Languages of Iran
| Languages of Iran | |
|---|---|
| Official languages | Persian |
| Main languages | Persian 53%, Azerbaijani and other Turkic dialects 18% (e.g Qashqai, Turkmen), Kurdish 10%, Gilaki and Mazandarani 7%, Luri 6%, Arabic 2%, Balochi 2%, and other languages (Tati, Talysh, Armenian, Georgian, Neo-Aramaic, Circassian, Hebrew) 1%[1] |
| Minority languages | Armenian, Georgian, Circassian, Assyrian, and Hebrew |
| Sign languages | Persian Sign Language |
| Common keyboard layouts | |
Language Policy and Planning of Iran
The current Language Policy of Iran is addressed on chapter two of the Constitution of the Islamic Republic of Iran (Articles 15 & 16). It asserts that the Persian language is the Lingua Franca of the Iranian nation and as such, bound to be used through all official government communications and schooling system. In addition, the constitution also recognizes the Arabic language as the language of Islam, giving it a formal status as the language of religion, and regulates its spreading within the Iranian national curriculum.
Due to the nation's unique social and ethnic diversity, the constitution also acknowledges and permits the use of minority languages in the mass media as well as within the schools, in order to teach their literature. The minority languages of Iran do not receive a formal status and are not officially regulated by the authorities.[2]
The first legislation which granted the Persian language its status was initiated back in 1906, as part of an electoral law that positioned it as the official language of the state of Iran, its government, its political institutions and its legal system. In the course of time this enactment followed by others, which eventually lead to a monolingual policy by the Iranian regime.
Perceiving multilingualism as a threat to the nation’s unity and Territorial integrity, and seeing the need to restrict minority languages’ use and to advance the Persian language’s hegemony, Iran’s language policy consists of a non-translation outline as well: all government, administration and educational settings are obliged to use merely Persian for any written communication. That includes political institutions (i.e. the Iranian Parliament), official bureaucratic communication (forms, signage etc.) and schooling (all children from the age of six and up are exposed only to Persian as the language of teaching and learning and of textbooks within the public school system). In other words, the Iranian authorities holds that minorities needs to learn the Iranian vernacular to an extent that will allow them to communicate with state institutions.[3]
With regard to the Iranian Language Planning, among the institutions accountable for advancing the Iranian Language Planning (e.g. Ministry of Education and Ministry of Science, Research and Technology) is the Academy of Persian Language and Literature, which was established on 1991. Constantly seeking to revise and elaborate the nation’s official language, this institute focuses on the linguistics of the Persian language and on the internal aspects of Language Planning, rather than on minority languages use within the Iranian society. Other aspects of Language Planning (e.g. sociolinguistic or functional literacy) have not been assigned to a formal institute and are currently handled free of any official master plan, by the educational ministries.[2]
