LibreOffice
 | |
 LibreOffice 6.0.1 Start Center | |
| Original author(s) | Star Division |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | The Document Foundation |
| Initial release | 25 January 2011 |
| Stable release | |
| Preview release |
6.1.3 RC1 (11 October 2018[3]) [±] |
| Repository |
|
| Written in | C++, Java, and Python[5] |
| Operating system |
Linux, Windows 7+ (XP and Vista for 5.x), macOS 10.9+, Android (Viewer);[6] Unofficial:[7] FreeBSD, OpenBSD,[8] NetBSD, Haiku, Solaris (v. 5.2.5) |
| Platform | x86-64 (all operating systems), IA-32, ARMel, ARMhf, ARM64, MIPS, MIPSel, PowerPC, ppc64el, S390x[9] |
| Standard(s) | OpenDocument |
| Available in | 115 languages[10] |
| Type | Office suite |
| License | MPLv2.0 (secondary license GPL, LGPLv3+ or Apache License 2.0)[11] |
| Website |
www |
LibreOffice is a free and open-source office suite, a project of The Document Foundation. It was forked from OpenOffice.org in 2010, which was an open-sourced version of the earlier StarOffice. The LibreOffice suite comprises programs for word processing, the creation and editing of spreadsheets, slideshows, diagrams and drawings, working with databases, and composing mathematical formulae. It is available in 110 languages.[10]
LibreOffice uses the international ISO/IEC standard OpenDocument file format (ODF) as its native format to save documents for all of its applications. LibreOffice also supports the file formats of most other major office suites, including Microsoft Office, through a variety of import/export filters.[12][13]
LibreOffice is available for a variety of computing platforms,[6] including Microsoft Windows, macOS, and Linux (including a LibreOffice Viewer for Android[14]), as well as in the form of an online office suite.[15][16] It is the default office suite of most popular Linux distributions.[17][18][19][20] It is the most actively developed free and open-source office suite, with approximately 50 times the development activity of Apache OpenOffice, the other major descendant of OpenOffice.org.[21]
The project was announced and a beta released on 28 September 2010. Between January 2011 (the first stable release) and October 2011, LibreOffice was downloaded approximately 7.5 million times.[22] The project claims 120 million unique downloading addresses from May 2011 to May 2015, excluding Linux distributions, with 55 million of those being from May 2014 to May 2015.[23]
Features
Included applications
.png)
| Component | Notes | |
|---|---|---|
| Writer | A word processor with similar functionality and file support to Microsoft Word or WordPerfect. It has extensive WYSIWYG word processing capabilities, but can also be used as a basic text editor.[13] | |
| Calc | A spreadsheet program, similar to Microsoft Excel or Lotus 1-2-3. It has a number of unique features, including a system which automatically defines series of graphs, based on information available to the user.[13][24] | |
| Impress | A presentation program resembling Microsoft PowerPoint. Presentations can be exported as SWF files, allowing them to be viewed on any computer with Adobe Flash Player installed.[13][25] | |
| Draw | A vector graphics editor and diagramming tool similar to Microsoft Visio and comparable in features to early versions of CorelDRAW. It provides connectors between shapes, which are available in a range of line styles and facilitate building drawings such as flowcharts. It also includes features similar to desktop publishing software such as Scribus and Microsoft Publisher.[26] It is also able to act as a PDF-file editor. | |
| Math | An application designed for creating and editing mathematical formulae. The application uses a variant of XML for creating formulas, as defined in the OpenDocument specification. These formulas can be incorporated into other documents in the LibreOffice suite, such as those created by Writer or Calc, by embedding the formulas into the document.[27] | |
| Base | A database management program, similar to Microsoft Access. LibreOffice Base allows for the creation and management of databases as well as the preparation of forms and reports that provide end users easy access to data. Like Access, it can be used to create small embedded databases that are stored with the document files (using Java-based HSQLDB and C++ based Firebird as its storage engine), and for more demanding tasks it can also be used as a front-end for various database systems, including Access databases (JET), ODBC/JDBC data sources, and MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL or Microsoft Access.[13][28] Work is ongoing to transition the embedded storage engine from HSQLDB to the Firebird SQL back-end. Firebird has been included in LibreOffice as an experimental option since LibreOffice 4.2.[29][30] | |
Operating systems
 Screenshot of LibreOffice 5.3 Writer using the MUFFIN interface running on Ubuntu 16.04 |
 LibreOffice Viewer on Android |
The Document Foundation developers target LibreOffice for Microsoft Windows (IA-32 and x86-64), Linux (IA-32, x86-64 and ARM) and macOS (x86-64).[31][32] Community ports for FreeBSD,[33] NetBSD,[34] OpenBSD and Mac OS X 10.5 PowerPC[35] receive support from contributors to those projects, respectively.[36][37][38] LibreOffice is also installable on OpenIndiana via SFE.[39]
Historically predecessors of LibreOffice, back to StarOffice 3, have run on Solaris with SPARC CPUs that Sun Microsystems made (and Oracle continued making for a while). Unofficial ports of LibreOffice, versions now obsolete, have supported SPARC. Current unofficial ports of LibreOffice 5.2.5 run only on Intel-compatible hardware, up to for Solaris 11.
In 2011, developers announced plans to port LibreOffice both to Android and to iOS.[40] A beta version of a document viewer for Android 4.0 or newer was released in January 2015;[14] In May 2015, LibreOffice Viewer for Android was released with basic editing capabilities.[41]
The LibreOffice Impress Remote application for various mobile operating systems allows for remote control of LibreOffice Impress presentations.
