Jurchen people
| Jurchen people | |||||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 女真 | ||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 女眞 (variant) | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Korean name | |||||||||
| Hangul |
여진 (S. Korea) 녀진 (N. Korea) | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Russian name | |||||||||
| Russian | Чжурчжэни | ||||||||
| Romanization | Tzshurtzhehnie | ||||||||
| Khitan name | |||||||||
| Khitan | dʒuuldʒi (女直)[2] | ||||||||
| Mongolian name | |||||||||
| Mongolian |
Зүрчид, Зөрчид, Жүрчид Zu’rqid, Zo’rqid, Ju’rqid[3] | ||||||||
| Middle Chinese name | |||||||||
| Middle Chinese | /ɳɨʌX/ /t͡ɕiɪn/ | ||||||||
The Jurchen (Manchu: ᠵᡠᡧᡝᠨ Jušen; Chinese: 女真, Nǚzhēn, [nỳ.ʈʂə́n]), also known by many variant names, were a Tungusic people consisting of three major groups: Jianzhou Jurchens (Chinese: 建州女真), Yeren (Wild) Jurchens (Chinese: 野人女真), and Haixi Jurchens (Chinese: 海西女真) who traditionally inhabited the region of Manchuria — the most famous of these Jurchen peoples are the Jianzhou and are commonly referred to as simply "Jurchens". Around 1630, the Jianzhou Jurchens reformed and combined with their neighbors as the Manchu. The Wild Jurchens went on to form the Nanai, Evenks, Negidals, Oroqen and Nivkh.[4] The Haixi Jurchens had poor relations with the Jianzhou, eventually being fully conquered and absorbed into the Manchu ethnicity. The Jurchen established the Jin Dynasty, whose empire conquered the Northern Song in 1127, gaining control of most of North China. Jin control over China lasted until their 1234 conquest by the Mongols. The Manchus would later conquer the Ming and establish the Qing Dynasty, which ruled China until their overthrow in 1911.
Name
The initial Khitan form of the name was said to be Lüzhen. The variant Nrjo-tsyin (now Nüzhen, whence English Nurchen) appeared in the 10th century under the Liao dynasty.[5] The Jurchens were also interchangeably known as the Nrjo-drik (now Nüzhi). This is traditionally explained as an effect of the Chinese naming taboo, with the character 真 being removed after the 1031 enthronement of Zhigu, Emperor Xingzong of Liao, because it appeared in the sinified form of his personal name.[5] Aisin-Gioro Ulhicun, however, argues that this was a later folk etymology and the original reason was uncertainty among dialects regarding the name's final -n.[6]
Jurchen is an anglicization of Jurčen,[3][7] an attempted reconstruction of this unattested original form of the native name,[8] which has been transcribed into Middle Chinese as Trjuwk-li-tsyin (竹里真)[lower-alpha 1] and into Khitan small script as Julisen.[6] The ethnonyms Sushen (Old Chinese: */siwk-[d]i[n]-s/) and Jizhen (稷真, Old Chinese: */tsək-ti[n]/)[9] recorded in geographical works like the Classic of Mountains and Seas and the Book of Wei are possibly cognates.[10] It was the source of Fra Mauro's Zorça[7] and Marco Polo's Ciorcia,[11] reflecting the Persian form of their name.[7] Vajda considers that the Jurchens' name probably derives from the Tungusic words for "reindeer people" and is cognate with the names of the Orochs of Khabarovsk Province and the Oroks of Sakhalin.[12] ("Horse Tungus" and "Reindeer Tungus" are still the primary divisions among the Tungusic cultures.)[13]
Janhunen argues that these records already reflect the Classical Mongolian plural form of the name, recorded in the Secret History as J̌ürčät,[8] and further reconstructed as *Jörcid,[11] The modern Mongolian form is Jürčid[3] whose medial -r- does not appear in the later Jurchen Jucen[11] or Jušen (Jurúna: ![]()
History
Prehistory
At the time of their notice by Chinese historians, the Jurchen inhabited the forests and river valleys of the land which is now divided between China's Heilongjiang Province and Russia's Primorsky Krai province. In earlier records, this area was known as the home of the Sushen (c. 1100 BC), the Yilou (around AD 200), the Wuji (c. 500), and the Mohe (c. 700).[16] Under the Qing and within modern scholarship,[lower-alpha 3] some sources stress the continuity between these earlier peoples with the Jurchen[18] but this remains conjectural.[19]
