 | October 25, 1888 | Orbits in the asteroid belt's outermost edge in a 3:4 orbital resonance with Jupiter |
| 288 Glauke | 32 | February 20, 1890 | Exceptionally slow rotation period of about 1200 hours (2 months) |
| 323 Brucia | 36 | December 22, 1891 | First asteroid discovered by means of astrophotography rather than visual observation |
| 433 Eros | 13×13×33 | August 13, 1898 | First near-Earth asteroid discovered and the second largest; first asteroid to be detected by radar; first asteroid orbited and landed upon |
| 490 Veritas | 115 | September 3, 1902 | Created in one of the largest asteroid-on-asteroid collisions of the past 100 million years |
| 588 Achilles | 135.5 | February 22, 1906 | First Jupiter trojan discovered |
| 624 Hektor | 370×195 | February 10, 1907 | Largest Jupiter trojan discovered |
| 719 Albert | 2.4 | October 3, 1911 | Last numbered asteroid to be lost then recovered |
| 1125 China | October 30, 1957 | First asteroid discovery to be credited to an institution rather than a person | |
| 1566 Icarus | 1.4 | June 27, 1949 | First Mercury crosser discovered |
| 1902 Shaposhnikov | 97 | April 18, 1972 | The most recent main-belt asteroid discovered that is ~100+ km in diameter |
| 2063 Bacchus | 1.1×1.1×2.6 | April 24, 1977 | |
| 3200 Phaethon | 5 | October 11, 1983 | First asteroid discovered from space; source of Geminids meteor shower. |
| 3753 Cruithne | 5 | October 10, 1986 | Unusual Earth-associated orbit |
| 4179 Toutatis | 4.5×2.4×1.9 | January 4, 1989 | Closely approached Earth on September 29, 2004 |
| 4769 Castalia | 1.8×0.8 | August 9, 1989 | First asteroid to be radar-imaged in sufficient detail for 3D modeling[16] |
| 5261 Eureka | ~2–4 | June 20, 1990 | First Mars trojan (Lagrangian point L5) discovered |
| 11885 Summanus | September 25, 1990 | First automated discovery of a near-Earth object (NEO) | |
| (29075) 1950 DA | 1.1 | February 23, 1950 | Will approach Earth very closely in 2880, collision unlikely (1 in 8,300 or 0.012%) [17] |
| 69230 Hermes | 0.3 | October 28, 1937 | Named but not numbered until its recovery in 2003 (65 years later) |
| 99942 Apophis | 0.3 | June 19, 2004 | First asteroid to rank greater than one on the Torino Scale (it was ranked at 2, then 4; now down to 0). Previously better known by its provisional designation 2004 MN4. |
| (433953) 1997 XR2 | 0.23 | December 4, 1997 | First asteroid to rank greater than zero on the impact-risk Torino Scale (it was ranked 1; now at 0) |
| 1998 KY26 | 0.030 | June 2, 1998 | Approached within 800,000 km of Earth |
| 2002 AA29 | 0.1 | January 9, 2002 | Unusual Earth-associated orbit |
| 2004 FH | 0.030 | March 15, 2004 | Discovered before it approached within 43,000 km of Earth on March 18, 2004. |
| 2008 TC3 | ~0.003 | October 6, 2008 | First Earth-impactor to be spotted before impact (on October 7, 2008) |
| 2010 TK7 | ~0.3 | October 2010 | First Earth trojan to be discovered |
| 2014 RC | ~0.017 | September 1, 2014 | Asteroid with fastest rotation: 16.2 seconds |
Spacecraft targets
| Name | Diameter (km) | Discovered | Spacecraft | Year(s) | Closest approach (km) | closest approach (asteroid radii) | Notes | Landmark(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Ceres | 952 | January 1, 1801 | Dawn | 2014–present | approx. 200 (planned) | 0.42 | Dawn took its first "close up" picture of Ceres in December 2014, and entered orbit in March 2015 | First dwarf planet visited by a spacecraft, largest asteroid visited by a spacecraft |
