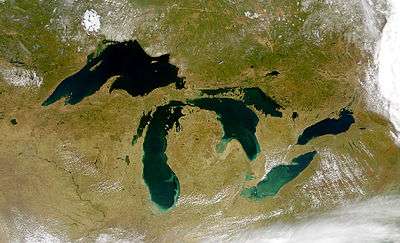
Lake Michigan
| Lake Michigan | |
|---|---|
 Landsat image | |
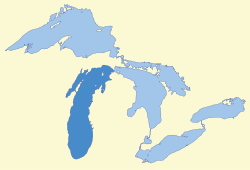 Map of Great Lakes (Lake Michigan in darker blue) | |
| Location | United States |
| Group | Great Lakes |
| Coordinates | 44°N 87°W / 44°N 87°WCoordinates: 44°N 87°W / 44°N 87°W |
| Lake type | Glacial |
| Primary inflows | Fox River, Grand River, Menominee River, Milwaukee River, Muskegon River, Kalamazoo River, St. Joseph River |
| Primary outflows | Straits of Mackinac, Chicago River, Calumet River |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Max. length | 307 mi (494 km) |
| Max. width | 118 mi (190 km) |
| Min. width | 91 mi (146 km) |
| Surface area | 22,404 sq mi (58,030 km2)[1] |
| Average depth | 279 ft (85 m) |
| Max. depth | 923 ft (281 m)[2] |
| Water volume | 1,180 cu mi (4,900 km3) |
| Residence time | 99 years |
| Shore length1 | 1,400 mi (2,300 km) plus 238 mi (383 km) for islands[3] |
| Surface elevation | 577 ft (176 m)[2] |
| Islands | see list |
| Settlements | see #Cities |
| References | [2] |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America and the only one located entirely within the United States. The other four Great Lakes are shared by the U.S. and Canada. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume[1] and the third-largest by surface area, after Lake Superior and Lake Huron (and is slightly smaller than the U.S. state of West Virginia). To the east, its basin is conjoined with that of Lake Huron through the wide Straits of Mackinac, giving it the same surface elevation as its easterly counterpart; the two are technically a single lake.[4]
Lake Michigan is shared, from west to east, by the U.S. states of Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana, and Michigan. Ports along its shores include Chicago; Milwaukee; Green Bay, Wisconsin; Gary, Indiana; and Muskegon, Michigan. The word "Michigan" originally referred to the lake itself, and is believed to come from the Ojibwe word michi-gami meaning "great water".[5]
History
Some of the earliest human inhabitants of the Lake Michigan region were the Hopewell Indians. Their culture declined after 800 AD, and for the next few hundred years, the region was the home of peoples known as the Late Woodland Indians. In the early 17th century, when western European explorers made their first forays into the region, they encountered descendants of the Late Woodland Indians: the Chippewa; Menominee; Sauk; Fox; Winnebago; Miami; Ottawa; and Potawatomi. The French explorer Jean Nicolet is believed to have been the first European to reach Lake Michigan, possibly in 1634 or 1638.[6] In the earliest European maps of the region, the name of Lake Illinois has been found in addition to that of "Michigan", named for the Illinois Confederation of tribes.[7]
Lake Michigan is joined via the narrow, open-water Straits of Mackinac with Lake Huron, and the combined body of water is sometimes called Michigan–Huron (also Huron–Michigan). The Straits of Mackinac were an important Native American and fur trade route. Located on the southern side of the Straits is the town of Mackinaw City, Michigan, the site of Fort Michilimackinac, a reconstructed French fort founded in 1715, and on the northern side is St. Ignace, Michigan, site of a French Catholic mission to the Indians, founded in 1671. In 1673, Jacques Marquette, Louis Joliet and their crew of five Métis voyageurs followed Lake Michigan to Green Bay and up the Fox River, nearly to its headwaters, in their search for the Mississippi River, cf. Fox–Wisconsin Waterway. The eastern end of the Straits was controlled by Fort Mackinac on Mackinac Island, a British colonial and early American military base and fur trade center, founded in 1781.[8]
With the advent of European exploration into the area in the late 17th century, Lake Michigan became part of a line of waterways leading from the Saint Lawrence River to the Mississippi River and thence to the Gulf of Mexico.[9] French coureurs des bois and voyageurs established small ports and trading communities, such as Green Bay, on the lake during the late 17th and early 18th centuries.[10]
In the 19th century, Lake Michigan played a major role in the development of Chicago and the Midwestern United States west of the lake. For example, 90% of the grain shipped from Chicago traveled east over Lake Michigan during the antebellum years, and only rarely falling below 50% after the Civil War and the major expansion of railroad shipping.[11]
The first person to reach the deep bottom of Lake Michigan was J. Val Klump, a scientist at the University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee. Klump reached the bottom via submersible as part of a 1985 research expedition.[12]
In 2007, a row of stones paralleling an ancient shoreline was discovered by Mark Holley, professor of underwater archeology at Northwestern Michigan College. This formation lies 40 feet (12 m) below the surface of the lake. One of the stones is said to have a carving resembling a mastodon. So far the formation has not been authenticated.[13][14]
The warming of Lake Michigan was the subject of a report by Purdue University in 2018. In each decade since 1980, steady increases in average surface temperature have occurred. This is likely to lead to decrease in native habitat and adversely effect native species survival.[15]
Geography
Lake Michigan is the only one of the Great Lakes wholly within the borders of the United States; the others are shared with Canada.[20] It lies in the region known as the American Midwest.
