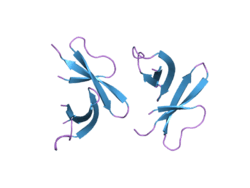DEFA4
Defensin, alpha 4 (DEFA4), also known as neutrophil defensin 4 or HNP4, is a human defensin peptide that is encoded by the DEFA4 gene.[3][4] HNP4 is expressed in the granules of the neutrophil where it defends the host against bacteria[5] and viruses.[6]
Function
Defensins are a peptide family of cytotoxic microbicides involved in innate immunity.[7] Members of the defensin family are distinguished by a conserved six-cysteine motif. Several human alpha defensin genes including HNP4 are clustered on chromosome 8. DEFA4 differs from other defensin genes by an extra 83-base segment that is apparently the result of a recent duplication within the coding region. HNP4 inhibits corticotropin-stimulated corticosterone production.[3]
References
- 1 2 3 ENSG00000285318 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000164821, ENSG00000285318 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: DEFA4; defensin, alpha 4, corticostatin (Homo sapiens)".
- ↑ Wu Z, Ericksen B, Tucker K, et al. (2004). "Synthesis and characterization of human alpha-defensins 4-6". J Pept Res. 64 (3): 118–25. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3011.2004.00179.x. PMID 15317502.
- ↑ Ericksen B, Wu Z, Lu W, Lehrer RI (2005). "Antibacterial Activity and Specificity of the Six Human α-Defensins". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 49 (1): 269–75. doi:10.1128/AAC.49.1.269-275.2005. PMC 538877. PMID 15616305.
- ↑ Wu Z, Cocchi F, Gentles D, et al. (3 January 2005). "Human neutrophil alpha-defensin 4 inhibits HIV-1 infection in vitro". FEBS Lett. 579 (1): 162–6. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.11.062. PMID 15620707.
- ↑ T Ganz; M E Selsted; D Szklarek; et al. (1985). "Defensins. Natural peptide antibiotics of human neutrophils". J Clin Invest. 76 (4): 1427–1435. doi:10.1172/JCI112120. PMC 424093. PMID 2997278.
Further reading
- Szyk A, Wu Z, Tucker K, et al. (2006). "Crystal structures of human α-defensins HNP4, HD5, and HD6". Protein Sci. 15 (12): 2749–60. doi:10.1110/ps.062336606. PMC 2242434. PMID 17088326.
- Mallow EB, Harris A, Salzman N, et al. (1996). "Human enteric defensins. Gene structure and developmental expression". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (8): 4038–45. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.8.4038. PMID 8626737.
- Bevins CL, Jones DE, Dutra A, et al. (1996). "Human enteric defensin genes: chromosomal map position and a model for possible evolutionary relationships". Genomics. 31 (1): 95–106. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0014. PMID 8808285.
- Gabay JE, Scott RW, Campanelli D, et al. (1989). "Antibiotic proteins of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86 (14): 5610–4. doi:10.1073/pnas.86.14.5610. PMC 297672. PMID 2501794.
- Davila S, Froeling FE, Tan A, et al. (2010). "New genetic associations detected in a host response study to hepatitis B vaccine". Genes Immun. 11 (3): 232–8. doi:10.1038/gene.2010.1. PMID 20237496.
- Kim E, Lee JE, Namkung JH, et al. (2009). "Single nucleotide polymorphisms and the haplotype in the DEFB1 gene are associated with atopic dermatitis in a Korean population". J. Dermatol. Sci. 54 (1): 25–30. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2008.12.005. PMID 19135873.
- Milanese M, Segat L, Arraes LC, et al. (2009). "Copy number variation of defensin genes and HIV infection in Brazilian children". J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 50 (3): 331–3. doi:10.1097/QAI.0b013e3181945f39. PMID 19194307.
- Palfree RG, Sadro LC, Solomon S (1993). "The gene encoding the human corticostatin HP-4 precursor contains a recent 86-base duplication and is located on chromosome 8". Mol. Endocrinol. 7 (2): 199–205. doi:10.1210/me.7.2.199. PMID 8469233.
- Furci L, Sironi F, Tolazzi M, et al. (2007). "Alpha-defensins block the early steps of HIV-1 infection: interference with the binding of gp120 to CD4". Blood. 109 (7): 2928–35. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-05-024489. PMID 17132727.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2002). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Wilde CG, Griffith JE, Marra MN, et al. (1989). "Purification and characterization of human neutrophil peptide 4, a novel member of the defensin family". J. Biol. Chem. 264 (19): 11200–3. PMID 2500436.
- Singh A, Bateman A, Zhu QZ, et al. (1988). "Structure of a novel human granulocyte peptide with anti-ACTH activity". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 155 (1): 524–9. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(88)81118-5. PMID 2843187.
- Konishi K, Gibson KF, Lindell KO, et al. (2009). "Gene Expression Profiles of Acute Exacerbations of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis". Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 180 (2): 167–75. doi:10.1164/rccm.200810-1596OC. PMC 2714820. PMID 19363140.
- Emonts M, Vermont CL, Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, et al. (2009). "Polymorphisms in PARP, IL1B, IL4, IL10, C1INH, DEFB1 and DEFA4 in meningococcal disease in three populations". Shock (Augusta, Ga.). 34 (1): 17–22. doi:10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181ce2c7d. PMID 20016407.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.