Moroccan worm lizard
| Moroccan Worm Lizard | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Family: | Blanidae |
| Genus: | Blanus |
| Species: | B. mettetali |
| Binomial name | |
| Blanus mettetali Bons, 1963 | |
 | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
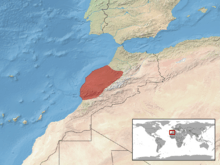
The Moroccan worm lizard (Blanus mettetali) is a species of reptiles in the family Blanidae. The species is endemic to Morocco.[2]
Etymology
The specific name, mettetali, is in honor of a Mr. Mettetal who was head of the Laboratory of Animal Biology, Faculty of Sciences of Morocco.[3]
Habitat
The natural habitats of B. mettetali are temperate forests, temperate shrubland, Mediterranean-type shrubby vegetation, arable land, and pastureland.
Conservation status
B. mettetali is threatened by habitat loss.
References
- ↑ "Blanus mettetali ". The Reptile Database. www.reptile-database.org.
- ↑ Busack, Stephen D. (5 February 1988). "Biochemical and Morphological Differentiation in Spanish and Moroccan Populations of Blanus and the Description of a New Species from Northern Morocco (Reptilia, Amphisbaenia, Amphisbaenidae)". Copeia. 1988 (1): 101–109. doi:10.2307/1445928. JSTOR 1445928.
- ↑ Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael. 2011. The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles. xiii + 296 pp. ISBN 978-1-4214-0135-5. (Blanus mettetali, p. 177).
External links
- Miras, J.A.M.; Joger, U.; Pleguezuelos, J.; Slimani, T. 2005. Blanus mettetali . 2006 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Downloaded on 29 July 2007.
Further reading
- Bons, J. 1963. "Notes sur Blanus cinereus (Vandelli), description d'une sous-espèce Marocaine: Blanus cinereus mettetali ssp. nov." Bulletin de la Société des Sciences naturelles et physiques du Maroc (1-2): 95-107.
Phylogeographical patterns
- Albert, E.M.; Zardoya, R.; García-París, M. (2007). "Phylogeographical and speciation patterns in subterranean worm lizards of the genus Blanus (Amphisbaenia: Blanidae)". Molecular Ecology. 16 (7): 1519–1531. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2007.03248.x. ISSN 0962-1083. PMID 17391273.
- Vaconcelos, Raquel; Harris, D. James; Carretero, Miguel (2006). "Phylogeography of the genus Blanus (worm lizards) in Iberia and Morocco based on mitochondrial and nuclear markers — preliminary analysis". Amphibia-Reptilia. 27 (3): 339–346. doi:10.1163/156853806778190033. ISSN 0173-5373.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.