| 4 Vesta | 529 | March 29, 1807 | Dawn | 2011–2012 | 210 | 0.76 | Dawn broke orbit on 5 September 2012 and headed to Ceres, where it arrived in March 2015 | First "big four" asteroid visited by a spacecraft, largest asteroid visited by a spacecraft at the time |
| 21 Lutetia | 120×100×80 | November 15, 1852 | Rosetta | 2010 | 3,162 | 64.9 | Flyby on 10 July 2010 | Largest asteroid visited by a spacecraft at the time |
| 243 Ida | 56×24×21 | September 29, 1884 | Galileo | 1993 | 2,390 | 152 | Flyby; discovered Dactyl | First asteroid with a moon visited by a spacecraft, largest asteroid visited by spacecraft at the time |
| 253 Mathilde | 66×48×46 | November 12, 1885 | NEAR Shoemaker | 1997 | 1,212 | 49.5 | Flyby | Largest asteroid visited by a spacecraft at the time |
| 433 Eros | 13×13×33 | August 13, 1898 | NEAR Shoemaker | 1998–2001 | 0 | 0 | 1998 flyby; 2000 orbited (first asteroid studied from orbit); 2001 landing | First asteroid landing, first asteroid orbited by a spacecraft, first near-Earth asteroid (NEA) visited by a spacecraft |
| 951 Gaspra | 18.2×10.5×8.9 | July 30, 1916 | Galileo | 1991 | 1,600 | 262 | Flyby | first asteroid visited by a spacecraft |
| 2867 Šteins | 4.6 | November 4, 1969 | Rosetta | 2008 | 800 | 302 | Flyby | First asteroid visited by the ESA |
| 4179 Toutatis | 4.5×~2 | February 10, 1934 | Chang'e 2 | 2012 | 3.2 | 0.70 | Flyby[18] | Closest asteroid flyby, first asteroid visited by China |
| 5535 Annefrank | 4.0 | March 23, 1942 | Stardust | 2002 | 3,079 | 1230 | Flyby | |
| 9969 Braille | 2.2×0.6 | May 27, 1992 | Deep Space 1 | 1999 | 26 | 12.7 | Flyby; followed by flyby of Comet Borrelly | |
| 25143 Itokawa | 0.5×0.3×0.2 | September 26, 1998 | Hayabusa | 2005 | 0 | 0 | Landed; returned dust samples to Earth | First asteroid with returned samples, smallest asteroid visited by a spacecraft, first asteroid visited by a non-NASA spacecraft |
| 162173 Ryugu | 1.0 | May 10, 1999 | Hayabusa2 | 2018-present | 0 (planned) | 0 | Multiple landers/rovers, sample return | First rovers on an asteroid |
Numbered minor planets that are also comets
| Name | Cometary name | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| 2060 Chiron | 95P/Chiron | First centaur discovered in 1977, later identified to exhibit cometary behaviour. Also one of two minor planets known to have a ring system |
| 4015 Wilson–Harrington | 107P/Wilson–Harrington | In 1992, it was realized that asteroid 1979 VA's orbit matched it with the positions of the lost comet Wilson–Harrington (1949 III) |
| 7968 Elst–Pizarro | 133P/Elst–Pizarro | Discovered in 1996 as a comet, but orbitally matched to asteroid 1979 OW7 |
| 60558 Echeclus | 174P/Echeclus | Centaur discovered in 2000, comet designation assigned in 2006 |
| 118401 LINEAR | 176P/LINEAR (LINEAR 52) | Main-belt comet–asteroid discovered to have a coma on November 26, 2005 |
The above table lists only numbered asteroids that are also comets. Note there are several cases where a non-numbered minor planets turned out to be a comet, e.g. C/2001 OG108 (LONEOS), which was provisionally designated 2001 OG108.