Statistics and bathymetry
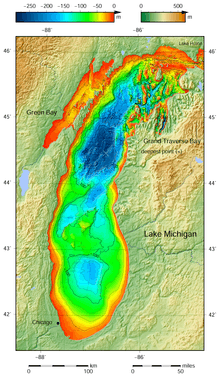
Lake Michigan has a surface area of 22,404 sq.mi (58,026 km2); (13,237 square miles, 34,284 km2 lying in Michigan state,[2] 7,358 square miles, 19,056 km2 in Wisconsin, 234 square miles, 606 km2 in Indiana, & 1,576 square miles, 4,079 km2 in Illinois) making it the largest lake entirely within one country by surface area (Lake Baikal, in Russia, is larger by water volume), and the fifth-largest lake in the world. It is the larger half of Lake Michigan–Huron, which is the largest body of fresh water in the world by surface area. It is 307 miles (494 km) long by 118 miles (190 km) wide with a shoreline 1,640 miles (2,640 km) long. The lake's average depth is 46 fathoms 3 feet (279 ft; 85 m), while its greatest depth is 153 fathoms 5 feet (923 ft; 281 m).[2][21] It contains a volume of 1,180 cubic miles (4,918 km³) of water. Green Bay in the northwest is its largest bay. Grand Traverse Bay in its northeast is another large bay. Lake Michigan's deepest region, which lies in its northern-half, is called Chippewa Basin (named after prehistoric Lake Chippewa) and is separated from South Chippewa Basin, by a relatively shallower area called the Mid Lake Plateau.[22][23]
Cities

Twelve million people live along Lake Michigan's shores, mainly in the Chicago and Milwaukee metropolitan areas. The economy of many communities in northern Michigan and Door County, Wisconsin is supported by tourism, with large seasonal populations attracted by the beauty and recreational opportunities offered by Lake Michigan.[24] Seasonal residents often have summer homes along the waterfront and return home for the winter. The southern tip of the lake near Gary, Indiana is heavily industrialized. Cities on the shores of Lake Michigan include:
|
Illinois
|
Indiana
|
Michigan
Wisconsin
Connection to ocean and open water

The Saint Lawrence Seaway and Great Lakes Waterway opened the Great Lakes to ocean-going vessels. Wider ocean-going container ships do not fit through the locks on these routes, and thus shipping is limited on the lakes. Despite their vast size, large sections of the Great Lakes freeze in winter, interrupting most shipping. Some icebreakers ply the lakes.
The Great Lakes are also connected by the Illinois Waterway to the Gulf of Mexico via the Illinois River (from Chicago) and the Mississippi River. An alternate track is via the Illinois River (from Chicago), to the Mississippi, up the Ohio, and then through the Tennessee-Tombigbee Waterway (combination of a series of rivers and lakes and canals), to Mobile Bay and the Gulf. Commercial tug-and-barge traffic on these waterways is heavy.
