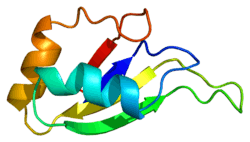HNRPD
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D0 (HNRNPD) also known as AU-rich element RNA-binding protein 1 (AUF1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HNRNPD gene.[5][6] Alternative splicing of this gene results in four transcript variants.
Function

This gene belongs to the subfamily of ubiquitously expressed heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs). The hnRNPs are nucleic acid binding proteins and they complex with heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA). The interaction sites on the RNA are frequently biased towards particular sequence motifs.[7] These proteins are associated with pre-mRNAs in the nucleus and appear to influence pre-mRNA processing and other aspects of mRNA metabolism and transport. While all of the hnRNPs are present in the nucleus, some seem to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The hnRNP proteins have distinct nucleic acid binding properties. The protein encoded by this gene has two repeats of quasi-RRM domains that bind to RNAs. It localizes to both the nucleus and the cytoplasm. This protein is implicated in the regulation of mRNA stability.[6]
Interactions
HNRPD has been shown to interact with SAFB[8] and Hsp27.[9] AUF1 also has been reported to interact with mRNAs such as Mef2c mRNA.[10]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000138668 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000000568 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Dempsey LA, Li MJ, DePace A, Bray-Ward P, Maizels N (August 1998). "The human HNRPD locus maps to 4q21 and encodes a highly conserved protein". Genomics. 49 (3): 378–384. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5237. PMID 9615222.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: HNRPD heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D (AU-rich element RNA binding protein 1, 37kDa)".
- ↑ Mazan-Mamczarz K, Kuwano Y, Zhan M, White EJ, Martindale JL, Lal A, Gorospe M (Jan 2009). "Identification of a signature motif in target mRNAs of RNA-binding protein AUF1". Nucleic Acids Research. 37 (1): 204–14. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn929. PMC 2615618. PMID 19033365.
- ↑ Arao Y, Kuriyama R, Kayama F, Kato S (August 2000). "A nuclear matrix-associated factor, SAF-B, interacts with specific isoforms of AUF1/hnRNP D". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 380 (2): 228–36. doi:10.1006/abbi.2000.1938. PMID 10933876.
- ↑ Sinsimer KS, Gratacós FM, Knapinska AM, Lu J, Krause CD, Wierzbowski AV, Maher LR, Scrudato S, Rivera YM, Gupta S, Turrin DK, De La Cruz MP, Pestka S, Brewer G (September 2008). "Chaperone Hsp27, a novel subunit of AUF1 protein complexes, functions in AU-rich element-mediated mRNA decay". Mol. Cell. Biol. 28 (17): 5223–37. doi:10.1128/MCB.00431-08. PMC 2519747. PMID 18573886.
- ↑ Panda AC, Abdelmohsen K, Yoon JH, Martindale JL, Yang X, Curtis J, Mercken EM, Chenette DM, Zhang Y, Schneider RJ, Becker KG, de Cabo R, Gorospe M (Aug 2014). "RNA-binding protein AUF1 promotes myogenesis by regulating MEF2C expression levels". Mol Cell Biol. 34 (16): 3106–19. doi:10.1128/MCB.00423-14. PMC 4135590. PMID 24891619.
Further reading
- Tay N, Chan SH, Ren EC (1992). "Identification and cloning of a novel heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C-like protein that functions as a transcriptional activator of the hepatitis B virus enhancer II". J. Virol. 66 (12): 6841–8. PMC 240284. PMID 1433497.
- Lahiri DK, Thomas JO (1986). "A cDNA clone of the hnRNP C proteins and its homology with the single-stranded DNA binding protein UP2". Nucleic Acids Res. 14 (10): 4077–4094. doi:10.1093/nar/14.10.4077. PMC 339847. PMID 3754960.
- Kajita Y, Nakayama J, Aizawa M, Ishikawa F (1995). "The UUAG-specific RNA binding protein, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D0. Common modular structure and binding properties of the 2xRBD-Gly family". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (38): 22167–75. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.38.22167. PMID 7673195.
- Zhang W, Wagner BJ, Ehrenman K, Schaefer AW, DeMaria CT, Crater D, DeHaven K, Long L, Brewer G (December 1993). "Purification, characterization, and cDNA cloning of an AU-rich element RNA-binding protein, AUF1". Mol. Cell. Biol. 13 (12): 7652–65. PMC 364837. PMID 8246982.
- Wagner BJ, Long L, Rao PN, Pettenati MJ, Brewer G (June 1996). "Localization and physical mapping of genes encoding the A+U-rich element RNA-binding protein AUF1 to human chromosomes 4 and X". Genomics. 34 (2): 219–22. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0269. PMID 8661052.