Minor planets that were misnamed and renamed
In earlier times, before the modern numbering and naming rules were in effect, asteroids were sometimes given numbers and names before their orbits were precisely known. And in a few cases duplicate names were given to the same object (with modern use of computers to calculate and compare orbits with old recorded positions, this type of error no longer occurs). This led to a few cases where asteroids had to be renamed.[19]
| Minor planet name | Description |
|---|---|
| 330 Adalberta | An object discovered March 18, 1892 by Max Wolf with provisional designation "1892 X" was named 330 Adalberta, but was lost and never recovered. In 1982 it was determined that the observations leading to the designation of 1892 X were stars, and the object never existed. The name and number 330 Adalberta was then reused for another asteroid discovered by Max Wolf on February 2, 1910, which had the provisional designation A910 CB. |
| 525 Adelaide and 1171 Rusthawelia | The object A904 EB discovered March 14, 1904 by Max Wolf was named 525 Adelaide and was subsequently lost. Later, the object 1930 TA discovered October 3, 1930 by Sylvain Arend was named 1171 Rusthawelia. In those pre-computer days, it was not realized until 1958 that these were one and the same object. The name Rusthawelia was kept (and discovery credited to Arend); the name 525 Adelaide was reused for the object 1908 EKa discovered October 21, 1908 by Joel Hastings Metcalf. |
| 715 Transvaalia and 933 Susi | The object 1911 LX discovered April 22, 1911 by H. E. Wood was named 715 Transvaalia. On April 23, 1920, the object 1920 GZ was discovered and named 933 Susi. In 1928 it was realized that these were one and the same object. The name Transvaalia was kept, and the name and number 933 Susi was reused for the object 1927 CH discovered February 10, 1927 by Karl Reinmuth. |
| 864 Aase and 1078 Mentha | The object A917 CB discovered February 13, 1917 by Max Wolf was named 864 Aase, and the object 1926 XB discovered December 7, 1926 by Karl Reinmuth was named 1078 Mentha. In 1958 it was discovered that these were one and the same object. In 1974, this was resolved by keeping the name 1078 Mentha and reusing the name and number 864 Aase for the object 1921 KE, discovered September 30, 1921 by Karl Reinmuth. |
| 1095 Tulipa and 1449 Virtanen | The object 1928 DC discovered February 24, 1928 by Karl Reinmuth was named 1095 Tulipa, and the object 1938 DO discovered February 20, 1938 by Yrjö Väisälä was named 1449 Virtanen. In 1966 it was discovered that these were one and the same object. The name 1449 Virtanen was kept and the name and number 1095 Tulipa was reused for the object 1926 GS discovered April 14, 1926 by Karl Reinmuth. |
| 1125 China and 3789 Zhongguo | The object 1928 UF discovered October 25, 1928 by Zhang Yuzhe (Y. C. Chang) was named 1125 China, and was later lost. Later, the object 1957 UN1 was discovered on October 30, 1957 at Purple Mountain Observatory and was initially incorrectly believed to be the rediscovery of the object 1928 UF. The name and number 1125 China were then reused for the object 1957 UN1, and 1928 UF remained lost. In 1986, the object 1986 QK1 was discovered and proved to be the real rediscovery of 1928 UF. This object was given the new number and name 3789 Zhongguo. Note Zhongguo is the Mandarin Chinese word for "China", in pinyin transliteration. |
| Asteroid 1317 and 787 Moskva | The object 1914 UQ discovered April 20, 1914 by G. N. Neujmin was named 787 Moskva (and retains that name to this day). The object 1934 FD discovered on March 19, 1934 by C. Jackson was given the sequence number 1317. In 1938, G. N. Neujmin found that asteroid 1317 and 787 Moskva were one and the same object. The sequence number 1317 was later reused for the object 1935 RC discovered on September 1, 1935 by Karl Reinmuth; that object is now known as 1317 Silvretta. |
See also
- Asteroid mining
- Asteroid Redirect Mission (proposed NASA mission)
- Centaur (minor planet)
- List of numbered Aten asteroids
- List of Amor asteroids
- List of Apollo asteroids
- List of asteroids named after people
- List of asteroids named after places
- List of instrument-resolved minor planets
- List of meteor air bursts
- List of minor planet moons
- List of Venus-crossing minor planets
- List of Earth-crossing minor planets
- List of Jupiter-crossing minor planets
- List of Mars-crossing minor planets
- List of Mercury-crossing minor planets
- List of Neptune-crossing minor planets
- List of Saturn-crossing minor planets
- List of Solar System objects by size
- List of Uranus-crossing minor planets
- Scattered disc object
- Oumuamua
Books
- Dictionary of Minor Planet Names, 5th ed.: Prepared on Behalf of Commission 20 Under the Auspices of the International Astronomical Union, Lutz D. Schmadel, ISBN 3-540-00238-3
References
- ↑ Savage, Don; Jones, Tammy; Villard, Ray (1995). "Asteroid or Mini-Planet? Hubble Maps the Ancient Surface of Vesta". Hubble Site News Release STScI-1995-20. Retrieved 2006-10-17.
