Baphia nitida
| Camwood | |
|---|---|
.jpg) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Genus: | Baphia |
| Species: | B. nitida |
| Binomial name | |
| Baphia nitida Lodd. | |
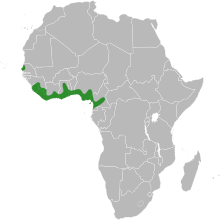 | |
| The distribution of Baphia nitida. | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
Baphia nitida (camwood, also barwood), also known as African sandalwood, is a shrubby, leguminous, hard-wooded tree from central west Africa. This wood is of a very fine colour, and is used in woodturning for making knife handles and similar articles.
The tree's bark and heartwood are commonly used to make a brilliant but non-permanent red dye, which is soluble in alkali.
Camwood is known as "osun" in Yoruba.
Pterocarpin is a pterocarpan found in B. nitida.[2]
Osun (camwood) extract is also used in some soaps and skin treatments, although there aren't published studies about its efficacy or safety.
References
- ↑ Soladoye MO (1985). "A revision of Baphia (Leguminosae-Papilionoideae)". Kew Bulletin. 40 (2): 291–386. doi:10.2307/4108263. JSTOR 4108263.
- ↑ Pterocarpin at knapsack_jsp
External links
- Dressler, S.; Schmidt, M. & Zizka, G. (2014). "Baphia nitida". African plants – a Photo Guide. Frankfurt/Main: Forschungsinstitut Senckenberg.

This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.