The Tungusic Mohe tribes were subjects of the multi-ethnic kingdom of Balhae. The Mohe enjoyed eating pork, practiced pig farming extensively, and were mainly sedentary. They used both pig and dog skins for coats. They were predominantly farmers and grew soybean, wheat, millet, and rice in addition to hunting.[20]
Jin dynasty
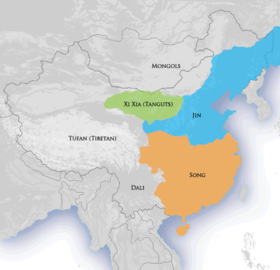
By the 11th century, the Jurchens had become vassals of the Khitan rulers of the Liao dynasty. The Jurchens in the Yalu River region had been tributaries of Goryeo since the reign of Wang Geon, who called upon them during the wars of the Later Three Kingdoms period, but the Jurchens switched allegiance between Liao and Goryeo multiple times out of expedience. They offered tribute to both courts out of political necessity and the attraction of material benefits.[21]
Wanyan Aguda, chief of the Wanyan tribe, unified the various Jurchen tribes in 1115 and declared himself emperor. In 1120 he seized Shangjing, also known as Linhuang Prefecture (臨潢府), the northern capital of the Liao dynasty.[22] During the Jin–Song Wars, the Jurchens invaded the Northern Song dynasty and overran most of northern China. The Jurchens initially created the puppet regimes of Da Qi and Da Chu but later adopted a dynastic name and became known as "Jin" 金, which means "gold", not to be confused with the earlier Jin 晋 dynasties named after the region around Shanxi and Henan provinces. The Jin dynasty captured the Northern Song dynasty's capital, Bianjing, in 1127. Their armies pushed the Song all the way south to the Yangtze River and eventually settled on a border with the Southern Song dynasty along the Huai River.
The name of the Jurchen dynasty in Chinese — meaning "gold"—is derived from the "Gold River" (Jurchen: Anchuhu; Manchu: Aisin) in their ancestral homeland. The Jurchens who settled into urban communities eventually intermarried with other ethnicities in China. The Jin rulers themselves came to follow Confucian norms.
After 1189, the Jin dynasty became increasingly involved in conflicts with the Mongols. By 1215, after losing much territory to the Mongols, the Jurchens moved their capital south from Zhongdu to Kaifeng. After a siege lasting about a year, Kaifeng fell to the Mongols in 1233. Emperor Aizong fled to Caizhou for shelter, but Caizhou also fell to the Mongols in 1234, marking the end of the Jin dynasty.
Ming dynasty

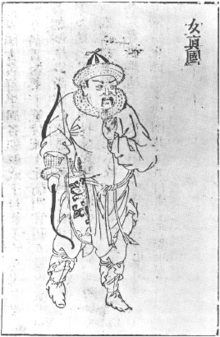
Chinese chroniclers of the Ming dynasty distinguished three different groups of Jurchens: the Wild Jurchens (野人女真; yěrén Nǚzhēn) of northernmost Manchuria, the Haixi Jurchens (海西女真) of modern Heilongjiang Province and the Jianzhou Jurchens of modern Jilin Province. They led a pastoral-agrarian lifestyle, hunting, fishing, and engaging in limited agriculture. In 1388, the Hongwu Emperor dispatched a mission to establish contact with the Odoli, Huligai and T'owen tribes.
The issue of controlling the Jurchens was a point of contention between Joseon Korea and the early Ming.[23]
The Yongle Emperor (r. 1402–1424) found allies among the various Jurchen tribes against the Mongols. He bestowed titles and surnames to various Jurchen chiefs and expected them to send periodic tribute. One of the Yongle Emperor's consorts was a Jurchen princess, which resulted in some of the eunuchs serving him being of Jurchen origin.[24] Chinese commanderies were established over tribal military units under their own hereditary tribal leaders. In the Yongle period, 178 commanderies were set up in Manchuria. Later on, horse markets were established in the northern border towns of Liaodong. Increased contact with the Chinese gave Jurchens the more complex and sophisticated organizational structures.