LibreOffice Online
LibreOffice Online is the online office suite edition of LibreOffice. It allows for the use of LibreOffice through a web browser by using the canvas element of HTML5. Development was announced at the first LibreOffice Conference in October 2011, and is ongoing.[42] The Document Foundation, IceWarp, and Collabora announced a collaboration to work on its implementation.[43][44] A version of the software was shown in a September 2015 conference,[45] and the UK Crown Commercial Service announced an interest in using the software.[46][47] On 15 December 2015, Collabora, in partnership with ownCloud, released a technical preview of Libreoffice Online branded as Collabora Online Development Edition (CODE).[48] In July 2016, Nextcloud and Collabora partnered to bring CODE to Nextcloud users.[49][50] By October 2016, Collabora had released nine updates to CODE.[51] The first source code release of LibreOffice Online was done with LibreOffice version 5.3 in February 2017.[15]
Unique features of LibreOffice
A detailed 60-page report in June 2015 compared the progress of the LibreOffice project with the related project Apache OpenOffice. It showed that "OpenOffice received about 10% of the improvements LibreOffice did in the period of time studied."[52]
Supported file formats
| File formats supported by LibreOffice | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Format | Extension | Type | Read | Write | Notes |
| AbiWord | ABW, ZABW | Document | From 4.2[53] | ||
| Adobe Flash | SWF | Graphics, multimedia | Yes[54] | Export from Impress | |
| Adobe PageMaker | PMD, PM3, PM4, PM5, PM6, P65 | Document, DTP | From 4.4[55][56] | ||
| AppleWorks word processing | CWK | Document | From 4.1[57] | Formerly called ClarisWorks | |
| Adobe Swatch Exchange | ASE | Color plate | From 5.0[58] | ||
| Adobe FreeHand | AGD, FHD | Graphics / Vector | Yes | ||
| Apple Keynote | KTH, KEY | Presentation | From 5.0[58] | ||
| Apple Numbers | Numbers | Spreadsheet | From 5.0[58] | ||
| Apple Pages | Pages | Document | From 5.0[58] | ||
| AportisDoc (Palm) | PDB | Document | Yes | Yes | Requires Java |
| AutoCAD DXF | DXF | Graphics / CAD | Yes | ||
| BMP file format | BMP | Graphics / Raster | Yes | Yes | |
| Comma-separated values | CSV, TXT | Text | Yes | Yes | |
| ClarisDraw | Graphics / Vector | Yes | |||
| CorelDRAW 6-X7 | CDR, CMX | Graphics / Vector | From 3.6[59][60] | ||
| Computer Graphics Metafile | CGM | Graphics | Yes | Binary-encoded only; not those using clear-text or character-based encoding | |
| Data Interchange Format | DIF | Spreadsheet | Yes | Yes[61] | |
| DBase, Clipper, VP-Info, FoxPro | DBF | Database | Yes | Yes | |
| DocBook | XML | XML | Yes | Yes | |
| Encapsulated PostScript | EPS | Graphics | Yes | Yes | |
| Enhanced Metafile | EMF | Graphics / Vector / Text | Yes | Yes | |
| EPUB | EPUB | eBook | From 6.0[62] | ||
| FictionBook | FB2 | eBook | From 4.2[53] | ||
| GIMP Palette | GPL | Color plate | From 4.4[55] | ||
| Gnumeric | GNM, GNUMERIC | Spreadsheet | From 5.1 | No | |
| Graphics Interchange Format | GIF | Graphics / Raster | Yes | Yes | |
| Hangul WP 97 | HWP | Document | Yes | Newer "5.x" documents are not supported | |
| HPGL plotting file | PLT | Graphics | Yes | ||
| HTML | HTML, HTM | Document, text | Yes | Yes | |
| Ichitaro 8/9/10/11 | JTD, JTT | Document | Yes | ||
| JPEG | JPG, JPEG | Graphics | Yes | Yes | |
| Lotus 1-2-3 | WK1, WKS, 123, wk3, wk4 | Spreadsheet | Yes[61] | ||
| Lotus Word Pro | Document | Yes[63] | |||
| MacDraft | Graphics / CAD | From 5.0[58] | |||
| MacDraw | Graphics / Vector | From 4.4[55] | |||
| MacDraw II | Graphics / Vector | From 4.4[55] | |||
| Macintosh Picture File[64] | PCT | Graphics | Yes | Yes | |
| MacWrite Pro 1.5 | Document | From 4.1[57] | |||
| MathML | MML | Math | Yes | Yes | |
| MET | MET | Yes | Yes | ||
| Microsoft Excel 2003 XML | XML | Spreadsheet | Yes | Yes | |
| Microsoft Excel 4/5/95 | XLS, XLW, XLT | Spreadsheet | Yes | Up to 3.6[65] | |
| Microsoft Excel 97–2003 | XLS, XLW, XLT | Spreadsheet | Yes | Yes | |
| Microsoft Excel 2007-2016 | XLSX | Spreadsheet | Yes | Yes | |
| Microsoft Excel Web Query File | IQY | Data sources, text | From 5.4[66] | ||
| Microsoft Office 2007-2016 Office Open XML | DOCX, XLSX, PPTX | Multiple formats | Yes | Yes | |
| Microsoft Pocket Excel | PXL | Spreadsheet | Yes | Yes | Requires Java |
| Microsoft Pocket Word | PSW | Document | Yes | Yes | Requires Java |
| Microsoft PowerPoint 97–2003 | PPT, PPS, POT | Presentation | Yes | Yes | |
| Microsoft PowerPoint 2007-2016 | PPTX | Presentation | Yes | Yes | |
| Microsoft Publisher | PUB | Document, DTP | From 4.0[65] | ||
| Microsoft RTF | RTF | Document | Yes | Yes | |
| Microsoft Word 2003 XML (WordprocessingML) | XML | Document | Yes | Yes | |
| Microsoft Word 4/5/6.0/95 | DOC, DOT | Document | Yes | Up to 3.6[65] | |
| Microsoft Word 97–2003 | DOC, DOT | Document | Yes | Yes | |
| Microsoft Word 2007-2016 | DOCX | Document | Yes | Yes | |
| Microsoft Word for Mac | Document | From 4.1[57] | Word 1–5.1 | ||
| Microsoft Word for Windows 2.0 | DOC, DOT | Document | Yes | Yes | |
| Microsoft Works | WPS, WKS, WDB | Multiple | Yes[63][56] | Microsoft Works for Mac formats since 4.1[57] | |
| Microsoft Write | WRI | Document | From 5.1 | No | |
| Microsoft Visio | VSD | Graphics / Vector | From 3.5[67][68] | ||
| Netpbm format | PGM, PBM, PPM | Graphics / Raster | Yes | Yes | |
| OpenDocument | ODT, FODT, ODS, FODS, ODP, FODP, ODG, FODG, ODF | Multiple formats | Yes | Yes | |
| Open Office Base | ODB | Database forms, data | Yes | Yes | |
| OpenOffice.org XML | SXW, STW, SXC, STC, SXI, STI, SXD, STD, SXM | Multiple formats | Yes | Yes | |
| PCX | PCX | Graphics | Yes | ||
| Photo CD | PCD | Presentation | Yes | ||
| PhotoShop | PSD | Graphics | Yes | ||
| Plain text | TXT | Text | Yes | Yes | Various encodings supported |
| Portable Document Format | Document | Yes | Yes | Including hybrid PDF[69] | |
| Portable Network Graphic | PNG | Graphics / Raster | Yes | Yes | |
| QuarkXPress 3–4 | QXP | Document, DTP | From 6.0[62] | ||
| Quattro Pro 6.0 | WB2, wq1, wq2 | Spreadsheet | Yes | ||
| RagTime for Mac | From 4.4[55] | ||||
| Scalable vector graphics | SVG | Graphics / Vector | Yes | Yes | |
| SGV | SGV | Yes | |||
| Software602 (T602) | 602, TXT | Document | Yes | ||
| StarOffice StarCalc 3/4/5 | SDC, VOR | Spreadsheet | Dropped in 4.0,[65] added back in 5.3[70] |
Up to 3.6[65] | |
| StarOffice StarDraw/StarImpress | SDA, SDD, SDP, VOR | Presentation | Dropped in 4.0,[65] added back in 5.3[70] |
Up to 3.6[65] | |
| StarOffice StarMath | SXM | Math | Up to 3.6[65] | Up to 3.6[65] | |
| StarOffice StarWriter 3/4/5 | SDW, SGL, VOR | Document | Dropped in 4.0,[65] added back in 5.3[70] |
Up to 3.6[65] | |
| Star Writer graphics | SGF | Graphics | Yes | ||
| Sony Broad Band eBook | RLF | eBook | From 4.4[55] | ||
| SunOS Raster | RAS | Graphics / Raster | Yes | Yes | |
| SVM | SVM | Graphics / Vector | Yes | Yes | |
| SYLK | SLK | Spreadsheet, file exchange | Yes | Yes | |
| Tagged Image File Format | TIF, TIFF | Graphics / Raster | Yes | Yes | |
| Truevision TGA (Targa) | TGA | Graphics / Raster | Yes | ||
| Unified Office Format | UOF, UOT, UOS, UOP | Multiple | Yes | Yes[61] | |
| Windows Metafile | WMF | Graphics / Vector, bitmap | Yes | Yes | |
| WordPerfect | WPD | Document | Yes[61] | ||
| WordPerfect Suite 2000/Office 1.0 | WPS | Document | Yes | ||
| WriteNow 4.0 | Document | From 4.1[57] | |||
| X BitMap | XBM | Graphics / Raster | Yes | ||
| X PixMap | XPM | Graphics / Raster | Yes | Yes | |
| Zoner Draw | ZMF | Graphics | From 5.3[70] | ||
Miscellaneous features
LibreOffice can use the GStreamer multimedia framework in Linux to render multimedia content such as videos in Impress and other programs.
