Lion of Saint Mark

The Lion of Saint Mark, representing the evangelist St Mark, pictured in the form of a winged lion holding a Bible, is the symbol of the city of Venice and formerly of the Venetian Republic.
It is also found in the symbol of the Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Alexandria. It appears in both merchant and military naval flags of the Italian Republic. The Lion of Saint Mark is also the symbol of the award of the Venice Film Festival, the "Golden Lion", and of the insurance company Assicurazioni Generali.
Symbolism
St Mark, represented as a lion, is derived from Mark’s description of John the Baptist as "...The voice of the one who cries in the wilderness: Prepare Ye the way of the Lord, make straight his paths."[1], which artists compared to a roaring lion.[2] The wings come from Ezekiel 1:10 and the application of the prophet’s vision of four winged creatures to the evangelists.[3] These appear again in Revelation 4:7.
A second connection of St. Mark and lions comes from a tale recounted by Severus Ebn-El-Mokafa: "Once a lion and lioness appeared to John Mark and his father Arostalis while they were traveling in Jordan. The father was very scared and begged his son to escape, while he awaited his fate. John Mark assured his father that Jesus Christ would save them and began to pray. The two beasts fell dead and as a result of this miracle, the father believed in Christ."[2]
In some depictions the lion rests his front paws on the ground, often in cities with rivers or in ones close to water, indicating the Venetian balanced power on land and sea.

St Mark and Venice
Venetian tradition states that when St. Mark was traveling through Europe, he arrived at a lagoon in Venice, where an angel appeared to him and said "Pax tibi Marce, evangelista meus. Hic requiescet corpus tuum." (May Peace be with you, Mark, my evangelist. Here your body will rest.) This (possibly apocryphal) tradition was used as justification by Rustico da Torcello and Bon da Malamocco[4] in 828[5] for stealing the remains of St. Mark from his grave in Alexandria,[6] and moving them to Venice, where they were eventually interred in the Basilica of St. Mark.[7]
A fifteen foot bronze statue of a lion stands atop a column of Egyptian granite in St Mark’s Square. It was brought to the lagoon during the 12th century, and remained there until Napoleon moved it to Paris. Returned in 1815, it fell and was rebuilt. It was moved from its pedestal only at the end of the 1800s for restoration and during the Second World War for safekeeping. The Lion underwent careful restoration work in the 1990s.[8] Restorers believe its body is roughly 2,300 years old.[9]
There are also lions carved in relief on the façade of the Doge's Palace, and at the Scuola Grande di San Marco[9] The Coat of Arms of Pope John Paul I contains the Lion of St. Mark in recognition of his previous position as Patriarch of Venice.
Depictions

St. Mark's lion, symbolising the Republic of Venice, also appears on the ensign of the Italian Navy. where it does not hold the gospel in its paw (as it does on the civil ensign, where the book is open at the words "Pax tibi Marce, evangelista meus", meaning "Peace to you Mark, my Evangelist") but wields a sword instead: such an image is consistent with the pictorial tradition from Venetian history, in which the book is shown open during peacetime and closed during wartime.
The Venetian lion appears in two distinct forms. One is as a winged animal resting on water, to symbolise dominance over the seas, holding St. Mark’s Gospel under a front paw. You can see these mighty animals all round the Mediterranean, usually on top of a classical stone column.[10] The other form is known as the lion “in moleca”, in the form of a crab. Here the lion is depicted full-faced with its wings circled around the head resembling the claws of a crustacean. It is emerging from water, so that the lion “in moleca” is associated with the lagoon and the city, whereas the standing winged lion is thought to be more associated with Venetian territory around the Mediterranean.[10]
Other elements often included in depictions of the lion include a halo over his head, a book, or a sword in its paws.
Gallery
 Flag of the Republic of Venice
Flag of the Republic of Venice 1651 map depicting the Lion of St Mark over Crete
1651 map depicting the Lion of St Mark over Crete
 Flag of the Republic of San Marco (1848)
Flag of the Republic of San Marco (1848)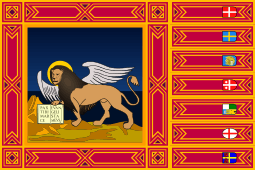 Flag of the Veneto Region
Flag of the Veneto Region Arms of Oberickelsheim
Arms of Oberickelsheim Coat of Arms of Pope John Paul I
Coat of Arms of Pope John Paul I Coat of Arms of the Republic of Venice and present Coat of Arms of Venice
Coat of Arms of the Republic of Venice and present Coat of Arms of Venice Lion of St. Mark seen on the Venetian Coat of Arms
Lion of St. Mark seen on the Venetian Coat of Arms Arms of Marxzell
Arms of Marxzell.svg.png) Arms of Saint-Marc-Jaumegarde
Arms of Saint-Marc-Jaumegarde Flag of the Septinsular Republic
Flag of the Septinsular Republic Flag of the United States of the Ionian Islands
Flag of the United States of the Ionian Islands- Winged lion sculpture atop the Generali Building in Jerusalem
.jpg) Lion of St. Mark from the Ansaldo SVA aircraft of the 87ma squadriglia, La Serenissima
Lion of St. Mark from the Ansaldo SVA aircraft of the 87ma squadriglia, La Serenissima
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lion of Saint Mark. |
- ↑ Mark 1:3
- 1 2 "St. Mark the Apostle, the Founder of the Coptic Church", Coptic Orthodox Diocese of the Southern United States
- ↑ "Saint Mark", Franciscan Media
- ↑ "Hellovenezia : The Lion of St. Mark". Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ↑ "Flags of the World : Venice". Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ↑ "A History of Venice". Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ↑ "Venice Monuments". Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ↑ "St Mark’s Small Square", Meraviglie di Venezia, Regione del Veneto
- 1 2 Wills, Garry. "'Venice: Lion City'", The New York Times, September 30, 2001
- 1 2 Robinson, Myra, "The Lions of Venice", Italy Magazine, July 14, 2011
External links
- Of Lions and Books (and Swords): an in-depth article about iconography of Lion of St Mark, explaining different meanings of open and closed books.