The Koreans dealt with the Jurchen military through appeals to material benefits and launching punitive expeditions. To appease them the Joseon court handed out titles and degrees, trading with them, and sought to acculturate them by having Korean women marry Jurchens and integrating them into Korean culture. These measures were unsuccessful and fighting continued between the Jurchen and the Koreans.[25][26] This relationship between the Jurchens and Koreans was ended by the Ming which envisioned the Jurchens as a form of protective border to the north.[27] In 1403, Ahacu, chieftain of Huligai, paid tribute to the Yongle Emperor. Soon after that, Mentemu, chieftain of Odoli clan of the Jianzhou Jurchens, defected from paying tribute to Korea, becoming a tributary to China instead. Yi Seong-gye, the first ruler of Joseon, asked the Ming dynasty to send Mentemu back but was refused.[28] The Yongle Emperor was determined to wrest the Jurchens out of Korean influence and have China dominate them instead.[29][30] The Koreans tried to persuade Mentemu to reject the Ming dynasty's overtures but were unsuccessful.[31][32][33][34] The Jurchen tribes presented tribute to the Ming dynasty in succession.[35] They were divided in 384 guards by the Ming dynasty[27] and the Jurchen became vassals to the Ming emperors.[36] The name given to the Jurchen land by the Ming dynasty was Nurgan. Later, a Korean army led by Yi-Il and Yi Sun-sin would expel them from Korea.
In 1409, the Ming government created the Nurgan Command Post (奴兒干都司) at Telin (present-day Tyr, Russia,[37] about 100 km upstream from Nikolayevsk-on-Amur in the Russian Far East) in the vicinity of Heilongjiang. The Jurchens came under the nominal administration of the Nurgan Command Post which lasted only 25 years and was abolished in 1434. Leaders of the Haixi and Jianzhou tribes did however accept the Ming titles.
From 1411 to 1433, the Ming eunuch Yishiha (who himself was a Haixi Jurchen[38]) led ten large missions to win over the allegiance of the Jurchen tribes along the Songhua River and Amur River. His fleet sailed down the Songhua into the Amur, and set up the Nurgan Command at Telin near the mouth of the Amur River. These missions are not well recorded in the Ming histories, but there exist two stone steles erected by Yishiha at the site of the Yongning Temple, a Guanyin temple commissioned by him at Telin.[39] The inscriptions on the steles are in four languages: Chinese, Jurchen, Mongol, and Tibetan. There is probably quite a lot of propaganda in the inscriptions, but they give a detailed record of the Ming court's efforts to assert suzerainty over the Jurchen. When Yishiha visited Nurgan for the 3rd time in 1413, he built a temple called Yongning Temple at Telin and erected the Yongning Temple Stele in front of it. Yishiha paid his 10th visit to Nurgan in 1432, during which he rebuilt the Yongning Temple and re-erected a stele in front of it. The stele bore the heading "Record of Re-building Yongning Temple". The setting up of the Nurgan Command Post and the repeated declarations to offer blessings to this region by Yishiha and others were all recorded in this and the first steles.
Establishment of the Manchu
Over a period of 30 years from 1586, Nurhaci, a chieftain of the Jianzhou Jurchens, united the Jurchen tribes, which was later renamed Manchu in 1635 by his son and successor, Hong Taiji. He created a formidable synthesis of tribal and interethnic institutions, providing the basis of the Manchu state and later the conquest of China by the Qing dynasty.
The creation of the Manchu ethnic group from the Jurchen people is linked to the creation of the Eight Banners by Hong Taiji.
Our gurun (tribe, state) originally had the names Manju, Hada, Ula, Yehe, and Hoifa. Formerly ignorant persons have frequently called [us] jušen. The term jušen refers to the Sibo and Chaomergen barbarians and has nothing to do with our gurun. Our gurun establishes the name Manju. Its rule will be long and transmitted over many generations. Henceforth persons should call our gurun its original name, Manju, and not use the previous demeaning name.
Culture

Jurchen culture shared many similarities with the hunter-gatherer lifestyle of Siberian-Manchurian tundra and coastal peoples. Like the Khitans and Mongols, they took pride in feats of strength, horsemanship, archery, and hunting. Both Mongols and Jurchens used the title Khan for the leaders of a political entity, whether "emperor" or "chief". A particularly powerful chief was called beile ("prince, nobleman"), corresponding with the Mongolian beki and Turkish beg or bey. Also like the Mongols and the Turks, the Jurchens did not observe primogeniture. According to tradition, any capable son or nephew could be chosen to become leader.