Visually, LibreOffice used the large "Tango style" icons that are used for the application shortcuts, quick launch icons, icons for associated files and for the icons found on the toolbar of the LibreOffice programs in the past.[71][72] They were also used on the toolbars and menus by default. Later LibreOffice integrated multiple icon themes to adapt the look and feel of specific desktop environment, such as Colibre for Windows, and Elementary for GNOME.[73]
LibreOffice also ships with a modified theme which looks native on GTK-based Linux distributions. It also renders fonts via Cairo on Linux distributions; this means that text in LibreOffice is rendered the same as the rest of the Linux desktop.[74]
LibreOffice has a feature similar to WordArt called Fontwork.[75]
Licensing
The LibreOffice project uses a dual LGPLv3 (or later) / MPL 2.0 license for new contributions to allow the license to be upgraded.[76] Since the core of the OpenOffice.org codebase was donated to the Apache Software Foundation, there is an ongoing effort to get all the code rebased to ease future license updates. At the same time, there were complaints that IBM had not in fact released the Lotus Symphony code as open source, despite having claimed to. It was reported that some LibreOffice developers wanted to incorporate some code parts and bug fixes which IBM already fixed in their OpenOffice fork.[77]
Scripting and extensions
LibreOffice supports third-party extensions.[78] As of July 2017, the LibreOffice Extension Repository lists more than 320 extensions.[79] Another list is maintained by the Apache Software Foundation[80] and another one by the Free Software Foundation.[81] Extensions and scripts for LibreOffice can be written in C++, Java, CLI, Python, and LibreOffice Basic. Interpreters for the latter two are bundled with most LibreOffice installers, so no additional installation is needed. The application programming interface for LibreOffice is called "UNO" and is extensively documented.[82]
LibreOffice Basic
LibreOffice Basic is a programming language similar to Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) but based on StarOffice Basic. It is available in Writer, Calc and Base. It is used to write small programs known as "macros", with each macro performing a different task, such as counting the words in a paragraph.[83]
History
ooo-build, Go-oo and Oracle
Members of the OpenOffice.org community who were not Sun Microsystems employees had wanted a more egalitarian form for the OpenOffice.org project for many years; Sun had stated in the original OpenOffice.org announcement in 2000 that the project would eventually be run by a neutral foundation[84] and put forward a more detailed proposal in 2001.[85]
Ximian and then Novell had maintained the ooo-build patch set, a project led by Michael Meeks, to make the build easier on Linux and due to the difficulty of getting contributions accepted upstream by Sun, even from corporate partners. It tracked the main line of development and was not intended to constitute a fork.[86] It was also the standard build mechanism for OpenOffice.org in most Linux distributions[87] and was contributed to by said distributions.[88]
In 2007, ooo-build was made available by Novell as a software package called Go-oo (ooo-build had used the go-oo.org domain name as early as 2005[89]), which included many features not included in upstream OpenOffice.org. Go-oo also encouraged outside contributions, with rules similar to those later adopted for LibreOffice.[90]
Sun's contributions to OpenOffice.org had been declining for some time,[91] they remained reluctant to accept contributions[92] and contributors were upset at Sun releasing OpenOffice.org code to IBM for IBM Lotus Symphony under a proprietary contract, rather than under an open source licence.[93]
Sun was purchased by Oracle Corporation in early 2010. OpenOffice.org community members were concerned by Oracle's behaviour towards open source software,[94] the Java lawsuit against Google[95] and Oracle's withdrawal of developers[96] and lack of activity on or visible commitment to OpenOffice.org, as had been noted by industry observers[97] – as Meeks put it in early September 2010, "The news from the Oracle OpenOffice conference was that there was no news."[98] Discussion of a fork started soon after.[99]
The Document Foundation and LibreOffice
On 28 September 2010, The Document Foundation was announced as the host of LibreOffice, a new derivative of OpenOffice.org. The Document Foundation's initial announcement stated their concerns that Oracle would either discontinue OpenOffice.org, or place restrictions on it as an open source project, as it had on Sun's OpenSolaris.[100][101][102][103]
LibreOffice 3.3 beta used the ooo-build build infrastructure and the OpenOffice.org 3.3 beta code from Oracle, then adding selected patches from Go-oo.[104] Go-oo was discontinued in favour of LibreOffice. Since the office suite that was branded "OpenOffice.org" in most Linux distributions was in fact Go-oo, most moved immediately to LibreOffice.[105]
Oracle was invited to become a member of The Document Foundation. However, Oracle demanded that all members of the OpenOffice.org Community Council involved with The Document Foundation step down from the OOo Community Council, claiming a conflict of interest.[106]
Naming
The name "LibreOffice" was picked after researching trademark databases and social media, as well as after checks were made to see if it could be used for URLs in various countries.[107] Oracle rejected requests to donate the OpenOffice.org brand to the project.[108]
LibreOffice was initially named BrOffice in Brazil. OpenOffice.org had been distributed as BrOffice.org by the BrOffice Centre of Excellence for Free Software because of a trademark issue.[109]
End of OpenOffice.org and beginning of Apache OpenOffice
Oracle announced in April 2011 that it was ending its development of OpenOffice.org and would lay off the majority of its paid developers.[110] In June 2011, Oracle announced[111] that it would donate the OpenOffice.org code and trademark to the Apache Software Foundation, where the project was accepted for a project incubation process within the foundation, thus becoming Apache OpenOffice. In an interview with LWN in 2011, Ubuntu founder Mark Shuttleworth blamed The Document Foundation for destroying OpenOffice.org because it did not license code under Oracle's Contributor License Agreement.[112] But former Sun executive Simon Phipps denies this is the case:
The act of creating The Document Foundation and its LibreOffice project did no demonstrable harm to Oracle's business. There is no new commercial competition to Oracle Open Office (their commercial edition of OO.o) arising from LibreOffice. No contributions that Oracle valued were ended by its creation. Oracle's ability to continue development of the code was in no way impaired. Oracle's decision appears to be simply that, after a year of evaluation, the profit to be made from developing Oracle Open Office and Oracle Cloud Office did not justify the salaries of over 100 senior developers working on them both. Suggesting that TDF was in some way to blame for a hard-headed business decision that seemed inevitable from the day Oracle's acquisition of Sun was announced is at best disingenuous.[113]
In March 2015, an LWN.net comparison of LibreOffice with its cousin project Apache OpenOffice concluded that "LibreOffice has won the battle for developer participation".[114]
Release history
| Legend: | Old version | Older version, still supported | Current stable version |
|---|
| Branch | Version | Release date | Notes | Screenshot |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.x | 3.3 beta | 28 September 2010 | Initial release based on OpenOffice.org and ooo-build; 80,000 downloads[115] |  First LibreOffice 3.3 beta: startup center and About box |
| 3.3 | 25 January 2011[116] | First-introduced features unique to LibreOffice:[117]
|
 LibreOffice Calc 3.3 | |
| 3.4 | 3 June 2011 | New features include:[119]
|
 Redesigned Move/Copy Sheet dialog in LibreOffice Calc 3.4 | |
| 3.5 | 14 February 2012[68] | New features include:
|
 LibreOffice Impress 3.5.5 | |
| 3.6 | 8 August 2012 | New features include:[125]
This was the last version to support the Windows 2000 operating system. |
 Libreoffice Math 3.6 | |
| 4.x | 4.0 | 7 February 2013[126] | New features include:[65]
|
 LibreOffice Writer 4.0 with "GNU – I" Persona showing comment set for text range |
| 4.1 | 25 July 2013 (final)[130] | New features include:[131]
|
 LibreOffice 4.1.5, showing sidebar and text frame with gradient background | |
| 4.2 | 30 January 2014 | New features include:[53]
|
LibreOffice 4.2.1, showing a character border and Sifr icons in the interface | |
| 4.3 | 30 July 2014 | New features include:[137]
|
 LibreOffice 4.3 showing the updated tango icon set | |
| 4.4 | 29 January 2015 |
New features include:[55]
|
 LibreOffice Writer 4.4 | |
| 5.x | 5.0 | 5 August 2015[138] |
New features include:[58]
Calc:
Math:
Draw:
Core and filters:
|
_Sifr_v%C3%A4limus%2C_Stiilid_k%C3%BClgkast.png) LibreOffice Writer 5.0 in Estonian showing style previews in Sidebar. Note the expanded icon set. The selected icon theme is Sifr. |
| 5.1 | 10 February 2016[139] | New features include:[140] Writer:
Calc:
Impress:
Math:
Core and filters:
|
 LibreOffice Writer 5.1 showing the flat Breeze icon set, reorganised items in sidebar, whitespace hiding in the document, and the 'Always correct to' spellcheck submenu. | |
| 5.2 | 3 August 2016[141] | New features include:[142] Writer:
Calc:
Impress:
Filters:
GUI:
|
||
| 5.3 | 1 February 2017[15] | New features include:[70] Writer:
Calc:
Impress:
Draw:
Base:
Text Layout:
Filters:
GUI:
Online:
Experimental features:
|
||
| 5.4 | 28 July 2017[143] | New features include:[143][66] Writer:
Calc:
Impress & Draw:
Core:
Filters:
Online:
This was the last version to support the Windows XP and Vista operating system.[144] |
||
| 6.x | 6.0 | 31 January 2018[16] | New features include:[62][145]
Writer:
Calc:
Impress:
Core and filters:
GUI:
|
|
| 6.1 | 8 August 2018[146] | New features include:[73]
Writer:
Calc:
Draw:
Base:
Core / General:
|
Versions
Since March 2014 and version 4.2.2, two different major "released" versions of LibreOffice are available at any time, in addition to development versions (numbered release candidates and dated nightly builds).[147] The versions are designated to signal their appropriateness for differing user requirements.[148] Releases are designated by three numbers separated by dots. The first two numbers represent the major version (branch) number, and the final number indicates the bugfix releases made in that series. LibreOffice designates the two release versions as:
- "Fresh" – the most recent major version (branch), which contains the latest enhancements but which may have introduced bugs not present in the "still" release.
- "Still" (formerly "Stable") – the previous major version, which, by the time it has become the "still" version, has had around six months of bug fixing. It is recommended for users for whom stability is more important than the latest enhancements.
Release schedule
LibreOffice uses a time-based release schedule for predictability, rather than a "when it's ready" schedule. New major versions are released around every six months, in January or February and July or August of each year. The initial intention was to release in March and September, to align with the schedule of other free software projects.[149] Minor bugfix versions of the "fresh" and "still" release branches are released frequently.
Users and deployments
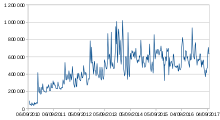
The Document Foundation estimated in September 2011, that there were 10 million users worldwide who had obtained LibreOffice via downloads or CD-ROMs. Over 90% of those were on Windows, with another 5% on OS X. LibreOffice is the default office suite for most Linux distributions, and is installed when the operating system is installed or updated. Based on International Data Corporation reckonings for new or updated Linux installations in 2011, The Document Foundation estimated a subtotal of 15 million Linux users. This gave a total estimated user base of 25 million users in 2011.[150] In September 2013, after two years, the estimated number of LibreOffice users was 75 million.[151] A million new unique IP addresses check for downloads each week.[152] In August 2016, the number of LibreOffice users was estimated at 120 million.[153]
In 2011, the Document Foundation set a target of 200 million users worldwide before the end of 2020.[150]
LibreOffice has seen various mass deployments since its inception:
2003–2010
- In 2003–2004, the Brazilian corporation Serpro started migrating its software to BrOffice (the local version of LibreOffice at the time), with estimated value of BRL 3.5 million (approximately US$1.2 million at the time), and became a case study for similar initiatives in Brazil, particularly in e-government.[154]
- In 2005, the French Gendarmerie announced its migration to OpenOffice.org.[155] It planned to migrate 72,000 desktop machines to a customised version of Ubuntu with LibreOffice by 2015.[156]
- In 2010, the Irish city of Limerick gradually started migrating to open-source solutions to free itself from vendor lock-in and improve its purchase negotiation power. One of the key aspects of this move has been the use of LibreOffice.[157]
2011
- The administrative authority of the Île-de-France region (which includes the city of Paris) included LibreOffice in a USB flash drive given to students which contains free open-source software. The USB flash drive is given to approximately 800,000 students.[40][158]
- It was announced that thirteen hospitals of the Copenhagen region would gradually switch to LibreOffice, affecting "almost all of the 25,000 workers".[159]
2012
- The Greek city of Pylaia-Chortiatis migrated its PCs to use LibreOffice. The local Linux user group estimated cost savings to be at least €70,000.[160]
- In July, the Spanish city of Las Palmas switched its 1,200 PCs to using LibreOffice, citing cost savings of €400,000.[161]
- The administration of Umbria, Italy, started a project to migrate an initial group of 5,000 civil workers to LibreOffice.[162]
- The city of Largo, Florida, US has been a long-time user[163] of open-source software using Linux thin clients. Originally using OpenOffice.org, the city of Largo switched to LibreOffice in 2013.[164]
2013
- In June, the government of the Italian province of South Tyrol will be switching 7,000 PCs in administration and "many more thousands" of PCs in health services using LibreOffice and ODF.[165]
- In August, the administration of the Spanish autonomous region of Valencia has completed the migration of all 120,000 PCs of the administration, including schools and courts, to LibreOffice.[166]
- The German city of Munich announced that it would transition from OpenOffice to LibreOffice in the near future. This is in line with Munich's long term commitment to using open-source software. Munich uses LiMux, an Ubuntu Linux derivative, on nearly all of the city's 15,000 computers.[167][168] The city of Munich is the second public administration to join the advisory board at the Document Foundation.[169] News appeared in 2014 that the Council is considering migrating back to Microsoft Windows & Microsoft Office[170] but was later denied.[171] Based on a study, the mayor of Munich, Dieter Reiter, initiated the re-investigation of the scenario of migrating back to Microsoft systems.[172] The trustworthiness of the study is questionable because the company has been "Microsoft's Alliance Partner of the Year" for nine years.[173] Further details were issued by the Document Foundation.[174]
2014
- The French city of Toulouse announced it saved €1 million by migrating thousands of workstations to LibreOffice.[175][176]
2015
- The Italian Ministry of Defence announced that it would install LibreOffice on 150,000 PCs.[177]
- The Italian city of Bari replaced Microsoft Office with LibreOffice on its 1,700 PCs.[178]
- LibreOffice was officially made available for all UK Government agencies nationwide.[179] Annual cost saving on a subscription for 6,500 users compared to MS Office is approximately 900,000 GBP.[180]
- In July 2015, the IT project manager working for the administration of Nantes (France’s sixth largest city) talked about the ongoing switch of its 5,000 workstations to LibreOffice started in 2013. According to the IT project manager, the switch to LibreOffice allowed the administration to save €1.7 million.[181]
- As of 2015, LibreOffice is installed on almost all of the 500,000 workstations of the 11 French ministries members of the MIMO working group.[182] The MIMO working group was the first public administration to join the advisory board at the Document Foundation.[183]
2016
- The Taiwanese county of Yilan would purchase no more Microsoft Office licenses and turned to ODF and LibreOffice.[184]
- The Vietnam Posts and Telecommunications Group switched all of its PCs (more than 15,000) to LibreOffice.[185]
- Lithuanian police switched to LibreOffice on over 8,000 workstations, citing cost savings of €1 million.[186]
2017
- The majority (75%) of municipalities in the Walloon region of Belgium use open source software and services which include LibreOffice. As of March 2017, over 20,000 public administration staff and many times more citizens use the services.[187]
- The Spanish autonomous region of Galicia announced plans to finalize its switch to LibreOffice at several central government services and ministries, making LibreOffice the only office productivity suite on 6,000 workstations.[188]
- The city of Rome, Italy, began installing LibreOffice on all of its 14,000 PC workstations, in parallel to the existing proprietary office suite. It is one of the planned steps to increase the city's use of free and open-source software, aiming to reduce lock-in to IT vendors.[189]
Conferences
Starting in 2011, The Document Foundation has organized the annual LibreOffice Conference, as follows:
- 2011 – Paris, France – 12–15 October[190]
- 2012 – Berlin, Germany – 17–19 October[191]
- 2013 – Milano, Italy – 24–27 September[192]
- 2014 – Bern, Switzerland – 3–5 September[193][194]
- 2015 – Aarhus, Denmark – 23–25 September[195][196]
- 2016 – Brno, Czech Republic – 7–9 September[197][198]
- 2017 – Rome, Italy – 11–13 October[199][200]
- 2018 – Tirana, Albania – 26–28 September[201]
- 2019 – Almería, Spain[202]
Derivatives
- Collabora supplies branded and customised LibreOffice versions LibreOffice Vanilla for Mac,[203] GovOffice,[46] Collabora Office,[151] Collabora Online Development Edition (CODE)[204] and Collabora Online.[205]
- EuroOffice is a derivative of LibreOffice with free and non-free extensions developed by Hungarian-based MultiRacio Ltd.[206][207]
- "LibreOffice powered by CIB" is a branded and customized version of LibreOffice developed by Germany-based CIB software GmbH.[208][209]
- NeoOffice 2017 and later versions are based on LibreOffice.[210] Previous versions included stability fixes from LibreOffice.[211]
- OxOffice is a derivative of LibreOffice (originally a derivative of OpenOffice.org[212]) with enhanced support for the Chinese language.[213]
References
- ↑ "Announcement of LibreOffice 6.1.2 at LibreOffice Conference". The Document Foundation. Retrieved 2018-09-27.
