Gulf of Oman
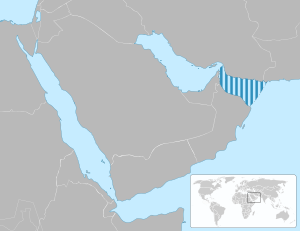


The Gulf of Oman or Sea of Oman (Arabic: خَلِيج عُمَان khalīj ʿumān; Persian: دریای عمان daryâ-ye omân) is a strait (and not an actual gulf) that connects the Arabian Sea with the Strait of Hormuz, which then runs to the Persian Gulf. It borders Iran and Pakistan on the north, Oman on the south, and the United Arab Emirates on the west.
Extent
The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the Gulf of Oman as follows:[1]
On the Northwest: A line joining Ràs Limah (25°57'N) on the coast of Arabia and Ràs al Kuh (25°48'N) on the coast of Iran (Persia)
On the Southeast: The Northern limit of the Arabian Sea [A line joining Ràs al Hadd, East point of Arabia (22°32'N) and Ràs Jiyùni (61°43'E) on the coast of Pakistan].
Bordering countries
Ecology
In 2018, scientists confirmed the Gulf of Oman contains one of the world's largest marine dead zones, where the ocean contains little or no oxygen and marine wildlife can not exist. The dead zone encompasses nearly the entire 63,700-square-mile Gulf of Oman. The cause is a combination of increased ocean warming, and increased runoff of nitrogen and phosphorus from fertilizers.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ "Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd edition" (PDF). International Hydrographic Organization. 1953. Retrieved 7 February 2010.
- ↑ "Scientists Confirm Florida-Sized Dead Zone in the Gulf of Oman". Yale Environment 360. April 30, 2018. Retrieved April 30, 2018.
Further reading
- "The Book of Duarte Barbosa" by Duarte Barbosa, Mansel Longworth Dames. 1989. p. 79. ISBN 81-206-0451-2
- "The Natural History of Pliny". by Pliny, Henry Thomas Riley, John Bostock. 1855. p. 117
- "The Countries and Tribes of the Persian Gulf" by Samuel Barrett Miles - 1966. p. 148
- "The Life & Strange Surprising Adventures of Robinson Crusoe of York, Mariner". by Daniel Defoe. 1895. p. 279
- "The Outline of History: Being a Plain History of Life and Mankind". by Herbert George Well. 1920. p. 379.
- "The New Schaff-Herzog Encyclopedia of Religious Knowledge" by Johann Jakob Herzog, Philip Schaff, Albert Hauck. 1910. p. 242