Unlike the Mongols,[40][41] the Jurchens were a sedentary[42][12] and agrarian society. They farmed grain and millet as their primary cereal crops, grew flax and raised oxen, pigs, sheep, and horses.[43]"At the most", the Jurchen could only be described as "semi-nomadic" while the majority of them were sedentary.[21]
Jurchen similarities and differences with the Mongols were emphasized to various degrees by Nurhaci out of political expediency.[44] Nurhaci once said to the Mongols that "the languages of the Chinese and Koreans are different, but their clothing and way of life is the same. It is the same with us Manchus (Jušen) and Mongols. Our languages are different, but our clothing and way of life is the same." Later, Nurhaci indicated that the bond with the Mongols was not based on any real shared culture, but rather on pragmatic reasons of "mutual opportunism". He said to the Mongols, "You Mongols raise livestock, eat meat and wear pelts. My people till the fields and live on grain. We two are not one country and we have different languages".[45]
During the Ming dynasty, the Jurchens lived in sub-clans (mukun or hala mukun) of ancient clans (hala). Not all clan members were blood related, and division and integration of different clans was common. Jurchen households (boo) lived as families (booigon) consisting of five to seven blood-related family members and a number of slaves. Households formed squads (tatan) to engage in tasks related to hunting and food gathering and formed companies (niru) for larger activities, such as war.
Haixi, Jianzhou, Yeren
The Haixi Jurchens were "semi-agricultural, the Jianzhou Jurchens and Maolian (毛怜) Jurchens were sedentary, while hunting and fishing was the way of life of the "Wild Jurchens".[46] Hunting, horseback archery, horsemanship, livestock raising, and sedentary agriculture were all practiced by Jianzhou Jurchens.[47] The Jurchen way of life (economy) was described as agricultural. They farmed crops and raised animals.[48] Jurchens practiced slash-and-burn agriculture in the areas north of Shenyang.[49]
“建州毛怜则渤海大氏遗孽,乐住种,善缉纺,饮食服用,皆如华人,自长白山迤南,可拊而治也。" "The (people of) Chien-chou and Mao-lin [YLSL always reads Mao-lien] are the descendants of the family Ta of Po-hai. They love to be sedentary and sow, and they are skilled in spinning and weaving. As for food, clothing and utensils, they are the same as (those used by) the Chinese. (Those living) south of the Ch'ang-pai mountain are apt to be soothed and governed."
Pigtail
In 1126, the Jurchens initially ordered male Han Chinese within their conquered territories to adopt the Jurchen hairstyle by shaving the front of their heads and adopting Jurchen dress, but the order was later lifted.[52] Jurchens were impersonated by Han rebels who wore their hair in the Jurchen "pigtail" to strike fear within their population.[53] During the Qing dynasty, the Manchus, who descended from the Jurchens, similarly made Han Chinese men shave the front of their head and wear the rest of their hair in a queue, or soncoho (辮子; biànzi), the traditional Manchu hairstyle.
Dogs
Although their Mohe ancestors did not respect dogs, the Jurchens began to respect dogs around the time of the Ming dynasty and passed this tradition on to the Manchus. It was prohibited in Jurchen culture to use dog skin, and forbidden for Jurchens to harm, kill, or eat dogs. The Jurchens believed that the "utmost evil" was the usage of dog skin by Koreans.[54]
Burial
Until recently, it was uncertain what kind of burial rites existed among the Jurchens. In July 2012, Russian archaeologists discovered a Jurchen burial ground in Partizansky District of Primorye in Russia. Fifteen graves dating to the 12th or 13th centuries were found, consisting of the grave of a chieftain placed in the centre, with the graves of 14 servants nearby. All the graves contained pots with ashes, prompting the scientists to conclude that the Jurchens cremated the corpses of their dead. The grave of the chieftain also contained a quiver with arrows and a bent sword. The archaeologists propose that the sword was purposely bent, to signify that the owner would no longer need it in earthly life. The researchers planned to return to Primorye to establish whether this was a singular burial or a part of the larger burial ground.[55]
Religion
Jurchens practiced shamanic rituals and believed in a supreme sky goddess (abka hehe, literally sky woman). The Jurchens of the Jin dynasty practiced Buddhism, which became the prevalent religion of the Jurchens, and Daoism.[56] Under Confucian influence during the Qing dynasty the gender of the female sky deity was switched to a male sky father, Abka Enduri (abka-i enduri, abka-i han).[57]
Language
The early Jurchen script was invented in 1120 by Wanyan Xiyin, acting on the orders of Wanyan Aguda. It was based on the Khitan script that was inspired in turn by Chinese characters. The written Jurchen language died out soon after the fall of the Jin dynasty, though its spoken form survived. Until the end of the 16th century, when Manchu became the new literary language, the Jurchens used a combination of Mongolian and Chinese. The pioneering work on studies of the Jurchen script was done by Wilhelm Grube at the end of the 19th century.