- ↑ "The Document Foundation announces LibreOffice 6.0.6". The Document Foundation. Retrieved 2018-08-02.
- ↑ "Download LibreOffice (testing)". The Document Foundation. 2018-10-11. Retrieved 2018-10-13.
- ↑ "Download LibreOffice (testing)". The Document Foundation. 2018-10-04. Retrieved 2018-10-13.
- ↑ "Release Notes 4.0". Wiki. The Document Foundation. 13 November 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2013.
- 1 2 "System Requirements". The Document Foundation. 2011. Retrieved 7 August 2015.
- ↑ "Documentation/System Requirements - The Document Foundation Wiki". wiki.documentfoundation.org. Retrieved 2018-07-12.
- ↑ "OpenBSD ports". Retrieved 24 March 2018.
- ↑ "Debian – Details of package libreoffice in jessie". Debian project. Retrieved 12 July 2018.
- 1 2 "LibreOffice Fresh download – pick language". The Document Foundation. Retrieved 7 August 2015.
- ↑ "Licenses". The Document Foundation. Retrieved 16 December 2015.
- ↑ "About Converting Microsoft Office Documents". LibreOffice Help. The Document Foundation. 8 April 2013. Retrieved 16 February 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Features". The Document Foundation. Retrieved 16 February 2014.
- 1 2 "LibreOffice Viewer (Beta) now available for Android". The Document Foundation blog. The Document Foundation. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- 1 2 3 "The Document Foundation announces feature-rich LibreOffice 5.3". 1 February 2017. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
- 1 2 "The Document Foundation announces LibreOffice 6.0: power, simplicity, security and interoperability from desktop to cloud". January 31, 2018. Retrieved February 2, 2018.
- ↑ "Office apps". Ubuntu.com. Canonical Ltd. Retrieved 16 February 2014.
- ↑ "LibreOffice". Debian help. Debian. Retrieved 16 February 2014.
- ↑ "Office and productivity features". Fedora Project. Retrieved 16 February 2014.
- ↑ "openSUSE 11.4 Will Be First To Roll Out With LibreOffice". openSUSE news. openSUSE. 7 March 2011. Retrieved 16 February 2014.
- ↑ Corbet, Jonathan. "Development activity in LibreOffice and OpenOffice". LWN.net. Eklektix, Inc. Retrieved 11 March 2016.
- ↑ Thomson, Iain (28 September 2011). "On its first birthday, LibreOffice has reason to celebrate". United Kingdom: The Register. Retrieved 28 September 2011.
- ↑ Meeks, Michael (2 May 2015). "LibreOffice: What's New?" (PDF). OpenSUSE conference 2015 Den Haag. p. 4. Retrieved 4 May 2015.
Tracking direct download Update Ping origins. Excludes all Linux Distributions downloads ~120m so far ( + Linux ) This time last year @ openSUSE con. was ~65m
- ↑ "LibreOffice Calc". Libreoffice.org. Retrieved 24 November 2014.
- ↑ "LibreOffice Impress". Libreoffice.org. Retrieved 24 November 2014.
- ↑ "LibreOffice Draw". Libreoffice.org. Retrieved 24 November 2014.
- ↑ "LibreOffice Math". Libreoffice.org. Retrieved 24 November 2014.
- ↑ "LibreOffice Base". The Document Foundation. Retrieved 24 November 2014.
- ↑ "LibreOffice 4.2 released with new SQL preview feature : Firebird SQL backend". Firebird News. 30 January 2014. Retrieved 2 May 2015.
- ↑ "HSQLDB to be replaced by Firebird". LibreOfficeForum.org. Archived from the original on 19 March 2015. Retrieved 2 May 2015.
- ↑ Vignoli, Italo (29 July 2015). "The road to LibreOffice 5.0". The Document Foundation Blog. The Document Foundation.
- ↑ https://blog.documentfoundation.org/blog/2012/12/17/libreoffice-runs-on-the-raspberry-pi/
- ↑ "FreeBSD Ports: Editors". FreeBSD. 16 June 2013. Retrieved 16 June 2013.
- ↑ "The NetBSD Packages Collection: misc/libreoffice". Ftp.netbsd.org. 18 March 2010. Retrieved 24 June 2013.
- ↑ "Ftp - /pub/manulix/other/libreoffice/ :: Oregon State University Open Source Lab". ftp.osuosl.org. Retrieved 16 April 2017.
- ↑ "office". Redports. 30 October 2013. Retrieved 3 November 2013.
- ↑ Robert Nagy maintains the OpenBSD port of LibreOffice in collaboration with The Document Foundation.
- ↑ "LibreOffice was ported to OpenBSD in time for the 4.9 release". Openbsd.org. 1 May 2011. Retrieved 15 February 2012.
- ↑ "LibreOffice - OpenIndiana - OpenIndiana Wiki".
- 1 2 Paul, Ryan. "LibreOffice gaining momentum, heading to Android, iOS, and the Web". Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ↑ Vignoli, Italo (28 May 2015). "The Document Foundation announces LibreOffice Viewer for Android". The Document Foundation Blog. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ↑ Meeks, Michael (19 October 2011). "Stuff Michael Meeks is doing". Michael Meeks' blog. People.gnome.org. Retrieved 1 October 2015.
LibreOffice On-Line in slideware
- ↑ "LibreOffice in the browser, revealed in 2011, finally close to reality". Ars Technica.
- ↑ "LibreOffice moves to the cloud to take on Office Online and Google Docs". BetaNews.
