FAM114A2 (chromosome 5 open reading frame 3) is a gene on chromosome 5 in humans that encodes a protein FAM114A2. The protein function is not well known. FAM114A2 is, however, highly conserved in mammals with homologs both in fungi and plants.
Protein
The FAM114A2 protein is 505 amino acids long[5] with a molecular weight of 55.5 kdal and an isoelectric point of 4.66.[6] It is predicted to stay in the nucleus after translation [7]
There is evidence that c5orf3 interacts with another protein of unknown function from chromosome 5, c5orf4 [8]
This protein is thought to include a P loop [9] that suggests a role in ATP- and/or GTP-binding [10]
Gene
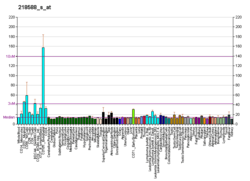
The FAM114A2 gene is located on chromosome 5 (5q31-33).[11] This gene has 14 exons spanning through its sequence.[5] The coding sequence is 2886 base pairs with a 5’ UTR of 94 base pairs and a 3’ UTR of 1273 base pairs.[5] It is expressed at high levels in most tissues of the human body.[11] It is also highly expressed in tissues in the human brain [12]
Further reading
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, et al. (2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes". Genome Res. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, et al. (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.