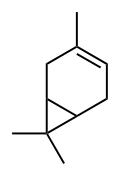
3-Carene
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
3,7,7-Trimethylbicyclo[4.1.0]hept-3-ene Car-3-ene | |
| Other names
Δ3-Carene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.367 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H16 | |
| Molar mass | 136.24 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.86 g/cm3 (20 °C)[1] |
| Boiling point | 170–172 °C (338–342 °F; 443–445 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
3-Carene is a bicyclic monoterpene consisting of fused cyclohexene and cyclopropane rings. It occurs as a constituent of turpentine,[2] with a content as high as 42% depending on the source. Carene has a sweet and pungent odor.[3], best described as fir needles, musky earth, and damp woodlands combination.[4]
A colorless liquid, it is not soluble in water, but miscible with fats and oils.[3] It is chiral, occurring naturally both as the racemate and enantio-enriched forms.
Reactions and uses
Treatment with peracetic acid gives 3,4-caranediol. Pyrolysis over ferric oxide induces rearrangement, giving p-cymene. Carene is used in the perfume industry and as a chemical intermediate.[2]
References
- 1 2 Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- 1 2 M. Eggersdorfer (2005). "Terpenes". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a26_205.
- 1 2 Merck Index (12th ed.). 1996. p. 300. 1885.
- ↑ Mediavilla, Vito, Simon Steinemann, Essential oil of Cannabis sativa L. strains. Journal of the International Hemp Association, 1997, 4(2):80-82.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.