Glycosyl
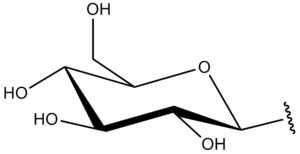
A glycosyl group is a univalent free radical or substituent structure obtained by removing the hemiacetal hydroxyl group from the cyclic form of a monosaccharide and, by extension, of a lower oligosaccharide. Glycosyl also reacts with inorganic acids, such as phosphoric acid, forming an ester such as glucose 1-phosphate.[1]
Examples
In cellulose, glycosyl groups link together 1,4-beta-D-glucosyl units to form chains of (1,4-beta-D-glucosyl)n. Other examples include ribityl in 6,7-Dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine, and glycosylamines.
Alternative substituent groups
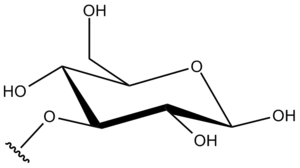
Instead of the hemiacetal hydroxyl group, a hydrogen atom can be removed to form a substituent, for example the hydrogen from the C3 hydroxyl of a glucose molecule. Then the substituent is called D-glucopyranos-3-O-yl as it appears in the name of the drug Mifamurtide.
See also
References
- ↑ Davies, Gideon; Henrissat, Bernard (September 1995). "Structures and mechanisms of glycosyl hydrolases". Structure. 3 (9): 853–859. doi:10.1016/S0969-2126(01)00220-9.