Carnot's theorem
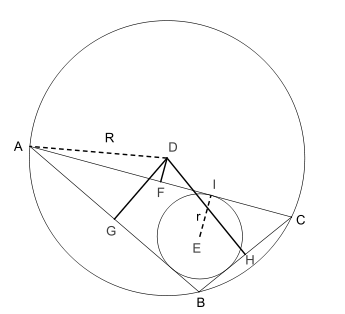
In Euclidean geometry, Carnot's theorem states that the sum of the signed distances from the circumcenter D to the sides of an arbitrary triangle ABC is
where r is the inradius and R is the circumradius of the triangle. Here the sign of the distances is taken to be negative if and only if the open line segment DX (X = F, G, H) lies completely outside the triangle. In the diagram, DF is negative and both DG and DH are positive.
The theorem is named after Lazare Carnot (1753–1823). It is used in a proof of the Japanese theorem for concyclic polygons.
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Carnot's theorem". MathWorld.
- Carnot's Theorem at cut-the-knot
- Carnot's Theorem by Chris Boucher. The Wolfram Demonstrations Project.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.