- ↑ Marius Nestor (1 October 2015). "LibreOffice Online Development Advances, Gains Image Manipulation, Advanced Toolbar". softpedia.
- 1 2 "Collabora deal will provide savings on Open Source office software". www.gov.uk.
- ↑ Silviu Stahie (20 October 2015). "UK Government Kicks Out Microsoft Office and Adopts LibreOffice". softpedia.
- ↑ "Collabora and ownCloud announce Partnership and release CODE for LibreOffice Online developers". 15 December 2015. Retrieved 24 October 2016.
- ↑ "Nextcloud and Collabora Bring Online Office To Everybody". nextcloud.com. 2016-07-19. Retrieved 2017-11-17.
- ↑ "Nextcloud and Collabora Partner to Offer Community and Enterprise Solution for Online Office". Collabora. 2016-07-19. Retrieved 2017-11-17.
- ↑ "CODE updates". 13 October 2016. Retrieved 24 October 2016.
- ↑ Linton, Susan (5 June 2015). "Apache OpenOffice versus LibreOffice". ostatic. ostatic. Retrieved 22 June 2015.
OpenOffice received about 10% of the improvements LibreOffice did in the period of time studied.
- 1 2 3 The Document Foundation: LibreOffice 4.2 ReleaseNotes.
- ↑ "Impress Features". The Document Foundation. Retrieved 24 November 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Libreoffice 4.4 Release Notes". The Document Foundation Wiki. The Document Foundation.
- 1 2 "DLP/Libraries - The Document Foundation Wiki". Retrieved 12 December 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Strba, Fridrich (21 June 2013). "LibreOffice import filter for legacy Mac file-formats – smile and say "mwaw"!". fridrich.blogspot.de. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "LibreOffice 5.0 Release Notes". The Document Foundation Wiki. The Document Foundation. 4 December 2015. Retrieved 23 December 2015.
- ↑ "LibreOffice CorelDraw import filter - support of version x7 landed". Retrieved 25 August 2015.
- ↑ "LibreOffice 3.6: Release Notes - The Document Foundation Wiki". Retrieved 12 December 2017.
- 1 2 3 "LibreOffice 6.0: Release Notes - The Document Foundation Wiki". Retrieved 12 December 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 Florian Effenberger (25 January 2011). "The Document Foundation launches LibreOffice 3.3". Blog.documentfoundation.org. Retrieved 16 November 2011.
- ↑ About.Com – PCT File. Retrieved 12 January 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 "4.0 New Features and Fixes: LibreOffice". LibreOffice.org. Archived from the original on 8 March 2013. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
Dropped support for export to legacy Word and Excel (version 6.0/95) files.
- 1 2 "LibreOffice 5.4: Release Notes". The Document Foundation Wiki. The Document Foundation. Retrieved 30 July 2017.
- ↑ "LibreOffice 3.5: Release Notes - The Document Foundation Wiki". Retrieved 12 December 2017.
- 1 2 Thomson, Iain (14 February 2012). "LibreOffice debugs and buffs up to v.3.5". The Register. Retrieved 15 February 2012.
- ↑ Phipps, Simon (17 August 2012). "How Microsoft was forced to open Office". InfoWorld. Retrieved 2 January 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "LibreOffice 5.3: Release Notes". The Document Foundation Wiki. The Document Foundation. Retrieved 23 January 2017.
- ↑ "Tango style OpenOffice.org". Tango.freedesktop.org. 12 September 2008. Retrieved 16 November 2011.
- ↑ "OpenOffice.org 3.0 icons". Ui.openoffice.org. Archived from the original on 27 July 2011. Retrieved 16 November 2011.
- 1 2 "LibreOffice 6.1: Release Notes". The Document Foundation's Wiki. Retrieved 9 August 2018.
- 1 2 3 "LibreOffice 3.4 New Features and Fixes". The Document Foundation. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ "Fontwork For Graphical Text Art". LibreOffice.
- ↑ "Developers". The Document Foundation. Retrieved 30 March 2012.
- ↑ Corbet, Jonathan (16 January 2013). "A discordant symphony". LWN.net. Retrieved 9 February 2013.
- ↑ Bergmann, Stephan (7 July 2006). ".oxt, .uno.pkg, .zip". dev@extensions.openoffice.org (Mailing list). Archived from the original on 5 May 2009. Retrieved 10 August 2007.
- ↑ "Extension – LibreOffice: Extension". The Document Foundation. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- ↑ "Apache OpenOffice Extensions". Apache OpenOffice. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- ↑ "OpenOfficeExtensions/List". Free Software Foundation. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- ↑ "LibreOffice API Documentation". The Document Foundation. Retrieved 26 June 2015.
- ↑ Bain, Mark Alexander. "An introduction to OpenOffice.org Basic". NewsForge. Retrieved 3 March 2007.
- ↑ "SUN MICROSYSTEMS OPEN SOURCES STAROFFICE TECHNOLOGY". Sun Microsystems. 19 July 2000. Retrieved 19 January 2012.
- ↑ "The OpenOffice.org Foundation". Sun Microsystems. 4 November 2001. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- ↑ "About ooo-build". Ximian. 18 October 2003. Archived from the original on 18 October 2003. Retrieved 5 January 2013.
- ↑ James, Daniel (7 May 2007). "Meek not geek - Interview with Michael Meeks of OpenOffice.org". Tux Deluxe. Archived from the original on 29 September 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2013.
- ↑ Meeks, Michael (21–24 July 2004). "The World of OpenOffice" (PDF). In John W. Lockhart. Proceedings of the Linux Symposium. Linux Symposium 2004. 2. Ottawa, Ontario. pp. 361–366. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 May 2014. Retrieved 17 April 2015.
- ↑ Meeks, Michael (28 January 2005). "ooo-build 1.3.8 Announced". LWN.net. Retrieved 1 October 2013.
- ↑ Hillesley, Richard (29 January 2009). "Healthcheck: OpenOffice: Calling a cat a dog". The H Open. p. 4. Archived from the original on 8 December 2013. Retrieved 26 June 2013.
- ↑ Meeks, Michael (10 October 2008). "Measuring the true success of OpenOffice.org". Stuff Michael Meeks is doing. People.gnome.org. Retrieved 5 January 2013.
- ↑ Yoshida, Kohei (2 October 2007). "History of Calc Solver". Roundtrip to Shanghai via Tokyo. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
- ↑ Phipps, Simon (20 May 2011). "OpenOffice.org and contributor agreements". LWN.net. Retrieved 16 June 2013.
- ↑ Schestowitz, Roy (28 September 2010). "LibreOffice is Launched, Offering Independence from Oracle". TechRights. Retrieved 8 October 2013.
- ↑ Wallen, Jack (7 September 2010). "Could Oracle fracture open source community?". ZDNet. Retrieved 8 October 2013.
- ↑ Dölle, Mirko (4 November 2010). "Die Woche: Bad Company Oracle?" [The Week: Bad Company Oracle?]. Heise Open Source (in German). Heinz Heise. Retrieved 19 October 2013.
Nach der Übernahme von Sun hatte Oracle offenbar etliche Entwickler vom OpenOffice-Projekt abgezogen, was zu empfindlichen Verzögerungen bei der Weiterentwicklung geführt hat. [After the acquisition of Sun, Oracle apparently took several developers off the OpenOffice project, which led to severe delays in development.]
- ↑ Noyes, Katherine (23 August 2010). "Don't Count on Oracle to Keep OpenOffice.org Alive". PC World Linux Line. Retrieved 12 October 2014.
- ↑ Hillesley, Richard (28 September 2010). "LibreOffice – A fresh page for OpenOffice". The H Online. Heinz Heise. Archived from the original on 6 December 2013. Retrieved 7 October 2010.
