Frost Belt
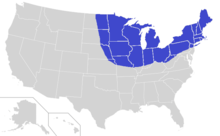
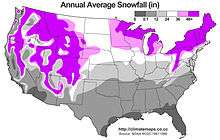
The Frost Belt is a region of the United States generally considered to most of the northern United States from the intermountain West, to the Midwest, Great Lakes, and New England. The region is known for its cold, frost-producing winters and heavy snowfall.
For many years, the Frost Belt was the center of American economic activity and the most populous part of the United States. However, a shift away from domestic manufacturing beginning in the 1970s dealt a heavy blow to the region's economy. For most of the latter 20th century, the Frost Belt's population declined as Americans and people seeking to retire relocated to the warm climates of the sun belt across the southern United States. As the population of the sun belt area increased, economic and investment opportunities followed as well, and much of the frost belt was no longer the leading economic region of the United States. Census results for the past several decades have indicated a population shift from the Frost Belt to the Sun Belt.[1][2]
See also
References
- ↑ Deering, Joseph A. (March 2004). "Janet Rothenberg Pack, Growth and Convergence in Metropolitan America". Journal of Sociology and Social Welfare. Retrieved 2011-02-28.
- ↑ Dirk Johnson (1999-02-06). "In the Frost Belt, a Place in the Sun". The New York Times. Retrieved 2009-02-08.