Dynasties in Chinese history
 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANCIENT | |||||||
| Neolithic c. 8500 – c. 2070 BCE | |||||||
| Xia dynasty c. 2070 – c. 1600 BCE | |||||||
| Shang dynasty c. 1600 – c. 1046 BCE | |||||||
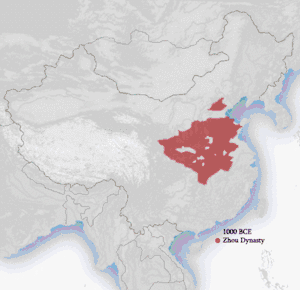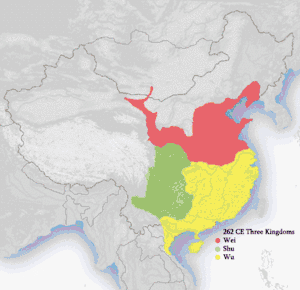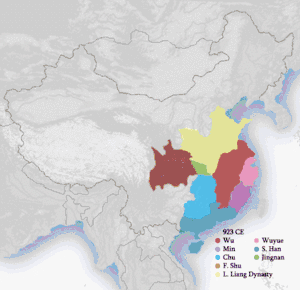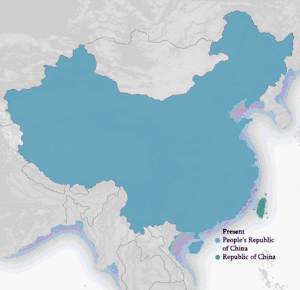
| Zhou dynasty c. 1046 – 256 BCE | |||||||
| Western Zhou | |||||||
| Eastern Zhou | |||||||
| Spring and Autumn | |||||||
| Warring States | |||||||
| IMPERIAL | |||||||
| Qin dynasty 221–206 BCE | |||||||
| Han dynasty 206 BCE – 220 CE | |||||||
| Western Han | |||||||
| Xin dynasty | |||||||
| Eastern Han | |||||||
| Three Kingdoms 220–280 | |||||||
| Wei, Shu and Wu | |||||||
| Jin dynasty 265–420 | |||||||
| Western Jin | |||||||
| Eastern Jin | Sixteen Kingdoms | ||||||
| Northern and Southern dynasties 420–589 | |||||||
| Sui dynasty 581–618 | |||||||
| Tang dynasty 618–907 | |||||||
| (Second Zhou dynasty 690–705) | |||||||
| Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms 907–960 |
Liao dynasty 907–1125 | ||||||
| Song dynasty 960–1279 |
|||||||
| Northern Song | Western Xia | ||||||
| Southern Song | Jin | ||||||
| Yuan dynasty 1271–1368 | |||||||
| Ming dynasty 1368–1644 | |||||||
| Qing dynasty 1644–1912 | |||||||
| MODERN | |||||||
| Republic of China 1912–1949 | |||||||
| People's Republic of China 1949–present | |||||||
The following is a chronology of the dynasties in Chinese History since 2000 years before Common Era.
Background
One might incorrectly infer from viewing historical timelines that transitions between dynasties occur abruptly and smoothly. Rather, dynasties were often established before the complete overthrow of an existing reign, or continued for a time after they had been effectively defeated. For example, the conventional date 1645 marks the year in which the Qing dynasty armies overthrew the preceding Ming dynasty, according to the dynastic cycle of China. However, the Qing dynasty was established in 1636 (or even 1616, albeit under a different name), while the last Ming dynasty pretender was not deposed until 1663. This change of ruling houses was a messy and prolonged affair, and the Qing took almost twenty years to extend their control over the whole of China. It is therefore inaccurate to assume China changed suddenly and all at once in the year 1645.
