Drum memory

| Computer memory types |
|---|
| Volatile |
| RAM |
| Historical |
|
| Non-volatile |
| ROM |
| NVRAM |
| Early stage NVRAM |
| Magnetic |
| Optical |
| In development |
| Historical |
|
Drum memory was a magnetic data storage device invented by Gustav Tauschek in 1932 in Austria.[1][2] Drums were widely used in the 1950s and into the 1960s as computer memory.
For many early computers, drum memory formed the main working memory of the computer. It was so common that these computers were often referred to as drum machines.[3] Some drum memories were also used as secondary storage.[4]
Drums were displaced as primary computer memory by magnetic core memory which was a better balance of size, speed, cost, reliability and potential for further improvements.[5] Similarly, drums were replaced by hard disk drives for secondary storage, which were also less expensive and denser. The manufacture of drums ceased in the 1970s.
Design
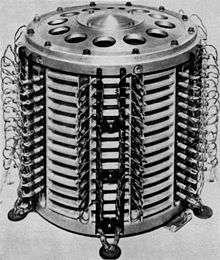
A drum memory contained a large metal cylinder, coated on the outside surface with a ferromagnetic recording material. It could be considered the precursor to the hard disk drive (HDD), but in the form of a drum rather than a flat disk. In most designs, one or more rows of fixed read-write heads ran along the long axis of the drum, one for each track. The drum's controller simply selected the proper head and waited for the data to appear under it as the drum turned (rotational latency). Not all drum units were designed with each track having its own head. Some, such as the English Electric DEUCE drum and the Univac FASTRAND had multiple heads moving a short distance on the drum in contrast to modern HDDs, which have one head per platter surface.
The performance of a drum with one head per track is determined almost entirely by the rotational latency, whereas in an HDD its performance includes a rotational latency delay plus the time to position the head over the desired track (seek time). In the era when drums were used as main working memory, programmers often did optimum programming—the programmer[NB 1] positioned code on the drum in such a way as to reduce the amount of time needed for the next instruction to rotate into place under the head. They did this by timing how long it would take after loading an instruction for the computer to be ready to read the next one, then placing that instruction on the drum so that it would arrive under a head just in time. This method of timing-compensation, called the "skip factor" or "interleaving" (interleaving in disk storage), was used for many years in storage memory controllers.
Use and legacy
Tauschek's original drum memory (1932) had a capacity of about 500,000 bits (62.5 kilobytes).[2]
One of the earliest functioning computers to employ drum memory was the Atanasoff–Berry computer (1942). It stored 3000 bits; however, it employed capacitance rather than magnetism to store the information. The outer surface of the drum was lined with electrical contacts leading to capacitors contained within.
Magnetic drums were developed for the US Navy during WW II with the work continuing at Engineering Research Associates (ERA) in 1946 and 1947.[7] An experimental study was completed at ERA and reported to the Navy on June 19, 1947.[7] Other early drum storage device development occurred at Birkbeck College[8] (University of London), Harvard University,[7] IBM[7] and the University of Manchester.[7] An ERA drum was the internal memory for the Atlas 1 computer delivered to the US Navy in October 1950.[7] Thru mergers ERA became a division of UNIVAC shipping the Series 1100 drum as a part of the UNIVAC File Computer in 1956; each drum stored 180,000 characters.[7]
The first mass-produced computer, the IBM 650, had about 8.5 kilobytes of drum memory (later doubled to about 17 kilobytes in the Model 4).
As late as 1980, PDP-11/45 machines using magnetic core main memory and drums for swapping were still in use at many of the original UNIX sites.
In modern-day BSD Unix and its descendants, /dev/drum is the name of the default virtual memory (swap) device, deriving from the use of drum secondary-storage devices as backup storage for pages in virtual memory.[9]
Drum memory is referenced in The Story of Mel, in which the skilled programmer Mel optimizes programs written for a drum memory computer (the RPC 4000) by taking advantage of the time to process an instruction and the time for the drum to rotate so that the next instruction or data can be read, or optimizing in the opposite direction when the program should wait before proceeding.
Magnetic drum memory units were used in the Minuteman ICBM launch control centers from the beginning in the early 1960s until the REACT upgrades in the mid-90's.
See also
Notes
References
- ↑ US Patent 2,080,100 Gustav Tauschek, Priority date August 2, 1932, subsequent filed as German Patent DE643803, "Elektromagnetischer Speicher für Zahlen und andere Angaben, besonders für Buchführungseinrichtungen" (Electromagnetic memory for numbers and other information, especially for accounting institutions)
- 1 2 Universität Klagenfurt (ed.). "Magnetic drum". Virtual Exhibitions in Informatics. Retrieved 2011-08-21.
- ↑ Datamation, September 1967, p.25, "For Bendix and Ramo-Wooldridge, the G-20 and RW-400 were parallel core machines rather than serial drum machines of the type already in their product lines."
- ↑ e.g., IBM 2301 Drum Storage
- ↑ Matick, Richard (1977). Computer Storage Systems & Technology. Wiley. p. 15.
- ↑ SOAP II - Symbolic Optimal Assembly Program for the IBM 650 Data Processing System (PDF), IBM, 24-4000-0
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Eric D. Daniel; C. Denis Mee; Mark H. Clark (1998). Magnetic Recording: The First 100 Years. Wiley-IEEE. ISBN 0-7803-4709-9.
- ↑ Campbell-Kelly, Martin (April 1982). "The Development of Computer Programming in Britain (1945 to 1955)". IEEE Annals of the History of Computing. 4 (2): 121–139. doi:10.1109/MAHC.1982.10016.
- ↑ "FreeBSD drum(4) manpage". Retrieved 2013-01-27.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Drum memory. |
- The Story of Mel: the classic story about one programmer's drum machine hand-coding antics: Mel Kaye.
- Librascope LGP-30: The drum memory computer referenced in the above story, also referenced on Librascope LGP-30.
- Librascope RPC-4000: Another drum memory computer referenced in the above story
- Oral history interview with Dean Babcock