Central Canada
| Central Canada | |
| Region | |
| Country | Canada |
|---|---|
| Provinces | Ontario, Quebec |
| Area | 2,265,154 km2 (874,581 sq mi) [1] |
| Population | 21,612,855 (2016) [1] |
| Density | 10/km2 (26/sq mi) |
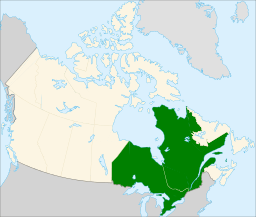 Map of Central Canada, defined politically | |
Central Canada (sometimes the Central provinces) is a region consisting of Canada's two largest and most populous provinces: Ontario and Quebec.[2] Geographically, they are not at the centre of the country but instead toward the east. Due to their high populations, Ontario and Quebec have traditionally held a significant amount of political power in Canada, leading to some amount of resentment from other regions of the country. Before Confederation, the term "Canada" specifically referred to Central Canada. Today, the term "Central Canada" is less often used than the names of the individual provinces. This has led to a sense of Western alienation.
Geography
The longitudinal centre of Canada passes just east of Winnipeg, Manitoba; the geographic centre of Canada is located near Baker Lake, Nunavut.
Before Confederation, the region known as Canada was what is now called Central Canada. Southern Ontario was once called Upper Canada and later Canada West, and southern Quebec Lower Canada and later Canada East. Both were made part of the United Province of Canada in 1841.[3]
Population
Combined, the two provinces have approximately 20 million inhabitants which represents 62% of Canada's population. They are represented in the House of Commons of Canada by 199 Members of Parliament (Ontario: 121, Quebec: 78) out of a total of 338. The southern portions of the two provinces — particularly the Quebec City–Windsor Corridor — are the most urbanized and industrialized areas of Canada, containing the country's two largest cities, Toronto and Montreal, and the national capital, Ottawa.
- Census Metropolitan Areas, 2007 population estimates[4]
- Toronto, ON: 5,606,320
- Montréal, QC: 3,814,300
- Ottawa, ON–Gatineau, QC: 1,158,300
- Québec, QC: 723,300
- Hamilton, ON: 716,200
- London, ON: 465,700
- Kitchener, ON: 463,600
- St. Catharines–Niagara, ON: 396,800
- Oshawa, ON: 344,400
- Windsor, ON: 332,100
- Sherbrooke, QC: 218,700
- Sudbury, ON: 162,000
- Kingston, ON: 155,000
- Saguenay, QC: 152,100
- Trois-Rivières, QC: 142,600
- Thunder Bay, ON: 125,400
See also
| Look up Central Canada in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
References
- 1 2 "Estimates of population, Canada, provinces and territories". Statistics Canada.
- ↑ "National Post View: Couillard touts the force of Central Canada". National Post. 12 May 2015. Retrieved 8 November 2015.
- ↑ Constitutional Act of 1791, Act of Union 1840, British North America Acts (1867)
- ↑ Statistics Canada - Population of census metropolitan areas (2001 Census boundaries) Archived December 11, 2007, at the Wayback Machine.