Anthony's poison arrow frog
| Anthony's poison arrow frog | |
|---|---|
| Epipedobates anthonyi, in the Leipzig Botanical Garden, Germany | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Dendrobatidae |
| Genus: | Epipedobates |
| Species: | E. anthonyi |
| Binomial name | |
| Epipedobates anthonyi (Noble, 1921) | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
|
Phyllobates anthonyi Noble, 1921 | |
Anthony's poison arrow frog (Epipedobates anthonyi ) is a species of poison dart frog in the family Dendrobatidae. The species is endemic to Ecuador and Peru.
Etymology
The specific name, anthonyi, is in honor of American mammalogist Harold Elmer Anthony (1890–1970), who was Curator of Mammals at the American Museum of Natural History.[3]
Description
Anthony's poison arrow frog has a snout-to-vent length of about 19 to 26 mm (0.7 to 1.0 in). The hind legs are short and robust. The dorsal surface is usually dark red or brown and there are several yellowish-white oblique stripes and a central longitudinal stripe.[4]
Geographic range
Anthony's poison arrow frog is known only from a number of locations in southwestern Ecuador and northwestern Peru at heights of between 153 and 1,769 m (502 and 5,804 ft) above sea level.[1]
Habitat
The natural habitat of E. anthonyi is the leaf litter on the floor of tropical dry forests, especially near streams.[1]
Biology
Anthony's poison arrow frog is diurnal and terrestrial. Males are territorial. A clutch of 15 to 40 eggs is laid on the ground among leaf litter, and the male guards them till they hatch in about two weeks. He then carries the tadpoles on his back to a suitable water body where they develop (through metamorphosis) into frogs in about sixty days.[4]
Status
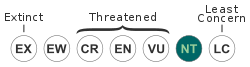
Anthony's poison arrow frog is listed as "Near Threatened" by the IUCN. Its population seems stable but it has a limited range, estimated to be less than 20,000 square kilometres (7,700 sq mi), and its habitat is being degraded by pollution from agrochemicals. It is also collected for medicinal use.[1]
References
- 1 2 3 4 Coloma, Luis A.; Ron, Santiago; Lötters, Stefan; Venegas, Pablo (2010). "Epipedobates anthonyi ". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. IUCN. 2010: e.T55213A11268789. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2010-2.RLTS.T55213A11268789.en. Retrieved 3 January 2018.
- ↑ Frost, Darrel R. (2017). "Epipedobates anthonyi (Noble, 1921)". Amphibian Species of the World: an Online Reference. Version 6.0. American Museum of Natural History. Retrieved 24 August 2017.
- ↑ Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2013). The Eponym Dictionary of Amphibians. Exeter, England: Pelagic Publishing Ltd. xiii + 262 pp. ISBN 978-1-907807-41-1.
- 1 2 Maxon, Jeni (2008-12-09). "Epipedobates anthonyi ". AmphibiaWeb. Retrieved 2013-12-21.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Epipedobates anthonyi. |
Further reading
- Noble GK (1921). "Five new species of Salientia from South America". American Museum Novitates (29): 1-7. (Phyllobates anthonyi, new species, pp. 5–6, Figure 5).