Cortex (botany)
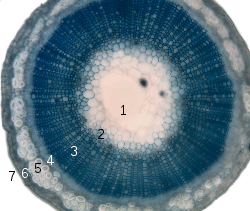
Cross-section of a flax plant stem:
1. Pith
2. Protoxylem
3. Xylem I
4. Phloem I
5. Sclerenchyma (bast fibre)
6. Cortex
7. Epidermis
1. Pith
2. Protoxylem
3. Xylem I
4. Phloem I
5. Sclerenchyma (bast fibre)
6. Cortex
7. Epidermis
A cortex is the outermost layer of a stem or root in a plant.
In botany, the cortex is the outermost layer of the stem or root of a plant, bounded on the outside by the epidermis and on the inside by the endodermis. In plants, it is composed mostly of differentiated cells, usually large thin-walled parenchyma cells of the ground tissue system. The outer cortical cells often acquire irregularly thickened cell walls, and are called collenchyma cells. Some of the outer cortical cells may contain chloroplasts. It is responsible for the transportation of materials into the central cylinder of the root through diffusion and may also be used for food storage in the form of starch.[1]
See also
References
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.