- ↑ van der Meijs, Sander (30 September 2010). "OpenOffice-coup al jaren in de maak" [OpenOffice coup years in the making]. WebWereld (in Dutch). Retrieved 6 July 2013.
- ↑ "OpenOffice.org Community announces The Document Foundation". The Document Foundation. 28 September 2010. Archived from the original on 30 September 2010. Retrieved 9 November 2011.
- ↑ Collins, Barry. "OpenOffice group breaks away from Oracle". PC Pro. Retrieved 9 November 2011.
- ↑ Clarke, Gavin. "OpenOffice files Oracle divorce papers". The Register. Retrieved 9 November 2011.
- ↑ Paul, Ryan. "Document Foundation forks OpenOffice.org, liberates it from Oracle". Ars Technica. Retrieved 9 November 2011.
- ↑ Schulz, Charles-H. (28 September 2010). "Give up spoon-feeding: Use a fork instead". Standards and Freedom (blog). Retrieved 7 October 2013.
- ↑ Jake Edge (28 September 2010). "Michael Meeks talks about LibreOffice and the Document Foundation". Linux Weekly News.
- ↑ Paul, Ryan. "Oracle wants LibreOffice members to leave OOo council". Ars Technica. Retrieved 23 February 2011.
- ↑ Noack, Christoph (3 October 2010). "Agreeing on the child's name ... a simple task?". Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ↑ "OpenOffice.org Community announces The Document Foundation". The Document Foundation. 28 September 2010. Archived from the original on 6 September 2011. Retrieved 21 October 2010.
- ↑ Effenberger, Florian (6 December 2010). "LibreOffice development extends to Brazil". TDF Blog. The Document Foundation. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- ↑ Paul, Ryan (April 2011). "Oracle gives up on OpenOffice after community forks the project". Ars Technica. Retrieved 19 April 2011.
- ↑ "Statements on OpenOffice.org Contribution to Apache" (Press release). Oracle Corporation. 1 June 2011. Retrieved 14 October 2011.
- ↑ Edge, Jake. "Mark Shuttleworth on companies and free software". LWN. Retrieved 7 May 2014.
- ↑ Simon Phipps (May 2011). "OpenOffice.org and contributor agreements". LWN.net. Retrieved 29 January 2014.
- ↑ Jonathan Corbet (15 March 2015). "Development activity in LibreOffice and OpenOffice". LWN.net. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- ↑ Ihlenfeld, Jens (15 October 2010). "Zweite Beta des Openoffice.org-Forks Libreoffice" [Second Beta of Openoffice.org-Fork LibreOffice] (in German). Golem.de. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ Camen, Kroc (25 January 2011). "The Document Foundation Launches LibreOffice 3.3". OSNews Inc. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ "New Features". The Document Foundation. Archived from the original on 16 February 2012. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Brinkmann, Martin (25 July 2013). "Two days after OpenOffice 4, LibreOffice 4.1 is released". ghacks.net. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ "Release Notes 3.4". The Document Foundation Wiki. The Document Foundation. 26 January 2014. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- 1 2 3 "The Document Foundation Announces LibreOffice 3.4.0". The Document Foundation Blog. The Document Foundation. 3 June 2011. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ Meeks, Michael (9 May 2011). "LibreOffice is the future of Free Software Office suites". Michael Meeks' blog at people.gnome.org. gnome.org. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ "v3.5 release notes". The Document Foundation Wiki. The Document Foundation. 15 February 2014. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ Noyes, Katherine (23 January 2012). "10 Things to Look Forward to in LibreOffice 3.5". PC World. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ Gorman, Michael (14 February 2012). "LibreOffice updates to version 3.5, brings grammar check, bigger Calc workbooks, and more". Engadget. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ "3.6 New Features and Updates". The Document Foundation. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ "The Document Foundation Announces LibreOffice 4.0". TDF Blog. The Document Foundation. 7 February 2013. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ "LibreOffice 4.0 ReleaseNotes". The Document Foundation. 15 February 2014. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ "LibreOffice 4.0 RC1 supports Firefox-compatible themes". The H Open: News and Features H-online.com. Heinz Heise. 14 January 2013. Archived from the original on 7 December 2013. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ Holesovsky, Jan (Kendy) (10 January 2013). "LibreOffice 4.0: Use Firefox Personas in your favorite office suite". Artax (Linux server) at the Karlin computer lab, Faculty of Math and Physics. Charles University in Prague. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ "Release Plan / 4.1". The Document Foundation Wiki. The Document Foundation. 19 February 2014. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- 1 2 "LibreOffice 4.1 ReleaseNotes". The Document Foundation. 30 July 2013. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 Scherschel, Fabian (28 May 2013). "LibreOffice 4.1.0 Beta 1 arrives with over a thousand changes". The H Open. Heinz Heise. Archived from the original on 7 December 2013. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ Walker-Morgan, Dj (24 June 2013). "LibreOffice 4.1's first release candidate arrives". The H. Heinz Heise. Archived from the original on 7 December 2013. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ "Shared formula to reduce memory usage". kohei.us. 15 August 2013. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (29 October 2013). "LibreOffice Lands A Ton of GPU OpenCL Functions". Phoronix. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ "AbiWord Import filter". freedesktop.org. 13 January 2014. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ "LibreOffice 4.3 ReleaseNotes". The Document Foundation Wiki. The Document Foundation. 3 March 2014. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ↑ "The road to LibreOffice 5.0". 29 July 2015. Retrieved 3 August 2015.
- ↑ "The Document Foundation announces LibreOffice 5.1". 10 February 2016. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
- ↑ "LibreOffice 5.1 Release Notes". The Document Foundation Wiki. The Document Foundation. 10 February 2016. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
- ↑ "LibreOffice 5.2 "fresh" released, for Windows, Mac OS and GNU/Linux". 3 August 2016. Retrieved 9 September 2016.
- ↑ "LibreOffice 5.2 Release Notes". The Document Foundation Wiki. The Document Foundation. Retrieved 23 January 2016.
- 1 2 "LibreOffice 5.4 released with new features for Writer, Calc and Impress". 28 July 2017. Retrieved 30 July 2017.
- ↑ "LibreOffice 6.0: Release Notes". January 31, 2018. Retrieved April 13, 2018.
- ↑ "Wednesday Community #4". The Document Foundation Blog. February 7, 2018. Retrieved February 8, 2018.
- ↑ "The Document Foundation announces LibreOffice 6.1, a major release which shows the power of a large and diverse community of contributors". 8 August 2018. Retrieved 9 August 2018.
- ↑ Simon Phipps (13 March 2014). "LibreOffice Gets Fresh and Stable". ComputerworldUK. Retrieved 2 April 2014.
- ↑ "Release Notes". The Document Foundation. Retrieved 16 February 2018.
- ↑ "Release Plan". The Document Foundation Wiki. Retrieved 25 March 2011.
- 1 2 "The Document Foundation celebrates its first anniversary". The Document Foundation Blog. 28 September 2011. Retrieved 28 September 2011.
- 1 2 "Watch out Microsoft, Collabora is bringing value added LibreOffice". Muktware. September 2013. Archived from the original on 29 July 2014. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- ↑ Meeks, Michael. "The spreadsheet is dead. Long live the spreadsheet!". Hexus. Retrieved 7 May 2014.
- ↑ "LibreOffice 5.2 includes classified documents and a streamlined interface". PCWorld. Retrieved 1 March 2017.
- ↑ de Lima, Francival Rodrigues. "Histórico do BrOffice.org no SERPRO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). softwarelivre.gov.br. Retrieved 26 July 2013.
