Hann function
The Hann function, named after the Austrian meteorologist Julius von Hann, is a discrete window function given by
or
or, in terms of the haversine function,
Spectrum
The Hann window is a linear combination of modulated rectangular windows . From Euler's formula
Due to the basic properties of the Fourier transform, its spectrum is
with the spectrum of the rectangular window
If windows are time-shifted around 0 the modulation factor vanishes and the signs in front of the 1/4 terms change to +.
Name
Hann function is the original name, in honour of von Hann; however, the erroneous "Hanning" function is also heard of on occasion, derived from the paper in which it was named, where the term "hanning a signal" was used to mean applying the Hann window to it. The confusion arose from the similar Hamming function, named after Richard Hamming.
Use
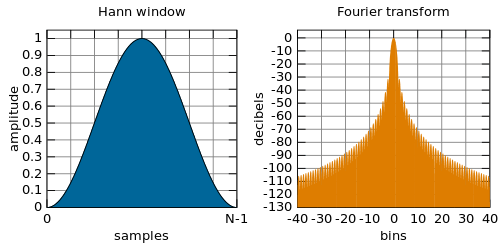
The Hann function is typically used as a window function in digital signal processing to select a subset of a series of samples in order to perform a Fourier transform or other calculations.
i.e. (using continuous version to illustrate)
The advantage of the Hann window is very low aliasing, and the tradeoff slightly is a decreased resolution (widening of the main lobe).
See also
References
- Harris, F. J. (1978). "On the use of windows for harmonic analysis with the discrete Fourier transform". Proceedings of the IEEE. 66: 51. doi:10.1109/PROC.1978.10837.
- Blackman, R. B.; Tukey, J. W. (1958). "The Measurement of Power Spectra from the Point of View of Communications Engineering - Part I". Bell System Technical Journal. 37: 185. doi:10.1002/j.1538-7305.1958.tb03874.x.
External links