Pleasure boats can also enter or exit the Great Lakes by way of the Erie Canal and Hudson River in New York. The Erie Canal connects to the Great Lakes at the east end of Lake Erie (at Buffalo, NY) and at the south side of Lake Ontario (at Oswego, NY).
Beaches

Lake Michigan has many beaches. The region is often referred to as the "Third Coast"[25] of the United States, after those of the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. The sand is often soft and off-white, known as "singing sands" because of the squeaking noise (caused by high quartz content) it emits when walked upon. Some beaches have sand dunes covered in green beach grass and sand cherries, and the water is usually clear and cool, between 55 and 80 °F (13 and 27 °C),[26] even in the late summer months. However, because prevailing westerly winds tend to move the surface water toward the east, there is a flow of warmer water to the Michigan shore in the summer.[27]
The sand dunes located on the east shore of Lake Michigan are the largest freshwater dune system in the world. In fact, in multiple locations along the shoreline, the dunes rise several hundred feet above the lake surface. Large dune formations can be seen in many state parks, national forests and national parks along the Indiana and Michigan shoreline. Some of the most expansive and unique dune formations can be found at Indiana Dunes National Lakeshore, Saugatuck Dunes State Park, Warren Dunes State Park, Hoffmaster State Park, Silver Lake State Park, Ludington State Park, and Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore. Small dune formations can be found on the western shore of Lake Michigan at Illinois Beach State Park and moderate sized dune formations can be found in Kohler-Andrae State Park and Point Beach State Forest in Wisconsin. A large dune formation can be found in Whitefish Dunes State Park in Wisconsin in the Door Peninsula. Lake Michigan beaches in Northern Michigan are the only place in the world, aside from a few inland lakes in that region, where one can find Petoskey stones, the state stone.
The beaches of the western coast and the northernmost part of the east coast are often rocky, with some sandy beaches due to local conditions; while the southern and eastern beaches are typically sandy and dune-covered. This is partly because of the prevailing winds from the west (which also cause thick layers of ice to build on the eastern shore in winter).
The Chicago city waterfront is composed of parks, beaches, harbors and marinas, and residential developments connected by the Chicago Lakefront Trail. Where there are no beaches or marinas, stone or concrete revetments protect the shoreline from erosion. The Chicago lakefront is quite walkable; it is possible to stroll past parks, beaches, and marinas for about 24 miles (39 km) between the city's southern and northern limits along the lake.
Ferries

Two passenger and vehicle ferries operate ferry services on Lake Michigan, both connecting Wisconsin on the western shore with Michigan on the east. From May to October, the historic steam ship, SS Badger, operates daily between Manitowoc, Wisconsin, and Ludington, Michigan,[28] connecting U.S. Highway 10 between the two cities. The Lake Express, established in 2004, carries passengers and vehicles across the lake between Milwaukee, Wisconsin, and Muskegon, Michigan.
Islands
- The Beaver Island archipelago in Charlevoix County, Michigan, includes Beaver Island, Garden Island, Grape Island, Gull Island, Hat Island, High Island, Hog Island, Horseshoe Island, Little Island, Pismire Island, Shoe Island, Squaw Island, Trout Island, and Whiskey Island.
- The Fox Islands in Leelanau County, Michigan, consist of North Fox Island and South Fox Island.
- The Manitou Islands, North Manitou Island and South Manitou Island, are in Leelanau County, Michigan.
- Islands within Grand Traverse Bay include Bassett Island, Bellow Island, and Marion Island.
- Islands south of the Garden Peninsula in Delta County, Michigan include Gravelly Island, Gull Island, Little Gull Island, Little Summer Island, Poverty Island, Rocky Island, St. Martin Island, and Summer Island.
- Islands in Big Bay de Noc in Delta County, Michigan include Round Island, Saint Vital Island, and Snake Island.
- Islands in Little Bay de Noc in Delta County, Michigan include Butlers Island and Sand Island.
- Wilderness State Park in Emmet County, Michigan contains Temperance Island and Waugoshance Island.
- Epoufette Island, Gravel Island, Little Hog Island, and Naubinway Island are located in Mackinac County, Michigan, in the area of Epoufette, Michigan and Naubinway, Michigan.
- Green Island and St. Helena Island are in the vicinity of the Mackinac Bridge, in Mackinac County, Michigan.