- ↑ Carry, B.; et al. (2009). "Physical properties of (2) Pallas" (PDF). Retrieved 13 September 2015.
- ↑ "JPL Small-Body Database Search Engine: asteroids and orbital class (IMB or MBA or OMB) and diameter > 120 (km)". JPL's Solar System Dynamics Group. Retrieved 2012-04-16.
- 1 2 "Recent Asteroid Mass Determinations". Maintained by Jim Baer. Last updated 2010-12-12. Access date 2011-09-02.
- ↑ Baer, James; Steven R. Chesley (2008). "Astrometric masses of 21 asteroids, and an integrated asteroid ephemeris" (PDF). Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy. Springer Science+Business Media B.V. 2007. 100 (2008): 27–42. Bibcode:2008CeMDA.100...27B. doi:10.1007/s10569-007-9103-8. Retrieved 2008-11-11.
- 1 2 Pitjeva, E. V. (May 2005). "High-Precision Ephemerides of Planets—EPM and Determination of Some Astronomical Constants" (PDF). Solar System Research. 39 (3): 184. Bibcode:2005SoSyR..39..176P. doi:10.1007/s11208-005-0033-2.
- ↑ Pitjeva, E. V. (2004). "Estimations of masses of the largest asteroids and the main asteroid belt from ranging to planets, Mars orbiters and landers". 35th COSPAR Scientific Assembly. Held 18–25 July 2004, in Paris, France. p. 2014. Bibcode:2004cosp...35.2014P.
- ↑ Michalak, G. (2001). "Determination of asteroid masses". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 374 (2): 703–711. Bibcode:2001A&A...374..703M. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20010731. Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ↑ Michalak, G. (2001), assumed masses of perturbing asteroids used in calculations of perturbations of the test asteroids.
- ↑ "(99942) Apophis Ephemerides for 13 Apr 2029". NEODyS (Near Earth Objects - Dynamic Site). Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ↑ "(99942) Apophis Ephemerides for 13 Apr 2029". Minor Planet Center Ephemeris Service - Dynamic Site).
- ↑ "JPL Small-Body Database Search Engine: Asteroids and i > 90 (deg)". JPL Solar System Dynamics. Retrieved 2016-09-12.
- ↑ Morais, M.H.M.; F. Namouni. "Asteroids in retrograde resonance with Jupiter and Saturn". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society Letters (in press). arXiv:1308.0216. Bibcode:2013MNRAS.436L..30M. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slt106.
- ↑ 2008 DG8 and Ceres in 1930
- ↑ 1999 LE31 approaches to Jupiter and Saturn
- ↑ "1994 Release #9412" (Press release). NASA. 1994-02-18. Retrieved 2008-04-17.
- ↑ "29075 (1950 DA) Earth Impact Risk Summary". NASA/JPL Near-Earth Object Program Office. 7 December 2015. Retrieved 11 March 2018.
- ↑ Chang'E 2 images of Toutatis – December 13, 2012 – The Planetary Society
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2004-07-03. Retrieved 2004-04-27.