Possible Jurchen descendants
A caste of "degraded" outcasts said to be descended from the Jurchen existed in Ningbo, Zhejiang Province, during the Qing dynasty, around 3,000 people in a class called to-min (惰民; duòmín). Samuel Wells Williams gave an account of them in his book "The Middle kingdom: a survey of the ... Chinese empire and its inhabitants":
There are local prejudices against associating with some portions of the community, though the people thus shut out are not remnants of old castes. The tankia, or boat-people, at Canton form a class in some respects beneath the other portions of the community, and have many customs peculiar to themselves. At Ningpo there is a degraded set called to min, amounting to nearly three thousand persons, with whom the people will not associate. The men are not allowed to enter the examinations or follow an honorable calling, but are play-actors, musicians, or sedan-bearers; the women are match-makers or female barbers and are obliged to wear a peculiar dress, and usually go abroad carrying a bundle wrapped in a checkered handkerchief. The tankia at Canton also wear a similar handkerchief on their head, and do not cramp their feet. The to min are supposed to be descendants of the Kin, who held northern China in A.D. 1100, or of native traitors who aided the Japanese, in 1555-1563, in their descent upon Chehkiang. The tankia came from some of the Miautsz' tribes so early that their origin is unknown.[58][59][60][61]
See also
Notes
- ↑ The Japanese government and Franke give the modern Mandarin pronunciation Zhulizhen.[5]
- ↑ First attested in a late 15th-century glossary for the Ming Bureau of Translators.[14]
- ↑ For example, the Japanese government, who traced them to the "Wanyen tribe of the Mohos" around Mt Xiaobai, and Huang, who connected them to the Heishui or Blackwater Mohe.[17]
- ↑ Grand Dictionnaire Ricci de la Langue Chinoise, Vol. IV, Paris: Institut Ricci, 2001, p. 697 . (in French) & (in Chinese)
- ↑ 遼朝國號非「哈喇契丹(遼契丹)」考 Archived 27 September 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
- 1 2 3 Hoong 2005, p. 28
- ↑ 满洲历史上的东海女真
- 1 2 3 4 Franke (1994), p. 216.
- 1 2 Aisin Gioro & Jin 2007, p. 12.
- 1 2 3 Pelliot (1959), p. 366.
- 1 2 Pelliot (1959), p. 367.
- ↑ Baxter-Sagart.
- ↑ 《汲冢周书》.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Janhunen 2004, pp. 67 ff.
- 1 2 Vajda 2000.
- ↑ Stolberg 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 Kane 1997, p. 232.
- ↑ Elliott 2001, p. 51.
- ↑ Elliott 2001, p. 47–48.
- ↑ Huang 1990, pp. 239–282.
- ↑ Elliott 2001, p. 47.
- ↑ Elliott 2001, p. 48.
- ↑ Gorelova 2002, pp. 13-14.
- 1 2 Breuker 2010, pp. 220-221.
- ↑ Mote 1999, p. 195.
- ↑ Wang 2010, p. 301.
- ↑ Mitamura 1970, p. 54.
- ↑ Seth 2006, p. 138.
- ↑ Seth 2010, p. 144.
- 1 2 Peterson 2006, p. 15
- ↑ Meng 2006, p. 120
- ↑ Zhang 2008, p. 29.
- ↑ Dardess 2012, p. 18.
- ↑ Goodrich 1976, p. 1066.
- ↑ Peterson 2002, p. 13.
- ↑ Clark 1998, pp. 286-7.
- ↑ Zhang 2008, p. 30.
- ↑ Meng 2006, p. 21
- ↑ Cosmo 2007, p. 3.
- ↑ Объекты туризма — Археологические. Тырские храмы Archived 3 September 2009 at the Wayback Machine. (Regional government site explaining the location of the Tyr (Telin) temples: just south of the Tyr village) (in Russian)
- ↑ Shih-Shan Henry Tsai, "Perpetual Happiness: The Ming Emperor Yongle". Published by University of Washington Press, 2002. ISBN 0295981245 Partial text on Google Books. p. 158.
- ↑ Telin Stele (from: "Политика Минской империи в отношении чжурчженей (1402 -1413 гг.)" (The Jurchen policy of the Ming Empire), in "Китай и его соседи в древности и средневековье" (China and its neighbors in antiquity and the Middle Ages), Moscow, 1970. (in Russian)
- ↑ Franke 1994, p. 217.
- ↑ Rachewiltz 1993, p. 112.
- ↑ Williamson 2011.
- ↑ Franke 1990, p. 416.
- ↑ Perdue 2009, p. 127.
- ↑ Peterson 2002, p. 31.
- ↑ Chan 1988, p. 266.
- ↑ Rawski 1996, p. 834.
- ↑ Wurm, Mühlhäusler & Tyron 1996, p. 828.