- Islands surrounding the Door Peninsula in Wisconsin include Chambers Island, Fish Island, Gravel Island, Spider Island, Horseshoe Island, the Sister Islands, Detroit Island, Green Island, Hog Island, Pilot Island, Plum Island, Rock Island, the Strawberry Islands and Washington Island. The northern half of the peninsula is technically an island itself, due to the Sturgeon Bay Ship Canal.
- Northerly Island is a 91-acre (37 ha) man-made island in Chicago. It is the home of the Adler Planetarium, the former site of Meigs Field, and the current site of the temporary concert venue Charter One Pavilion each summer.
- Other islands included Fisherman Island in Charlevoix County, Michigan and Ile aux Galets in Emmet County, Michigan.
- Plum Island (Wisconsin) is an island at the western shore of Lake Michigan in the southern part of the town of Washington in Door County, Wisconsin.
Parks



The National Park Service maintains the Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore and Indiana Dunes National Lakeshore. Parts of the shoreline are within the Hiawatha National Forest and the Manistee National Forest. The Manistee National Forest section of the shoreline includes the Nordhouse Dunes Wilderness. The Lake Michigan division of the Michigan Islands National Wildlife Refuge is also within the lake.
There are numerous state and local parks located on the shores of the lake or on islands within the lake. A partial list follows.
- Chicago Park District Beaches
- Duck Lake State Park
- Fayette Historic State Park
- Fisherman's Island State Park
- Grand Haven State Park
- Grand Mere State Park
- Harrington Beach State Park
- Holland State Park
- Hoffmaster State Park
- Illinois Beach State Park
- Indian Lake State Park
- Indiana Dunes State Park
- Kohler-Andrae State Park
- Lake Park, Milwaukee
- Ludington State Park
- Leelanau State Park
- Mears State Park
- Muskegon State Park
- Newport State Park
- Orchard Beach State Park
- Peninsula State Park
- Racine Zoo
- Saugatuck Dunes State Park
- Silver Lake State Park
- Traverse City State Park
- Terry Andrae State Park
- Van Buren State Park
- Warren Dunes State Park
- Wells State Park
- Wilderness State Park
Lighthouses
Hydrology

The Milwaukee Reef, running under Lake Michigan from a point between Milwaukee and Racine to a point between Grand Haven and Muskegon, divides the lake into northern and southern basins. Each basin has a clockwise flow of water, deriving from rivers, winds, and the Coriolis effect. Prevailing westerly winds tend to move the surface water toward the east, producing a moderating effect on the climate of western Michigan. There is a mean difference in summer temperatures of 5 to 10 degrees Fahrenheit (2 to 5 degrees Celsius) between the Wisconsin and Michigan shores.[27]
Hydrologically Michigan and Huron are the same body of water (sometimes called Lake Michigan-Huron), but are normally considered distinct. Counted together, it is the largest body of fresh water in the world by surface area. The Mackinac Bridge is generally considered the dividing line between them. Both lakes are part of the Great Lakes Waterway. The main inflow to Lake Michigan from Lake Superior, through Lake Huron, is controlled by the locks operated by the bi-national Lake Superior Board of Control[29]
Historic High Water
- The lake fluctuates from month to month, with the highest lake levels typically experienced in the summer. The normal high-water mark is 2.00 feet (0.61 m) above datum 577.5 ft (176.0 m). In the summer of 1986, Lakes Michigan and Huron reached their highest level during the period during which records have been kept, at 5.92 ft (1.80 m) above datum.[30] The high water records began in February 1986 and lasted through the year, ending with January 1987. Water levels ranged from 3.67 ft (1.12 m) to 5.92 feet (1.80 m) above Chart Datum.[30] On February 21, 1986, the waters neared the all-time maximum for the period during which records have been kept.[31]
Historic Low Water
- Lake levels tend to be the lowest in winter. The normal low water mark is 1.00 foot (0.30 m) below datum 577.5 ft (176.0 m). In the winter of 1964, Lakes Michigan and Huron reached their lowest level at 1.38 feet (0.42 m) below datum.[30] As with the highwater records, monthly low water records were set each month from February 1964 through January 1965. During this twelve-month period water levels ranged from 1.38 feet (0.42 m) to 0.71 feet (0.22 m) below Chart Datum.[30]
In January 2013, Lake Michigan's monthly mean water levels dipped to an all-time low of 576.2 ft (175.6 m),[32] reaching their lowest ebb since record keeping began in 1918. The lakes were 29 in (0.74 m) below their long-term average and had declined 17 inches since January 2012.[33] Keith Kompoltowicz, chief of watershed hydrology for the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers' district office in Detroit, explained that biggest factors leading to the lower water levels in 2013 were a combination of the "lack of a large snowpack" in the winter of 2011/2012 coupled with very hot and dry conditions in the summer of 2012.[32]
Drinking water
Lake Michigan, like the other Great Lakes, supplies drinking water to millions of people in bordering areas. The lakes are collectively administered by the state and provincial governments adjacent to them pursuant to the Great Lakes Compact.
