Equity co-investment
An equity co-investment (or co-investment) is a minority investment, made directly into an operating company, alongside a financial sponsor or other private equity investor, in a leveraged buyout, recapitalization or growth capital transaction. In certain circumstances, venture capital firms may also seek co-investors.
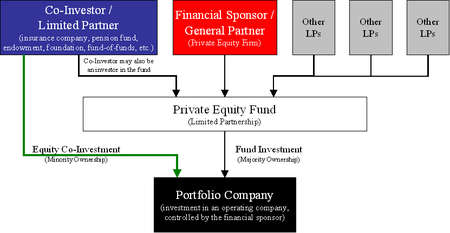
Private equity firms seek co-investors for several reasons. Most important of these is that co-investments allow a manager to make larger investments without either dedicating too much of the fund's capital to a single transaction (i.e., exposure issues) or sharing the deal with competing private equity firms. Co-investors bring a friendly source of capital.
Typically, co-investors are existing limited partners in an investment fund managed by the lead financial sponsor in a transaction. Unlike the investment fund however, co-investments are made outside the existing fund and as such co-investors rarely pay management fees or carried interest on an individual investment. Co-investments are typically passive, non-controlling investments, as the private equity firm or firms involved will exercise control and perform monitoring functions. For large private equity fund of funds and other investors, co-investments are a means of increasing exposure to attractive transactions and making investments that have a higher return potential because of the lower economics paid to the general partner. As a result, many private equity firms offer co-investments to their largest and most important investors as an incentive to invest in future funds.
See also
References
- CalPERS - Private Equity Industry Dictionary
- AltAssets Glossary
- AltAssets: The direct route
- Co-investments in funds of funds and separate accounts
