Kaveri
| Cauvery | |
| River | |
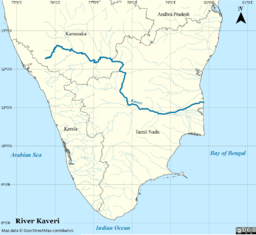 Map of the Kaveri river basin | |
| Country | India |
|---|---|
| Tributaries | |
| - left | Harangi Reservoir, Hemavati, Shimsha, Arkavathy |
| - right | Lakshmana Tirtha, Kabini, Bhavani river, Noyyal, Amaravati River, Moyar River |
| Source | Talakaveri, Kodagu, Western Ghats, Karnataka |
| - location | Karnataka (ಕರ್ನಾಟಕ), India |
| - elevation | 1,276 m (4,186 ft) |
| - coordinates | 12°23′N 75°29′E / 12.383°N 75.483°E |
| Mouth | Poompuhar, Tamil Nadu (தமிழ் நாடு) |
| - location | Bay of Bengal, India |
| - elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| - coordinates | 11°21′40″N 79°49′46″E / 11.36111°N 79.82944°ECoordinates: 11°21′40″N 79°49′46″E / 11.36111°N 79.82944°E |
| Length | 805 km (500 mi) [1] |
| Basin | 81,155 km2 (31,334 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| - average | 677 m3/s (23,908 cu ft/s) [2] |
| Discharge elsewhere (average) | |
| - Grand Anicut (South) | 400.716 m3/s (14,151 cu ft/s) [3] |
Kaveri (anglicized as Cauvery), also referred as Ponni, is an Indian river flowing through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. It is the third largest after Godavari and Krishna in south india and the largest in Tamil Nadu which on its course, bisects the state into North and South. Originating in the foothills of Western Ghats at Talakaveri, Kodagu in Karnataka it flows generally south and east through Karnataka and Tamil Nadu and across the southern Deccan plateau through the southeastern lowlands, emptying into the Bay of Bengal through two principal mouths in Poompuhar, Tamil Nadu. Amongst the river valleys, the Kaveri delta forms one of the most fertile regions in the country.
The Kaveri basin is estimated to be 81,155 square kilometres (31,334 sq mi) with many tributaries including Harangi, Hemavati, Kabini, Bhavani, Arkavathy, Lakshmana Tirtha, Noyyal and Arkavati. The river's basin covers three states and a Union Territory as follows: Tamil Nadu, 43,856 square kilometres (16,933 sq mi); Karnataka, 34,273 square kilometres (13,233 sq mi); Kerala, 2,866 square kilometres (1,107 sq mi), and Puducherry, 160 square kilometres (62 sq mi).[4] Rising in southwestern Karnataka, it flows southeast some 800 kilometres (500 mi) to enter the Bay of Bengal. In Mandya district it forms the island of Shivanasamudra, on either side of which are the scenic Shivanasamudra Falls that descend about 100 metres (330 ft).[5] The river is the source for an extensive irrigation system and for hydroelectric power.[6] The river has supported irrigated agriculture for centuries and served as the lifeblood of the ancient kingdoms and modern cities of South India. Access to the river's waters has pitted Indian states against each other for decades.
River course
After the river leaves the Kodagu hills and flows onto the Deccan plateau, it forms two islands in mandya district's Srirangapatna and Shivanasamudra. First, comes the Srirangapatna which forms the sangam and then comes Shivanasamudra. At Shivanasamudra the river drops 98 metres (320 ft), forming the famous Shivanasamudra Falls known separately as Gagana Chukki and Bhara Chukki.[7] Asia's first hydroelectric plant (built in 1902) was on the left falls and supplied power to the city of Bangalore.
In its course through Karnataka, the channel is interrupted by 12 "anekattu" (dams) for the purpose of irrigation. From the Anekattu at Madadkatte, an artificial channel is diverted at a distance of 116 kilometres (72 mi), irrigating an area of 4,000 hectares (10,000 acres), and ultimately bringing its water supply to the town of Mandya.
Three kilometres away from Srirangapatna, the Kaveri is the basis for the Ranganthittu Bird Sanctuary. Near Srirangapatna is also an aqueduct, the Bangara Doddi Nala, which was constructed in the 17th century by the Wodeyar maharaja of Mysore, Ranadhira Kantirava, in memory of his favourite consort. It is said to be the only aqueduct where the water from a river, dammed upstream, is carried by the aqueduct over the very same river few miles downstream . This aqueduct also served as a motorable bridge until 1964.The kabini river tributary of Kaveri joins Kaveri at Tirumakudal Narasipura where triveni sangama takesplace along with mythological river Spatika. The Moyar River is an east flowing river originates in the Mudumalai, Bandipur, and Wayanad National Parks draining the Nilgiri Hills in Tamil Nadu and Karnataka and is one of the tributaries to the Kaveri River.
The river enters Tamil Nadu through Dharmapuri district leading to the flat plains where it meanders. It drops into the Hogenakkal Falls just before it arrives in the town of Hogenakkal in Tamil Nadu. The three minor tributaries, Palar, Chinnar and Thoppar enter into the Kaveri on her course, above Stanley Reservoir in Mettur, where the dam has been constructed. It then flows further through the length of Erode district where the river Bhavani, running through the breadth of the district, merges with it. The confluence of the rivers Kaveri, Bhavani and Akash Ganga (mythological) is at the exact place of Bhavani, Tamil Nadu Kooduthurai or Tiriveni Sangamam, Northern part of Erode City.