- ↑ Reardon-Anderson 2000, p. 504.
- ↑ 萧国亮 (2007-01-24). "明代汉族与女真族的马市贸易". 艺术中国(ARTX.cn). p. 1. Retrieved 25 July 2014.
- ↑ Serruys 1955, p. 22.
- ↑ Zhang 1984, pp. 97-8.
- ↑ Franke 1990, p. 417.
- ↑ Aisin Gioro & Jin 2007, p. 18.
- ↑ "A Large Burial Ground of the Jurchen People Has Been Found In Russia's Primorye :: Russia-InfoCentre". Russia-ic.com. 2012-07-27. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ↑ Ulrich Theobald. "Chinese History - Jin Dynasty (Jurchen) 金 religion and customs". www.chinaknowledge.de. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ↑ Judika Illes, Encyclopedia of Spirits: The Ultimate Guide to the Magic of Fairies, Genies, Demons, Ghosts, Gods & Goddesses (2009)
- ↑ Samuel Wells Williams (1848). The Middle kingdom: a survey of the ... Chinese empire and its inhabitants ... (3 ed.). NEW YORK: Wiley & Putnam. p. 321. Retrieved 8 May 2011. (Original from Harvard University)
- ↑ Samuel Wells Williams (1882). The Middle Kingdom: a survey of the geography, government, literature, social life, arts, and history of the Chinese empire and its inhabitants, Volume 1 (revised ed.). NEW YORK: C. Scribner's Sons. p. 412. Retrieved 8 May 2011. (Original from Harvard University)
- ↑ Samuel Wells Williams (1883). The middle kingdom; a survey of the Chinese empire and its inhabitants (revised ed.). p. 412. Retrieved 8 May 2011.
- ↑ China monthly review, Volume 8. Millard Publishing Co., inc. 1919. p. 264. Retrieved 8 May 2011. (Original from the University of Michigan)
References
- Aisin Gioro, Ulhicun; Jin, Shi (2007), "Manchuria from the Fall of the Yuan to the Rise of the Manchu State (1368–1636)" (PDF), Ritsumeikan Bungaku (No. 601), pp. 12–34
- Arnold, Lauren (1999), Mark Stephen Mir, ed., Princely Gifts and Papal Treasures: The Franciscan Mission to China and Its Influence on the Art of the West, 1250–1350, Desiderata Press, p. p. 179
- Association for Asian Studies. Ming Biographical History Project Committee (1976), Goodrich, Luther Carrington, ed., Dictionary of Ming Biography, 1368-1644, 2 (illustrated ed.), Columbia University Press, p. 1066, ISBN 023103833X
- Bretschneider, E. (2013), "Pei Shi Ki", Mediaeval Researches from Eastern Asiatic Sources: Fragments towards the Knowledge of the Geography and History of Central and Western Asia from the 13th to the 17th Century, Vol. I, London: Routledge, Trench, Trübner, & Co., p. 25
- Breuker, Remco E. (2010), Establishing a Pluralist Society in Medieval Korea, 918-1170: History, Ideology and Identity in the Koryŏ Dynasty, Volume 1 of Brill's Korean Studies Library, Leiden: Brill, pp. 220-221, ISBN 9004183256
- Chan Hok-lam (1988), "The Chien-wen, Yung-lo, Hung-hsi, and Hsüan-te Reigns, 1399–1435", in Frederick W. Mote; Denis Twitchett; John K. Fairbank, The Cambridge History of China, Vol. 7: The Ming Dynasty, 1368-1644, Pt. 1, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 182–304, ISBN 0521243327
- Clark, Donald N. (1998), "Sino-Korean Tributary Relations under the Ming", in Denis C. Twitchett; Frederick W. Mote, The Cambridge History of China, Vol. 8: The Ming Dynasty, 1368–1644, Pt. 2, England: Cambridge University Press, pp. 272–300, ISBN 0521243335
- Cosmo, Nicola Di (2007), The Diary of a Manchu Soldier in Seventeenth-Century China: "My Service in the Army", by Dzengseo, Volume 3 of Routledge Studies in the Early History of Asia (annotated ed.), Routledge, p. 3, ISBN 113578955X
- Dardess, John W. (2012), Ming China, 1368-1644: A Concise History of a Resilient Empire, Rowman & Littlefield, p. 18, ISBN 978-1-4422-0490-4
- Elliott, Mark C. (2001), The Manchu Way: The Eight Banners and Ethnic Identity in Late Imperial China (illustrated, reprint ed.), Stanford University Press, ISBN 0804746842
- Fox, Ralph (1936), Genghis Khan, Harcourt & Brace, p. 278