Environmental problems can still plague the lake. Steel mills and refineries operate near the Indiana shoreline. The Chicago Tribune reported that BP is a major polluter, dumping thousands of pounds of raw sludge into the lake every day from its Whiting, Indiana, oil refinery.[34] In March 2014 BP's Whiting refinery was responsible for spilling more than 1,600 US gallons (6,100 l) of oil into the lake.[35]
Fishing
Lake Michigan is home to a wide variety of fish species and other organisms. It was originally home to lake whitefish, lake trout, yellow perch, panfish, largemouth bass, smallmouth bass and bowfin, as well as some species of catfish. As a result of improvements to the Welland Canal in 1919, an invasion of sea lampreys and overharvesting, there has been a decline in native lake trout populations, ultimately causing an increase in the population of another invasive species, the alewife. As a result, salmonids, including various strains of brown trout, steelhead (rainbow trout), coho and chinook salmon, were introduced as predators in order to decrease the alewife population. This program was so successful that the introduced population of trout and salmon exploded, resulting in the creation of a large sport fishery for these introduced species. Lake Michigan is now stocked annually with steelhead, brown trout, and coho and chinook salmon, which have also begun natural reproduction in some Lake Michigan tributaries. However, several introduced invasive species, such as lampreys, round goby, zebra mussels and quagga mussels, continue to cause major changes in water clarity and fertility, resulting in knock-on changes to Lake Michigan's ecosystem, threatening the vitality of native fish populations.
Commercial fisheries
Fisheries in inland waters of the United States are small compared to marine fisheries. The largest fisheries are the landings from the Great Lakes, worth about $13 million in 2003.[36] Michigan’s commercial fishery today consists mainly of 150 tribe-licensed commercial fishing operations through the Chippewa-Ottawa Resource Authority (CORA) and tribes belonging to the Great Lakes Indian Fish and Wildlife Commission (GLIFWC), which harvest 50 percent of the Great Lakes commercial catch in Michigan waters, and 45 state-licensed commercial fishing enterprises.[37] The prime commercial species is the lake whitefish (Coregonus clupeaformis). The annual harvest declined from an average of 11 million pounds (5,000,000 kg) from 1981 through to 1999 to more recent annual harvests of 8 to 9.5 million pounds (3,600,000 to 4,300,000 kg). The price for lake whitefish dropped from $1.04/lb. to as low as $.40/lb during periods of high production.[37]
Sports fishing
Sports fishing includes salmon, whitefish, smelt, lake trout and walleye being major catches. In the late 1960s, successful stocking programs for Pacific salmon led to the development of Lake Michigan’s charter fishing industry.[38]
Shipping
Like all of the Great Lakes, Lake Michigan is today used as a major mode of transport for bulk goods. In 2002, 162 million net tons of dry bulk cargo were moved via the Lakes. This was, in order of volume: iron ore, grain and potash.[39] The iron ore and much of the stone and coal are used in the steel industry. There is also some shipping of liquid and containerized cargo, but most container vessels cannot pass the locks on the Saint Lawrence Seaway because the ships are too wide. The total amount of shipping on the lakes has been on a downward trend for several years.
Port of Chicago
The Port of Chicago, operated by the Illinois International Port District, has grain (14 million bushels) and bulk liquid (800,000 barrels) storage facilities along Lake Calumet. The central element of the Port District, Calumet Harbor, is maintained by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers.[40]

Tourism and recreation
Tourism and recreation are major industries on all of the Great Lakes:
- A few small cruise ships operate on Lake Michigan, including a couple of sailing ships.