- Kiledjian M, DeMaria CT, Brewer G, Novick K (1997). "Identification of AUF1 (heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D) as a component of the alpha-globin mRNA stability complex". Mol. Cell. Biol. 17 (8): 4870–6. PMC 232339. PMID 9234743.
- Wagner BJ, DeMaria CT, Sun Y, Wilson GM, Brewer G (March 1998). "Structure and genomic organization of the human AUF1 gene: alternative pre-mRNA splicing generates four protein isoforms". Genomics. 48 (2): 195–202. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.5142. PMID 9521873.
- Siomi MC, Fromont M, Rain JC, Wan L, Wang F, Legrain P, Dreyfuss G (July 1998). "Functional conservation of the transportin nuclear import pathway in divergent organisms". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (7): 4141–8. PMC 108998. PMID 9632798.
- Tolnay M, Vereshchagina LA, Tsokos GC (1999). "Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D0B is a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein". Biochem. J. 338 (2): 417–25. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3380417. PMC 1220068. PMID 10024518.
- Nagata T, Kurihara Y, Matsuda G, Saeki J, Kohno T, Yanagida Y, Ishikawa F, Uesugi S, Katahira M (March 1999). "Structure and interactions with RNA of the N-terminal UUAG-specific RNA-binding domain of hnRNP D0". J. Mol. Biol. 287 (2): 221–37. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1999.2616. PMID 10080887.
- Laroia G, Cuesta R, Brewer G, Schneider RJ (1999). "Control of mRNA decay by heat shock-ubiquitin-proteasome pathway". Science. 284 (5413): 499–502. doi:10.1126/science.284.5413.499. PMID 10205060.
- Blaxall BC, Dwyer-Nield LD, Bauer AK, Bohlmeyer TJ, Malkinson AM, Port JD (June 2000). "Differential expression and localization of the mRNA binding proteins, AU-rich element mRNA binding protein (AUF1) and Hu antigen R (HuR), in neoplastic lung tissue". Mol. Carcinog. 28 (2): 76–83. doi:10.1002/1098-2744(200006)28:2<76::AID-MC3>3.0.CO;2-0. PMID 10900464.
- Moraes KC, Quaresma AJ, Maehnss K, Kobarg J (January 2003). "Identification and characterization of proteins that selectively interact with isoforms of the mRNA binding protein AUF1 (hnRNP D)". Biol. Chem. 384 (1): 25–37. doi:10.1515/BC.2003.004. PMID 12674497.
- Arao Y, Kuriyama R, Kayama F, Kato S (2000). "A nuclear matrix-associated factor, SAF-B, interacts with specific isoforms of AUF1/hnRNP D". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 380 (2): 228–236. doi:10.1006/abbi.2000.1938. PMID 10933876.
- Grosset C, Chen CY, Xu N, Sonenberg N, Jacquemin-Sablon H, Shyu AB (September 2000). "A mechanism for translationally coupled mRNA turnover: interaction between the poly(A) tail and a c-fos RNA coding determinant via a protein complex". Cell. 103 (1): 29–40. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00102-1. PMID 11051545.
- Katahira M, Miyanoiri Y, Enokizono Y, Matsuda G, Nagata T, Ishikawa F, Uesugi S (August 2001). "Structure of the C-terminal RNA-binding domain of hnRNP D0 (AUF1), its interactions with RNA and DNA, and change in backbone dynamics upon complex formation with DNA". J. Mol. Biol. 311 (5): 973–88. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4862. PMID 11531333.
- Lapucci A, Donnini M, Papucci L, Witort E, Tempestini A, Bevilacqua A, Nicolin A, Brewer G, Schiavone N, Capaccioli S (May 2002). "AUF1 Is a bcl-2 A + U-rich element-binding protein involved in bcl-2 mRNA destabilization during apoptosis". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (18): 16139–46. doi:10.1074/jbc.M201377200. PMID 11856759.
- Tolnay M, Juang YT, Tsokos GC (2002). "Protein kinase A enhances, whereas glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta inhibits, the activity of the exon 2-encoded transactivator domain of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D in a hierarchical fashion". Biochem. J. 363 (Pt 1): 127–36. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3630127. PMC 1222459. PMID 11903055.
- Pioli PA, Hamilton BJ, Connolly JE, Brewer G, Rigby WF (September 2002). "Lactate dehydrogenase is an AU-rich element-binding protein that directly interacts with AUF1". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (38): 35738–45. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204002200. PMID 12107167.
- Shchors K, Yehiely F, Kular RK, Kotlo KU, Brewer G, Deiss LP (December 2002). "Cell death inhibiting RNA (CDIR) derived from a 3'-untranslated region binds AUF1 and heat shock protein 27". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (49): 47061–72. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202272200. PMID 12356764.