- Franke, Herbert (1990), "The Forest Peoples of Manchuria: Kitans and Jurchens", in Denis Sinor, The Cambridge History of Early Inner Asia, Vol. I, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 400–423
- Franke, Herbert (1994), "The Chin Dynasty", in Twitchett, Denis C.; Franke, Herbert, The Cambridge History of China, Vol. 6: Alien Regimes and Border States, 907–1368, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 215–320
- Gernet, Jacques (1972), Le Monde Chinois [A History of Chinese Civilization], Cambridge: translated by J.R. Foster and Charles Hartman for Cambridge University Press in 1982, p. 356
- Gorelova, Liliya M., ed. (2002), Handbook of Oriental Studies. Section 8 Uralic & Central Asian Studies, Manchu Grammar, Volume Seven Manchu Grammar, Brill Academic Pub, pp. 13–14, ISBN 9004123075
- Hoong Teik Toh (2005), Martin Gimm; Giovanni Stary; Michael Weiers, eds., Materials for a Geneaology of the Niohuru Clan with Introductory Remarks on Manchu Onomastics, Aetas Manjurica, No. 10, Wiesbaden: Otto Harrassowitz KG, p. 28
- Howorth, H.H. (October 1871), "The Origines of the Manchus", in James Summers, The Phœnix: A Monthly Magazine for India, Burma, Siam, China, Japan, & Eastern Asia, Vol. II, No. 16, London, p. 53
- Huang Pei (1990), "New Light on the Origins of the Manchu", Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies, Vol. 50 (No. 1), pp. 239–282
- Huttman, William (1843), "An Account of Peking", Fisher's Colonial Magazine and Commercial Maritime Journal, Vol. II, London: Fisher, Son, & Co., p. 178
- Janhunen, Juha (2004), "From Choson to Jucher: On the Possibilities of Ethnonymic Continuity in Greater Manchuria", in Marek Stachowski; Kinga Maciuszak, Studia Etymologica Cracoviensia, Vol. 9 (PDF), Krakow: Jagiellonian University Press, pp. 67 ff.
- Kane, Daniel (1997), "Language Death and Language Revivalism: The Case of Manchu", Central Asiatic Journal, Vol. 41 (No. 2), pp. 231–249
- Keane, Augustus Henry; Quiggin, A. Hingston; Haddon, A.C. (1920), Man: Past and Present, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, p. 279
- Lach, Donald F.; Kley, Edwin J. Van (1998), Asia in the Making of Europe, Vol. III, p. 1760
- Meng, Sen (2006), 满洲开国史讲义 (Lecture Notes on Early Manchu History), Zhonghua Book Co., ISBN 7101050301
- Mitamura, Taisuke (1970), Chinese eunuchs: the structure of intimate politics, C.E. Tuttle Co., p. 54
- Morgan, E. Delmar (1872), "An Expedition through Manchuria, from Pekin to Blagovestchensk, in 1870, by the Archimandrite Palladius, Chief of the Russo-Greek Church Mission at Pekin", The Journal of the Royal Geographical Society, Vol. XLII, London: William Clowes & Sons for John Murray, p. 159
- Morrison, Robert (1815–1823), A Dictionary of the Chinese Language in Three Parts, Macao: East India Company’s Press
- Morrison (1819), Dictionary, Pt. II, Vol. I, p. xvii-xviii
- Mote, Frederick (1999), Imperial China, 900-1800, Harvard University Press, p. 195
- Muto, Tomio (1939), Pan-Pacific, Pan-Pacific Union, pp. 113–114
- Pelliot, Paul (1959), Notes on Marco Polo, Vol. I, Paris: Imprimerie Nationale, §161: Ciorcia
- Perdue, Peter C (2009), China Marches West: The Qing Conquest of Central Eurasia (reprint ed.), Harvard University Press, p. 127, ISBN 0674042026, retrieved 10 March 2014
- Peterson, Willard J., ed. (2002), The Cambridge History of China, Vol. 9, Pt. 1: The Ch‘ing Dynasty to 1800, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 13, 31, ISBN 0-521-24334-3
- Rachewiltz, Igor De, ed. (1993), In the Service of the Khan: Eminent Personalities of the Early Mongol-Yüan Period (1200-1300), Volume 121 of Asiatische Forschungen, Otto Harrassowitz Verlag, p. 112, ISBN 3447033398, ISSN 0571-320X, retrieved 10 March 2014
- Ravenstein, Ernest George; Keane, Augustus Henry, eds. (1882), The Universal Geography, Vol. VII, J.S. Virtue & Co., p. 121
