NGC 752
| NGC 752 | |
|---|---|
 NGC 752 | |
| Observation data (J2000 epoch) | |
| Constellation | Andromeda |
| Right ascension | 01h 57m 41s[1] |
| Declination | +37° 47.1′[1] |
| Distance | 1,300 ly[2] (400 pc) |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.7[3] |
| Apparent dimensions (V) | 75′ |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Other designations | Caldwell 28 |
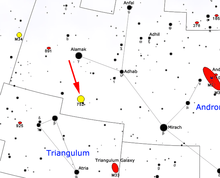
Map showing the location of NGC 752
NGC 752 (also known as Caldwell 28) is an open cluster in the constellation Andromeda. The cluster was discovered by Caroline Herschel in 1783 and cataloged by her brother William Herschel in 1786, although an object that may have been NGC 752 was described by Giovanni Batista Hodierna before 1654.[2]
The large cluster lies 1,300 light-years away from the Earth[2] and is easily seen through binoculars, although it may approach naked eye visibility under good observing conditions. A telescope reveals about 60 stars no brighter than 9th magnitude within NGC 752.[3][4]
Components
| NAME | Right ascension | Declination | Apparent magnitude (V) | Spectral type | Database references |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 752 1 (HD 11624) | 01h 54m 57.6607s | +37° 07' 41.845 | 6.281 | K0 | Simbad |
| NGC 752 2 (BD+36 345) | Simbad |
References
- 1 2 "NGC 752". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 10 February 2018.
- 1 2 3 Seligman, Courtney. "New General Catalogue objects: NGC 750 - 759". cseligman.com. Retrieved 10 February 2018.
- 1 2 Dunlop, Storm (2005). Atlas of the Night Sky. Collins. ISBN 0-00-717223-0.
- ↑ Frommert, Kronberg, SEDS: NGC 752
External links
- SEDS – NGC 752
- perseus.gr – NGC 752 in a hires LRGB CCD image
- NGC 752 on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.