Bis-tris methane
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
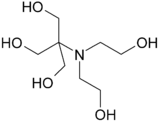
| IUPAC name
2-[Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]-2-(hydroxymethyl)propane-1,3-diol[1] | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 2205275 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.027.489 |
| EC Number | 230-237-7 |
| 4519 | |
| MeSH | Bistris |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number | TY2900000 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H19NO5 | |
| Molar mass | 209.24 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Odor | Odourless |
| Melting point | 102 to 103 °C (216 to 217 °F; 375 to 376 K) |
| 209.2 g L−1 (at 20 °C) | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 6.46 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 7.54 |
| UV-vis (λmax) | 280 nm |
| Absorbance | 0.15 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS signal word | WARNING |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P305+351+338 | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanols |
|
Related compounds |
Diethylhydroxylamine |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Bis-tris methane, also known as BIS-TRIS or BTM, is a buffering agent used in biochemistry. Bis-tris methane is an organic tertiary amine with labile protons having a pKa of 6.46 at 25 °C. It is an effective buffer between the pH 5.8 and 7.2. Bis-tris methane binds strongly to Cu and Pb ions as well as, weakly, to Mg, Ca, Mn, Co, Ni, Zn and Cd.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ "Bistris - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 23 June 2005. Identification. Retrieved 9 April 2012.
- ↑ Ferreira, Carlos M. H.; Pinto, Isabel S. S.; Soares, Eduardo V.; Soares, Helena M. V. M. (2015). "(Un)suitability of the use of pH buffers in biological, biochemical and environmental studies and their interaction with metal ions – a review". RSC Advances. 5 (39): 30989–31003. doi:10.1039/c4ra15453c. ISSN 2046-2069.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.