- Rawski, Evelyn S. (Nov 1996), "Presidential Address: Reenvisioning the Qing: The Significance of the Qing Period in Chinese History", The Journal of Asian Studies, Association for Asian Studies, 55 (4): 829–850, doi:10.2307/2646525, JSTOR 2646525
- Rawski, Evelyn S. (15 November 1998), The Last Emperors: A Social History of Qing Imperial Institutions, University of California Press, p. 43, ISBN 978-0-520-92679-0
- Reardon-Anderson, James (October 2000), "Land Use and Society in Manchuria and Inner Mongolia during the Qing Dynasty", Environmental History, Forest History Society and American Society for Environmental History, 5 (No. 4): 503–530, JSTOR 3985584
- Ross, John (1891), The Manchus, or, The Reigning Dynasty of China: Their Rise and Progress, London: Elliot Stock, p. 76
- Rossabi, Morris (1998), "The Ming and Inner Asia", in Denis C. Twitchett; Frederick W. Mote, The Cambridge History of China, Vol. 8: The Ming Dynasty, 1368–1644, Pt. 2, England: Cambridge University Press, pp. 221–71, ISBN 0521243335
- Seth, Michael J. (2006), A Concise History of Korea: From the Neolithic Period Through the Nineteenth Century, Rowman & Littlefield, p. 138, ISBN 978-0-7425-4005-7
- Seth, Michael J. (16 October 2010), A History of Korea: From Antiquity to the Present, Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, p. 144, ISBN 978-0-7425-6717-7
- Stolberg, Eva M. (2015), "Tungusic", in Steven Danver, Native Peoples of the World: An Encyclopedia of Groups, Cultures, and Contemporary Issues, Abingdon: Routledge, pp. 713–714
- Serruys, Henry (1955), Sino-J̌ürčed relations during the Yung-Lo period, 1403-1424, Volume 4 of Göttinger asiatische Forschungen, O. Harrassowitz, p. 22, ISBN 0742540057
- Williamson, Mitch (May 19, 2011), "Jurchen Jin Dynasty", Weapons and Warfare, archived from the original on 18 March 2014, retrieved 8 July 2014
- Vajda, Edward J. (2000), "Manchu (Jurchen)", East Asian Studies 210: Introduction to Nomadic Cultures, Western Washington University, retrieved 16 February 2014
- Wylie, Alexander (1855), Translation of the Ts'ing Wan K'e Mung, A Chinese Grammar of the Manchu Tartar Language, with Introductory Notes on Manchu Literature, Shanghai: London Mission Press, p. lxxvi
- Wang, Yuan-kang (6 December 2010), Harmony and War: Confucian Culture and Chinese Power Politics, Columbia University Press, p. 301, ISBN 978-0-231-52240-3
- Wei Cuiyi Wei Ts'ui-i; Karl W. Luckert (1998), Uighur Stories from along the Silk Road, University Press of America, p. 91
- Williams, Henry Smith (1904), The Historians' History of the World: Poland, The Balkans, Turkey, Minor Eastern States, China, Japan, Outlook Company, p. 272
- Wittfogel, Karl August; Fêng, Chia-shêng (March 1946), History of Chinese Society: Liao, 907-1125, Transactions of the American Philosophical Society, 36, American Philosophical Society, p. 10, ISBN 978-1-4223-7719-2
- Wylie, Alexander (1860), "On an Ancient Inscription in the Neu-chih Language", Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland, Vol. XVII, London: John W. Parker & Son, pp. 331–345


- Zhang Boquan (1984), 《金史简编》, Liaoning People's Publishing, pp. 97–98
- Zhang Feng (2008), "Traditional East Asian Structure from the Perspective of Sino-Korean Relations", International Relations Department The London School of Economics and Political Science: 29, 30, retrieved 18 April 2014,
Paper presented to ISA’s 49th Annual Convention, San Francisco, March 26–29, 2008
Further reading
- Wurm, Stephen Adolphe; Mühlhäusler, Peter; Tyron, Darrell T., eds. (1996), Atlas of Languages of Intercultural Communication in the Pacific, Asia, and the Americas, 1, International Council for Philosophy and Humanistic Studies, Walter de Gruyter, p. 828, ISBN 3110134179
External links
- Jurchen script
- (in Chinese) The Jurchen language and Script Website (Chinese Traditional Big5 code page) via Internet Archive
- The Russian news about the discovery of the Jurchen burial ground, July 2012