Further reading
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Behrends U, Jandl T, Golbeck A, et al. (2002). "Novel products of the HUD, HUC, NNP-1 and alpha-internexin genes identified by autologous antibody screening of a pediatric neuroblastoma library". Int. J. Cancer. 100 (6): 669–77. doi:10.1002/ijc.10550. PMID 12209604.
- Park S, Myszka DG, Yu M, et al. (2000). "HuD RNA recognition motifs play distinct roles in the formation of a stable complex with AU-rich RNA". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (13): 4765–72. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.13.4765-4772.2000. PMC 85909. PMID 10848602.
- Sakai K, Kitagawa Y, Hirose G (1999). "Analysis of the RNA recognition motifs of human neuronal ELAV-like proteins in binding to a cytokine mRNA". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 256 (2): 263–8. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.0282. PMID 10079173.
- Sakai K, Gofuku M, Kitagawa Y, et al. (1994). "A hippocampal protein associated with paraneoplastic neurologic syndrome and small cell lung carcinoma". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 199 (3): 1200–8. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1994.1358. PMID 7511893.
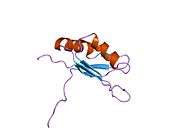
PDB gallery |
|---|
1d8z: SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE FIRST RNA-BINDING DOMAIN (RBD1) OF HU ANTIGEN C (HUC) 1d9a: SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE SECOND RNA-BINDING DOMAIN (RBD2) OF HU ANTIGEN C (HUC) 1fnx: SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE HUC RBD1-RBD2 COMPLEXED WITH THE AU-RICH ELEMENT 1fxl: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUD AND AU-RICH ELEMENT OF THE C-FOS RNA 1g2e: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUD AND AU-RICH ELEMENT OF THE TUMOR NECROSIS FACTOR ALPHA RNA |