- Many other water sports are practiced on the lakes, such as yachting, sea kayaking, diving, kitesurfing and lake surfing.
- The Great Lakes Circle Tour, a designated scenic road system, connects all of the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence River.[41]
- Great Lakes passenger steamers have been operating since the mid-1800s. Several ferries currently operate on the Great Lakes to carry passengers to various islands, including Beaver Island and Bois Blanc Island (Michigan). Currently, two car ferry services traverse Lake Michigan from around April to November: the SS Badger, a steamer from Ludington, Michigan, to Manitowoc, Wisconsin, and the Lake Express, a high speed catamaran from Milwaukee to Muskegon, Michigan.
See also

References
- 1 2 "Lake Michigan". Great-lakes.net. 2009-06-18. Archived from the original on 2010-01-01. Retrieved 2010-01-14.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Wright 2006, p. 64
- ↑ Shorelines of the Great Lakes Archived 2015-04-05 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Great Lakes Map". Michigan Department of Environmental Quality. 2013. Retrieved August 26, 2013.
- ↑ "Superior Watershed Partnership Projects". Archived from the original on September 28, 2007.
- ↑ Bogue 1985, pp. 7–13
- ↑ http://www.libs.uga.edu/darchive/hargrett/maps/1733d4.jpg
- ↑ "Colonial Fort Michilimackinac". Mighty Mac. Retrieved 2014-07-06.
- ↑ Bogue 1985, pp. 14–16
- ↑ Shelak 2003, p. 3
- ↑ Cronon, William (1991). Nature's Metropolis: Chicago and the Great West. New York, NY: W. W. Norton and Company. p. 87. ISBN 9780393072457.
- ↑ "Variations In Sediment Accumulation Rates And The Flux Of Labile Organic Matter In Eastern Lake Superior Basins". The Journal of Great Lakes Research. 1989. Archived from the original on 2012-12-03. Retrieved 2009-08-09.
- ↑ Flesher, John (2007-09-04). "Possible mastodon carving found on rock". Associated Press. Retrieved 2008-05-25.
- ↑ Flesher, John (2007-09-05). "Rock brings history to surface (pictures)". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 2012-09-15. Retrieved 2008-05-25.
- ↑ Briscoe, Tony (September 16, 2018). "Lake Michigan is warming. A new report says that could mean trouble for game fish". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved 2018-09-17.
- ↑ National Geophysical Data Center, 1996. Bathymetry of Lake Michigan. National Geophysical Data Center, NOAA. doi:10.7289/V5B85627 [access date: 2015-03-23].
- ↑ National Geophysical Data Center, 1999. Bathymetry of Lake Huron. National Geophysical Data Center, NOAA. doi:10.7289/V5G15XS5 [access date: 2015-03-23]. (only small portion of this map)
- ↑ National Geophysical Data Center, 1999. Global Land One-kilometer Base Elevation (GLOBE) v.1. Hastings, D. and P.K. Dunbar. National Geophysical Data Center, NOAA. doi:10.7289/V52R3PMS [access date: 2015-03-16].
- ↑ "About Our Great Lakes: Tour". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory (GLERL). Retrieved December 15, 2017.
- ↑ 05, US EPA,REG. "Geophysical Lake Michigan - US EPA". US EPA.
- ↑ "Chart: 14901 Edition: 15 Edition Date: August 2006 Clear Dates: NM – 12/17/2011 LNM – 12/6/2011";"Soundings in feet and fathoms". NOAA. Retrieved September 18, 2013.
- ↑ https://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/mgg/image/michiganlarge.jpg
- ↑ "Bathymetry of Lake Michigan". www.ngdc.noaa.gov.
- ↑ http://www.miseagrant.umich.edu/explore/coastal-communities/economic-vitality-and-the-great-lakes/
- ↑ "NOAA Great Lakes Region". NOAA. Retrieved 2015-09-15.
- ↑ "Michigan Sea Grant Coastwatch". Coastwatch.msu.edu. Retrieved 2010-01-14.
- 1 2 Hilton 2002, pp. 3–5
- ↑ "Schedule and Fares". SS Badger. Retrieved April 1, 2018.
- ↑ Briscoe, Tony (July 13, 2018). "What happens when Lake Superior has too much water?". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved 2018-07-15.