In addition, China was divided for short periods of its history, with different regions being ruled by different groups. During such periods, there was not any single dynasty ruling a unified China. As a case in point, there is much dispute about times in and after the Western Zhou period. In the Chinese historiographical tradition, each new dynasty would write the history of the dynasty which preceded it. This cycle was disrupted, however, when the Xinhai Revolution overthrew the Qing dynasty in favor of a republic. Even an attempt by Republicans to draft the history of the Qing was disrupted by the Chinese Civil War, which resulted in the division of China into the People's Republic of China on mainland China and the Republic of China on Taiwan.[1]
Dynasties of China
| Dynasty | Rulers | Ruling house or clan of houses | From | To | Term | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Chinese | Pinyin | Meaning | |||||
| Feudal dynasties | ||||||||
| Xia dynasty | 夏 | Xià | Tribe name | (list) | Sì (姒) | 2070 BCE | 1600 BCE | 470 years |
| Shang dynasty | 商 | Shāng | Toponym | (list) | Zǐ (子) | 1600 BCE | 1046 BCE | 554 years |
| Western Zhou dynasty | 西周 | Xī Zhōu | Toponym | (list) | Jī (姬) | 1046 BCE | 771 BCE | 275 years |
| Eastern Zhou dynasty | 東周 / 东周 | Dōng Zhōu | Toponym | (list) | Jī (姬) | 770 BCE | 256 BCE | 514 years |
| Spring and Autumn period | 春秋 | Chūn Qiū | As English | 770 BCE | 476 BCE | 294 years | ||
| Warring States period | 戰國 / 战国 | Zhàn Guó | As English | 476 BCE | 221 BCE | 255 years | ||
| Imperial dynasties | ||||||||
| Qin dynasty | 秦 | Qín | Toponym | (list) | Yíng (嬴) | 221 BCE | 207 BCE | 14 years |
| Western Han dynasty | 西漢 / 西汉 | Xī Hàn | Toponym | (list) | Liú (劉) | 202 BCE | CE 8 | 209 years |
| Xin dynasty | 新 | Xīn | "New" | (list) | Wáng (王) | CE 9 | CE 23 | 14 years |
| Eastern Han dynasty | 東漢 / 东汉 | Dōng Hàn | Toponym | (list) | Liú (劉) | CE 25 | CE 220 | 195 years |
| Three Kingdoms | 三國 / 三国 | Sān Guó | As English | (list) | Cáo (曹) Liú (劉 / 刘) Sūn (孫 / 孙) |
CE 220 | CE 280 | 60 years |
| Western Jin dynasty | 西晉 / 西晋 | Xī Jìn | Toponym | (list) | Sīmǎ (司馬) | CE 266 | CE 316 | 50 years |
| Eastern Jin dynasty | 東晉 / 东晋 | Dōng Jìn | Toponym | (list) | Sīmǎ (司馬) | CE 317 | CE 420 | 103 years |
| Southern and Northern dynasties | 南北朝 | Nán Běi Cháo | As English | (list) | various | CE 420 | CE 589 | 169 years |
| Sui dynasty | 隋 | Suí | Ducal title (随 homophone) |
(list) | Yáng (楊) | CE 581 | CE 618 | 37 years |
| Tang dynasty | 唐 | Táng | Ducal title | (list) | Lǐ (李) | CE 618 | CE 907 | 289 years |
| Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms | 五代十國
/ 五代十国 |
Wǔ Dài Shí Guó | As English | (list) | various | CE 907 | CE 960 | 53 years |
| Northern Song dynasty | 北宋 | Běi Sòng | Toponym | (list) | Zhào (趙) | CE 960 | CE 1127 | 167 years |
| Southern Song dynasty | 南宋 | Nán Sòng | Toponym | (list) | Zhào (趙) | CE 1127 | CE 1279 | 152 years |
| Liao dynasty | 遼 / 辽 | Liáo | "Vast" or "Iron" (Khitan homophone) |
(list) | Yelü ( |
CE 907 | CE 1125 | 218 years |
| Jin dynasty | 金 | Jīn | "Gold" | (list) | Wanggiya ( |
CE 1115 | CE 1234 | 119 years |
| Western Xia | 西夏 | Xī Xià | Toponym | (list) | Li (𘝾; 李) | CE 1038 | CE 1227 | 189 years |
| Western Liao | 西遼 / 西辽 | Xī Liáo | "Vast" or "Iron" (Khitan homophone) |
(list) | Yelü ( |
CE 1124 | CE 1218 | 94 years |
| Yuan dynasty | 元 | Yuán | "Great" or "Primacy" | (list) | Borjigin (ᠪᠣᠷᠵᠢᠭᠢᠨ; 孛兒只斤) |
CE 1271 | CE 1368 | 97 years |
| Ming dynasty | 明 | Míng | "Bright" | (list) | Zhū (朱) | CE 1368 | CE 1644 | 276 years |
| Qing dynasty | 清 | Qīng | "Pure" | (list) | Aisin Gioro (ᠠᡳᠰᡳᠨ ᡤᡳᠣᡵᠣ; 愛新覺羅) |
CE 1636 | CE 1912 | 276 years |
| Modern China | ||||||||
| Republic of China | 中華民國
/ 中华民国 |
Zhōnghuá Mínguó | "Chinese Republic" | (list) | various | CE 1912 | until CE 1949 controlled Chinese mainland, after CE 1949 de facto only controls Taiwan | controlled Chinese mainland for 37 years, de facto only controls Taiwan for 69 years |
| People's Republic of China | 中華人民共和國 /
中华人民共和国 |
Zhōnghuá Rénmín Gònghéguó | "Chinese People's Republic" | (list) | various | CE 1949 | present | 69 years |
See also
- History of China
- Conquest dynasties
- Timeline of Chinese history
- List of Chinese monarchs
- List of recipients of tribute from China
- List of tributaries of Imperial China
- Xia–Shang–Zhou Chronology Project
- Dynastic cycle
- Republic of China (1912-1949)
- People's Republic of China
- Yuan Shikai – claimed to be emperor of China from December 1915 to March 1916 as the Hongxian Emperor.
References
Citations
- ↑ "Chiang Kai-shek and retrocession". Taiwan: China Post. November 5, 2012. p. 2. Retrieved December 2, 2012.
Sources
- China Handbook Editorial Committee, China Handbook Series: History (trans., Dun J. Li), Beijing, 1982, 188–89; and Shao Chang Lee, "China Cultural Development" (wall chart), East Lansing, 1984.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dynasties of China. |
- Columbia University. Dynasties song