While passing through Erode, two more tributaries merge. Thirumani Mutharu joins it in a village called Kududurai in Namakkal District. Noyyal and Amaravathi join it in Karur district before it reaches Tiruchirapalli district. Here the river becomes wide, with a sandy bed, and flows in an eastern direction until it splits into two at upper Anicut about 14 kilometres (9 mi) west of Tiruchirappalli. The northern branch of the river is called the Kollidam while the southern branch retains the name Kaveri and then goes directly eastwards into Thanjavur District. These two rivers join again and form the Srirangam island that is a part of the city of Tiruchirapalli. The oldest functional dam[8]Grand Anicut or Kallanai was present at this place. From Thanjavur, the river splits and goes to few places in the Delta Kaveri.
Tributaries
Irrigation
The primary uses of Kaveri is providing water for irrigation, water for household consumption and the generation of electricity.
An estimate at the time of the first Five Year Plan puts the total flow of the Kaveri at 15 cubic kilometres (12,000,000 acre⋅ft), of which 60 percent was used for irrigation. [9]
The Torekadanahalli pumpstation sends 540 million litres (19,000,000 cu ft) per day of water from Kaveri 100 kilometres (62 mi) to Bangalore.[10][11]

The hydroelectric plant built on the left of Sivanasamudra Falls on the Kaveri in 1902 was the first hydroelectric plant in Asia.[5]
The Krishna Raja Sagara Dam has a capacity of 49 tmc ft.[12] and the Mettur Dam which creates Stanley Reservoir has a capacity of 93.4 tmc ft. (thousand million cubic ft)
In August 2003, inflow into reservoirs in Karnataka was at a 29-year low, with a 58% shortfall.[13] Water stored in Krishna Raja Sagara amounted to only 4.6 tmc ft.[13]
Water sharing
As per Supreme Court order (16 feb 2018)[14] Karnataka will get 400.4 tmc ft,Tamil Nadu 200.25 tmc ft,Kerala 30 tmc ft and Puducherry 7 tmc ft, and 14 tmc ft will be reserved for environmental protection.
Cauvery Water Management Authority (CWMA) and Cauvery Water Regulation Committee (CWRC) 2018
Acting on the Supreme Court's direction, the Centre constituted a Cauvery Water Management Authority (CMA) on 1st June 2018 to address the dispute over sharing of river water among Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Kerala and Puducherry.
On February 16 2018, the apex court had directed the government to form the CMA within six weeks in a verdict that marginally increased Karnataka's share of Cauvery water, reduced the allocation for Tamil Nadu and sought to settle the protracted water dispute between the two sout.
On June 22 2018, Despite opposition from Karnataka, the Central government constituted the Cauvery Water Regulation Committee as per the provisions in the Cauvery Management Scheme laid down by the Supreme Court.
Central Water Commission chairman, S. Masood Hussain will head the CWMA and chief engineer of the Central Water Commission, Navin Kumar will be the first chairman of the CWRC. While the CWMA is an umbrella body, the CWRC will monitor water management on a day-to-day basis, including the water level and inflow and outflow of reservoirs in all the basin states.
See also
References
- ↑ "INTEGRATED HYDROLOGICAL DATA BOOK" (PDF). Central Water Commission, India. p. 92. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 April 2016. Retrieved 13 November 2017.
- ↑ Kumar, Rakesh; Singh, R.D.; Sharma, K.D. (10 September 2005). "Water Resources of India" (PDF). Current Science. Bangalore: Current Science Association. 89 (5): 794–811. Retrieved 13 October 2013.
- ↑ "Gauging Station - Data Summary". RivDis. Archived from the original on 4 October 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2013.
- ↑ "INTEGRATED HYDROLOGICAL DATA BOOK" (PDF). Retrieved 6 September 2012.
- 1 2 "World Waterfall Database". Retrieved 9 November 2006.
- ↑ "Shivasamudram Falls". cauvery.com. Retrieved 11 November 2006.
- ↑ The Cauvery Trail : Kaveri has many religious and tourism spots between KRS and Mettur Archived 2 July 2014 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ http://www.water-technology.net/features/feature-the-worlds-oldest-dams-still-in-use/
- ↑ http://planningcommission.nic.in/plans/planrel/fiveyr/1st/1planch26.html
- ↑ "PINCHme: Try products from leading brands for FREE!".
- ↑ http://www.tce.co.in/infra/watersupply/bangalore.pdf#search=%22halli%20pipeline%20Bangalore%22%5Bpermanent+dead+link%5D
- ↑ "Corporation urged to chalk out water policy for Mysore city". The Hindu. Chennai, India. 26 March 2006.
- 1 2 "Cauvery reservoirs' inflow hits record low". Deccan Herald. Bangalore. 2 August 2003. Archived from the original on 6 April 2012. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ↑ http://sci.gov.in/supremecourt/2007/11993/11993_2007_Judgement_16-Feb-2018.pdf
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kaveri. |
- Cauvery Presentation on the Cavery River
- Kaveri Pushkaralu
- Kaveri Pushkaram 2017