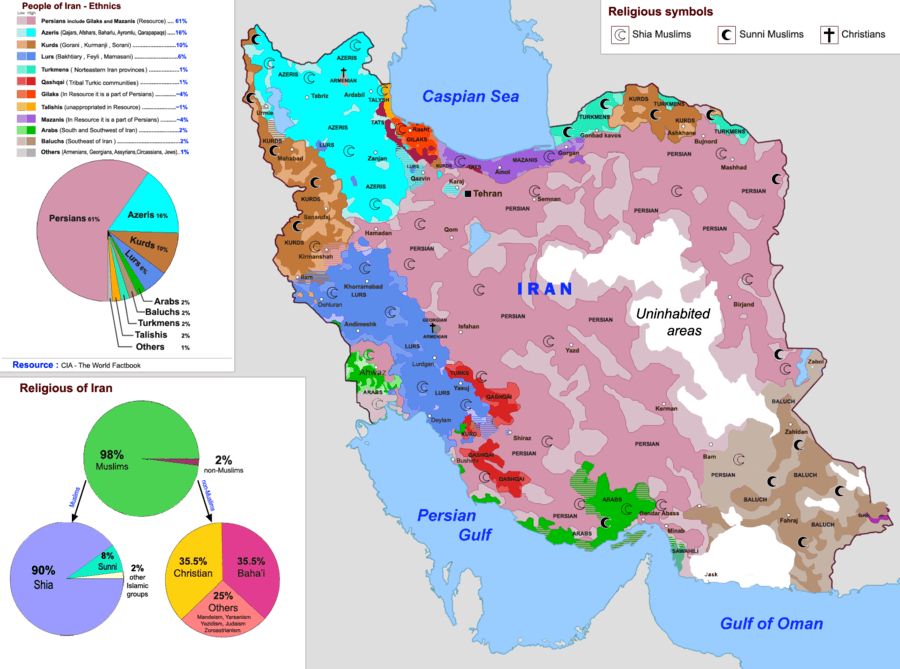
Languages of Iran
Different publications have reported different statistics for the languages of Iran. There have been some limited censuses taken in Iran in 2001, 1991, 1986 and 1949–1954.[4][5] The following are the languages with the greatest number of speakers (data from the CIA World Factbook):[1]
Classification categories of the spoken languages:
- Indo-European (Iranic mainly, smaller amounts of other branches represented mainly by Armenian, amongst others)
- Turkic (the majority being Azerbaijani, with smaller amounts of Turkmen, Qashqai, and Afshar)
- Semitic (mainly Arabic, but also Neo-Aramaic, Hebrew, and Mandean)
- Caucasian languages (such as Kartvelian, and Circassian)
CIA World Factbook
The following are the languages with the greatest number of speakers (data from the CIA World Factbook):[1]
Census in the 1990s
A census taken in the Iranian month of Mordad (July 21 – August 21) in 1991. In this census, all 49,588 mothers who gave birth in the country, were issued birth certificates. They were asked about their mother-tongue.[7] which were : 46.2% (Persian), 20.6% (Azerbaijani), 10% Kurdish, 8.9% Luri, 7.2% Gilaki and Mazandarani, 3.5% Arabic, 2.7% Baluchi, 0.6% Turkmen, 0.1% Armenian, and 0.2% Others (e.g. Circassian, Georgian, etc.). The local dialect of Arabic spoken in Iran is Khuzestani Arabic, an Iraqi Arabic dialect, but the varieties of Arabic taught across Iran to students in secondary schools, regardless of their ethnic or linguistic background, are Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, the latter a liturgical language of Islam.
Recent survey
A recent survey by the US-based organization "Terror Free Tomorrow" with error is +/- 3.1 percent margin and uniform sampling based on provincial populations mentions the breakdown as following:[8]
- Persian 50.5%
- Azeri 21.6%
- Kurd 7.6%
- Gilaki and Mazandarani 6.9%
- Lur 6.9%
- Arab 2.7%
- Baloch 1.4%
- Tati and Talysh 1%
- Turkmen 0.9%
- Other 1.2% (incl. Armenian, Georgian, Circassian, Assyrian Neo-Aramaic and other Assyrian dialects, Hebrew, Mandaic)
- Unknown/refused about 0.5%
Other estimations
In 1986, there was also a nationwide census done. See: (Farhad Nu’mani, Sohrab Behdad, Class and Labor in Iran: Did the Revolution Matter?, Published 2006, Syracuse University Press, 2006)[9] on the percentage of Iranians that known Persian, those who do not know and those who know it fluently.
According to the Kurdish-Belgian-American scholar Mehrdad Izady, whose work can be found at Columbia University School of International and Public Affairs, Gulf 2000 Project website,[10] the Iranian census of 2001 mentions that 68% of the population speaks Persian as a first language,[11] while he himself gives the following figures for 2014:
- Persian to include Luri and Bakhtiari 62.1%
- Azerbaijani 13.6%
- Kurdish 7%
- Gilaki 3%
- Mazandarani 2.8%
- Balochi 2.4%
- Arabic 1.6%
- Tourki 1.6%
- Qashqai 1.2%
- Tati 1.1%
- Raji 1%
- Turkmeni 0.9%
- Talysh 0.4%
- Other languages include Turkmen, Armenian, Georgian, Circassian, Syriac, Qashqai, Russian, Hebrew, Raji, Minabi, as well as other Western Iranian languages (Lari etc.)