- ↑ Guillemin, Christophe. "La gendarmerie nationale passe à OpenOffice" (in French). ZDNet France. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- ↑ Finley, Klint (September 2013). "French National Police Switch 37,000 Desktop PCs to Linux". Wired. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- ↑ "Limerick city council increasingly turning to open source". European Union. 19 March 2012. Retrieved 12 February 2013.
- ↑ Shankland, Stephen (18 October 2011). "LibreOffice expands users and reach". ZDNet. Retrieved 9 May 2012.
- ↑ "DK: 25,000 hospital staff Copenhagen region to use open source office suite". European Union. 18 August 2011. Retrieved 12 February 2013.
- ↑ "Greek municipality of Pilea-Hortiatis migrating to LibreOffice". European Union. 30 April 2012. Retrieved 12 February 2013.
- ↑ "Spain's Las Palmas' moves 1200 PCs to LibreOffice". European Union. 20 July 2012. Retrieved 12 February 2013.
- ↑ "Administration of the Italian region Umbria moving to LibreOffice". European Union. 2 October 2012. Retrieved 12 February 2013.
- ↑ "City of Largo, Florida | Infrastructure Division". Largo.com. Retrieved 27 February 2013.
- ↑ "LibreOffice Office Suite: Microsoft Losing International Ground To Open Source Migrations". Dailyflux.com. 24 November 2012. Archived from the original on 21 February 2013. Retrieved 27 February 2013.
- ↑ Henning, Edward (21 June 2013). "South Tyrol government to standardise on LibreOffice". The H Open. Heinz Heise. Archived from the original on 8 December 2013. Retrieved 23 June 2013.
- ↑ Hillenius, Gijs (22 August 2013). "Valencia region government completes switch to LibreOffice". Joinup. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- ↑ "Mayor of Munich: "EU laptops should have LibreOffice or OpenOffice" – Joinup". Europa (web portal).
- ↑ "Munich shifts to LibreOffice". ITworld. 17 October 2013. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ↑ "Munich 2nd public administration in Libreoffice NGO". 13 January 2015. Retrieved 15 February 2016.
- ↑ "After a 10-year Linux migration, Munich considers switching back to Windows and Office". ZDNet. 18 August 2014. Retrieved 2 February 2017.
- ↑ "Munich Linux councillor: 'We didn't propose a switch back to Windows'". The Inquirer. 28 August 2015. Retrieved 2 February 2017.
- ↑ "Externes IT Gutachten, Untersuchung der IT der Landeshauptstadt München (LHM)" (PDF). Accenture. Retrieved 15 February 2017.
- ↑ "Accenture and Avanade Named Microsoft 2016 Alliance Partner of the Year". Accenture. Retrieved 15 February 2017.
- ↑ "Statement by The Document Foundation about the upcoming discussion at the City of Munich to step back to Windows and MS Office". The Document Foundation. Retrieved 15 February 2017.
- ↑ "Toulouse saves 1 million euro with LibreOffice". Joinup. 23 July 2014. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 31 July 2014.
- ↑ "Moving to LibreOffice saves Toulouse 1 million".
- ↑ Hillenius, Gijs (15 September 2015). "Italian military to switch to LibreOffice and ODF". Joinup. European Open Source Observatory. Retrieved 15 September 2015.
- ↑ "Innovating in a time of budget cuts: Why the city of Bari swapped Microsoft for open source". ZDNet. 21 September 2015. Retrieved 23 September 2015.
- ↑ "LibreOffice officially made available for all UK Government agencies nationwide". OCS-Mag. Retrieved 28 October 2015.
- ↑ "Document interoperability expert: "Make ODF the default"". Joinup collaboration platform. European Commission. 18 October 2017. Retrieved 21 October 2017.
- ↑ "Nantes: "Change management key to switch to free software"". Retrieved 15 February 2015.
- ↑ "Free software group French ministries extends scope". Retrieved 15 February 2016.
- ↑ "The Document Foundation welcomes France's MIMO in the Advisory Board". Retrieved 15 February 2016.
- ↑ "確實執行訂立目標,宜蘭縣政府成功導入開源文書軟體". iThome.com.tw. 15 October 2017.
- ↑ "VNPT chuyển sang dùng phần mềm văn phòng nguồn mở LibreOffice" [VNPT switched to LibreOffice open source office software]. 3 March 2016. Retrieved 31 July 2017.
- ↑ "Lithuanian police switched to LibreOffice". 11 August 2016. Retrieved 5 August 2017.
- ↑ "Majority of towns in Wallonia now use open source". Joinup collaboration platform. European Commission. 5 May 2017. Retrieved 21 October 2017.
- ↑ "Galicia continues promotion of free software". 23 May 2017. Retrieved 5 August 2017.
- ↑ "City of Rome is getting ready for open source". Joinup collaboration platform. European Commission. 6 October 2017. Retrieved 21 October 2017.
- ↑ "LibreOffice conference | Open Document". Opendocument.xml.org. Retrieved 20 September 2012.
- ↑ "Welcome – LibreOffice Conference". Conference.libreoffice.org. Retrieved 4 August 2013.
- ↑ "Welcome – LibreOffice Conference". Conference.libreoffice.org. Retrieved 4 August 2013.
- ↑ "LibreOffice Conference 2014 Call for Paper". The Document Foundation. 5 March 2014. Retrieved 8 March 2014.
- ↑ "LibreOffice Conference 2014 in Bern, Switzerland". The Document Foundation. Retrieved 10 March 2017.
- ↑ "LibreOffice Conference 2015 in Aarhus, Denmark, from September 23 to September 25, 2015". The Document Foundation. 17 October 2014. Retrieved 2 November 2014.
- ↑ "LibreOffice Conference 2015 in Aarhus, Denmark". The Document Foundation. Retrieved 10 March 2017.
- ↑ "LibreOffice Conference 2016 in Brno (Czech Republic)". The Document Foundation. 12 October 2015. Retrieved 11 October 2016.
- ↑ "LibreOffice Conference 2016 in Brno, Czech Republic". The Document Foundation. Retrieved 10 March 2017.
- ↑ "LibreOffice Conference 2017 in Rome – register now!". The Document Foundation. 12 July 2017. Retrieved 31 July 2017.
- ↑ "LibreOffice Conference 2017, Rome Italy". The Document Foundation. Retrieved 31 July 2017.
- ↑ "LibOCon 2019 Call for Location". The Document Foundation. 5 March 2018. Retrieved 5 March 2018.
- ↑ "LibOCon 2019". The Document Foundation. 3 October 2018. Retrieved 7 October 2018.
- ↑ Tuke, Sam. "LibreOffice Vanilla: Fresh from the community to your Mac". Collabora Productivity. Collabora Productivity. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- ↑ "Collabora Online Development Edition (CODE)". Collabora. Retrieved 5 February 2017.
- ↑ "Collabora Online". Collabora. Retrieved 5 February 2017.
- ↑ Dajkó, Pál (28 May 2015). "Két magyar egyetemen is elérhető az EuroOffice" [EuroOffice available in two Hungarian universities]. ITcafé. Retrieved 14 October 2015.
- ↑ "EuroOffice homepage".
- ↑ "LibreOffice Powered by CIB". Retrieved 9 July 2017.
- ↑ "CIB-sponsored LibreOffice developer meeting". 22 October 2015. Retrieved 9 July 2017.
- ↑ Pluby (2 May 2017). "NeoOffice 2017 Beta Professional Edition released". trinity.neooffice.org. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- ↑ pluby (7 November 2013). "Mac App Store complaints". trinity.neooffice.org. Retrieved 25 December 2013.
- ↑ "Openoffice.org與OxOffice" [Openoffice.org and OxOffice]. iT邦. 15 October 2010. Retrieved 14 October 2015.
- ↑ "OSSII OxOffice Community Edition download".
External links
- Official website
- LibreOffice at Curlie (based on DMOZ)