- 1 2 3 4 Monthly bulletin of Lake Levels for The Great Lakes; September 2009; US Army Corps of Engineers, Detroit District
- ↑ "The Weather History for February 21st". Southwest Lower Michigan Weather History. National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office. Retrieved 23 February 2011.
- 1 2 Bivins, Larry (April 3, 2013). "Low Great Lakes water levels plague shipping, recreation". USA Today.
- ↑ Flesher, John (5 February 2013). "Two Great Lakes hit lowest water levels since record keeping began nearly a century ago". Vancouver Sun. Archived from <ury/7923713/story.html#ixzz2RxYTXcZr the original on 12 February 2013.
- ↑ Hawthorne, Michael. "BP gets break on dumping in lake". Chicago Tribune.
- ↑ Hawthorne, Michael. "BP raises estimate of Lake Michigan oil spill". Chicago Tribune.
- ↑ NOAA/NMFS: (2004) Fisheries of the United States, 2003 Archived 2007-08-10 at the Wayback Machine.
- 1 2 Michigan Commercial Fisheries Marketing and Product Development (PDF) (Report). Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Sea Grant.
- ↑ O'Keefe, Dan (2009). Charter Fishing in Michigan: A Profile of Customers and Economic Impacts (PDF) (Report). Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Sea Grant.
- ↑ Great Lakes Shipping Study (PDF) (Report). U.S. Department of Homeland Security. January 13, 2014.
- ↑ U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (November 2007). "Calumet Harbor, IL and IN". Retrieved on July 31, 2014.
- ↑ "Great Lakes Circle Tour". Great-lakes.net. 2005-07-05. Archived from the original on 2010-07-25. Retrieved 2011-02-19.
Further reading
- Bogue, Margaret Beattie (1985). Around the Shores of Lake Michigan: A Guide to Historic Sites. University of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 0-299-10004-9.
- Hilton, George Woodman (2002). Lake Michigan Passenger Steamers. Stanford University Press. ISBN 0-8047-4240-5.
- Hyde, Charles K.; Mahan, Ann; Mahan, John (1995). The Northern Lights: Lighthouses of the Upper Great Lakes. Detroit: Wayne State University Press. ISBN 978-0-814325-54-4.
- Oleszewski, Wes (1998). Great Lakes Lighthouses, American and Canadian: A Comprehensive Directory/Guide to Great Lakes Lighthouses. Gwinn: Avery Color Studios, Inc. ISBN 0-932212-98-0.
- Penrod, John (1998). Lighthouses of Michigan. Berrien Center: Pernod/Hiawatha. ISBN 978-0-942618-78-5.
- Penrose, Laurie; Penrose, Bill (1999). A Traveler’s Guide to 116 Michigan Lighthouses. Petoskey: Friede Publications. ISBN 978-0-923756-03-1.
- Shelak, Benjamin J. (2003). Shipwrecks of Lake Michigan. Big Earth Publishing. ISBN 1-931599-21-1.
- Wagner, John L. (1998). Michigan Lighthouses: An Aerial Photographic Perspective. East Lansing: John L. Wagner. ISBN 978-1-880311-01-1.
- Wright, John W., ed. (2006). The New York Times Almanac. Editors and reporters of The New York Times (2007 ed.). New York, New York: Penguin Books. ISBN 0-14-303820-6.
- Wright, Larry; Wright, Patricia (2006). Great Lakes Lighthouses Encyclopedia (Hardback ed.). Erin: Boston Mills Press. ISBN 1-55046-399-3.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lake Michigan. |
| Wikisource has the text of an 1879 American Cyclopædia article about Lake Michigan. |
- EPA's Great Lakes Atlas
- Great Lakes Coast Watch
- Michigan DNR map of Lake Michigan
- Official Michigan DNR Freshwater Fishing Regulations
- Bathymetry of Lake Michigan



- Lighthouses
- Bibliography on Michigan lighthouses
- Interactive map of lighthouses in area (northern Lake Michigan)
- Interactive map of lighthouses in area (southern Lake Michigan)
- Terry Pepper on lighthouses of the western Great Lakes
- Wagner, John L., Beacons Shining in the Night, Michigan lighthouse bibliography, chronology, history, and photographs, Clarke Historical Library, Central Michigan University