See also
References
- 1 2 3 "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". Cia.gov. Archived from the original on 2012-02-03. Retrieved 2017-01-17.
- 1 2 Riazi, Abdolmehdi. The Four Language Stages in the History of Iran. In: Martin, Peter W; Lin, Angel (Eds.). Decolonisation, Globalisation: Language-in-education Policy and Practice. (Buffalo: Multilingual Matters, Ltd. 2005). pp. 98-114.
- ↑ Haddadian-Moghaddam, Esmaeil; Meylaerts, Reine. What about Translation? Beyond “Persianization” as the Language Policy in Iran. Iranian Studies, Vol. 78, No. 6 (2015). pp. 851-870.
- ↑ Iran. rtish. Sitād-i Artish. Dāyirah-i Jughrāfiyāʾī. Title: Farhang-i jughrāfiyāʾī-i Irān : ābādīhā. Imprint: [Tihrān] : Dāyirah-i Jughrafiyāʾī-i Sitād-i Artish, 1328–1332 [1949–54] Description: 10 v. : illus., maps (part fold. col.) Notes: Vols. 1–9 compiled under the general editorship of Hossein ʻAlī Razmārā. See for summary: (Ehsan Hooshmand, “Faslnaameyeh Goftegoo”, “A closer look at religious and ethnic statistics in modern Iran”, 2005, Tehran)
- ↑ "فصلنامه گفتگو، شماره 43". Magiran.com. Retrieved 2017-01-17.
- ↑ "Iran – کاهش غیرمنتظره نرخ رشد جمعیت در ایران". DW Persian. Retrieved 19 July 2012.
- ↑ "در مرداد 1370، هنگام صدور شناسنامه براي نوزادان، درباره زبان ٤٩ هزار و ٥٥٨ مادر در سطح كشور سوال مطرح شد كه نتيجه حاكي از سهم حضور ٥٣٬٨ درصدي زبان هاى غيرفارسي در ايران بود. بر اساس نمونه گيري مذكور، توزيع سهم هر يك از زبان ها (به درصد) به اين شرح بود: ٤٦٬٢ فارسي؛ ٢٠٬٦ تركي آذربايجاني؛ ١٠ كردي؛ ٨٬٩ لري؛ ٧٬٢ درصد گيلكي و شمالي؛ ٣٬٥ عربي ؛ ٢٬٧ بلوچي؛ ٠٬٦ تركمني؛ ٠٬١ ارمني؛ و ٠٬٢ ساير زبان ها ". Source: زنجاني، حبيب الله، محمد ميرزايي، كامل شاپور و امير هوشنگ مهريار، جمعيت،توسعه، بهداشت باروري، چاپ دوم، تهران، نشر و تبليغ بشري، 1379. Zanjani, H., Mirzai,M., Shapur, K., Mehriyar, A.H.; “Population, Growth, Mortality Rate”, Second Edition, Tehran, Tabligh-e-Bashari Publishers, 2000
- ↑ "Executive Summary" (PDF). Terrorfreetomorrow.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-07-23. Retrieved 2017-01-17.
- ↑ (Farhad Nu’mani, Sohrab Behdad, Class and Labor in Iran: Did the Revolution Matter?, Published 2006, Syracuse University Press, 2006)
- ↑ "Iran : Linguistic Composition in 2014 (Summary)" (PNG). Gulf2000.columbia.edu. Retrieved 2017-01-17.
- ↑ "Mehrdad Izady (2006–2011)". Gulf2000.columbia.edu. Archived from the original (JPG) on 2013-10-01. Retrieved 2017-01-17.