Brighton and Sussex University Hospitals NHS Trust
| Type of Trust | |
|---|---|
| NHS hospital trust | |
| Trust Details | |
| Last annual budget | £550 million |
| Employees | 8200 |
| Chair | Mike Viggers |
| Chief Executive | Marianne Griffiths |
| Links | |
| Website | Brighton and Sussex University Hospital |
| Care Quality Commission reports | CQC |
Brighton and Sussex University Hospitals NHS Trust runs two acute hospitals, the Royal Sussex County Hospital in Brighton and the Princess Royal Hospital (Haywards Heath). Additionally, it also operates a number of other hospitals and medical facilities, including the Royal Alexandra Children's and Sussex Eye Hospitals in Brighton, Hove Polyclinic, the Park Centre for Breast Care in Preston Park and Hurstwood Park Neurosciences Centre in Haywards Heath. The Trust also provides services in Brighton General Hospital, Lewes Victoria Hospital, Bexhill Renal Satellite Unit, Eastbourne General Hospital and Worthing Hospital.
Development programme
The Trust is undergoing a £484.7 million public capital development programme for the modernisation of the Royal Sussex County Hospital, which has the oldest buildings in the NHS still used for acute care.[1] Treasury funding for the redevelopment was approved in May 2014.[2] Laing O'Rourke started work on the project on September 2014 by constructing temporary buildings.[3] The first phase is due for completion in 2020, with the overall programme due to be completed by 2024.[4]
After securing agreement from NHS Improvement, the Trust got planning permission in September 2017 for a £30 million redevelopment of the Royal Sussex County Hospital’s A&E department, including a new 70 bed short-stay ward. The new development is due to be completed by December 2018.[5]
Performance
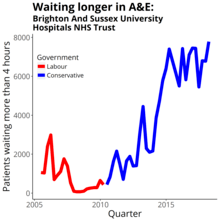
A Care Quality Commission report in 2014 said that accident and emergency services at Royal Sussex County Hospital were inadequate for responsiveness, suffered significant pressures and lacked sufficient physical space to deal with the number of patients that attended.[6]
The trust was one of 26 responsible for half of the national growth in patients waiting more than four hours in accident and emergency over the 2014/5 winter.[7] The trust spent £14.7 million on agency staff in 2014/5.[8]
In March 2015 it was announced that the trust's 5-year contract with Sodexo for cleaning, catering and portering services which started in December 2012 would be terminated early in July 2015 by mutual consent after problems with staff pay and safety concerns over equipment and cleanliness standards.[9]
It ended 2015/6 in deficit of £45 million.[10]
In June 2016 it reported a backlog of more than 9000 patients who had waited more than 18 weeks for treatment in breach of the target, and only 73% of current referrals were seen within the target. It did not expect to hit the target before March 2018.[11] Following an inspection in April 2016, the Trust was given a formal warning by the Care Quality Commission in June 2016. It was told to improve its risk management as patients were being put at unnecessary risk because they were not being dealt with properly or in appropriate areas, to ensure the care privacy and dignity of people attending hospital and to ensure patients are seen in line with national timescales for diagnosis and treatment.[12] It was put into special measures in October 2016.[13] It had its accreditation suspended by the United Kingdom Accreditation Service in 2016 when staff shortages affected turn round times.[14]
NHS Improvement removed the existing management and contracted the executive from Western Sussex NHS Foundation Trust to provide leadership to the Trust for three years from April 2017.[15]
The Care Quality Commission inspected the Trust’s two main hospitals in April 2017, whose ratings improved from Inadequate to Requires Improvement. The CQC said that they had found “significant improvements” across the Trust,[16] but recommended it stays in special measures.[17]
The CQC concluded that “There is no doubt that improvements have been made since our last inspection and that the staff involved in the delivery of that change should be congratulated. However, there remains an extensive programme of change to be delivered in order to attain an overall rating of good. The lack of consistent board and executive leadership has hampered the pace of change in the last twelve months and it is anticipated that the incoming management team can provide both stability and clarity of leadership that will lead to sustainable change."[18]
Controversy
A Care Quality Commission report in August 2014 found there had been a “significant increase” in disciplinary cases related to race discrimination.[6] The Black and Minority Ethnic Network in the Trust passed a vote of no confidence in the trust board in November 2015. A petition was circulated claiming that “BME people are being subjected to unprecedented levels of racial discrimination, harassment and victimisation.”[19]
History
In June 2012 the trust was fined £325,000 by the Information Commissioner's Office after highly sensitive files of tens of thousands of patients, including details of HIV treatment, ended up being sold on eBay.[20] In February 2014, the Trust announced it was updating its policy to include e-cigarettes in a blanket ban on smoking in its buildings and grounds. It established a joint venture, Frontier Pathology NHS Partnership, with Surrey and Sussex Healthcare NHS Trust in 2015.
See also
References
- ↑ "Analysed: the foundation trust pipeline in Sussex". Health Service Journal. 17 April 2012. Retrieved 3 November 2013.
- ↑ "Osborne agrees £420m for Brighton rebuild". Health Service Journal. 1 May 2014. Retrieved 27 May 2014.
- ↑ "O'Rourke starts work on £420m Brighton hospital". Construction Enquirer. 3 September 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ↑ https://www.bsuh.nhs.uk/about-us/hospital-redevelopment/about-the-redevelopment/
- ↑ http://www.theargus.co.uk/news/15533199.__30m_A_E_expansion_given_the_go_ahead/
- 1 2 "Brighton and Sussex records surge in race discrimination cases". Health Service Journal. 12 August 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ↑ "26 trusts responsible for half of national A&E target breach". Health Service Journal. 1 April 2015. Retrieved 3 May 2015.
- ↑ "Agency spending: the real picture". Health Service Journal. 26 November 2015. Retrieved 23 December 2015.
- ↑ "Hospital trust ends £15m contract for cleaning, catering and portering from private firm Sodexo". The Argus. 25 March 2015. Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- ↑ "Analysis: The trusts whose finances fell furthest despite 'urgent action'". Health Service Journal. 2 June 2016. Retrieved 31 July 2016.
- ↑ "Trust expects to fail RTT target until 2018". Health Service Journal. 1 June 2016. Retrieved 31 July 2016.
- ↑ "Hospitals in Haywards Heath and Brighton need 'significant improvements' - CQC". Mid-Sussex Times. 20 June 2016. Retrieved 19 September 2016.
- ↑ "More trusts put into financial special measures". Health Service Journal. 17 October 2016. Retrieved 20 December 2016.
- ↑ "Under-pressure NHS pathology venture puts patients at 'significant risk'". Health Service Journal. 14 March 2017. Retrieved 29 April 2017.
- ↑ "New buddying arrangement between BSUH and Western Sussex announced - Brighton and Sussex University Hospitals NHS Trust". Brighton and Sussex University Hospitals NHS Trust. 2016-11-14. Retrieved 2017-11-03.
- ↑ "Brighton and Sussex University Hospitals NHS Trust shows improvement says CQC | Care Quality Commission". www.cqc.org.uk. Retrieved 2017-11-03.
- ↑ "Trust makes 'significant' improvements toward moving out of special measures". The Argus. Retrieved 2017-11-03.
- ↑ "Royal Sussex County Hospital". www.cqc.org.uk. Retrieved 2017-11-03.
- ↑ "Hospital trust in racism row as black and minority ethnic staff call on leaders to stand down". The Argus. 13 November 2015. Retrieved 19 December 2015.
- ↑ "NHS trust fined over privacy breach". The Argus. 1 June 2012. Retrieved 3 November 2013.