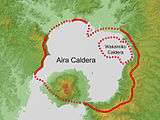
Aira Caldera
| Aira Caldera | |
|---|---|
| 姶良カルデラ | |
 Space radar image of Aira Caldera, with Sakurajima in the bay formed by the caldera. | |
| Highest point | |
| Coordinates | 31°40′01″N 130°40′01″E / 31.667°N 130.667°ECoordinates: 31°40′01″N 130°40′01″E / 31.667°N 130.667°E |
| Geography | |
| Geology | |
| Mountain type |
Caldera Somma volcano |
| Last eruption | c. 22,000 years ago |
Aira Caldera (姶良カルデラ Aira-Karudera) is a gigantic volcanic caldera in the south of the island of Kyūshū, Japan. The caldera was originally thought to have been created by a massive eruption, approximately 22,000 years ago. This eruption, whose widespread deposits are generically known as the Aira-Tanzawa tephra, is now thought to be rather older. The latest/best age estimates derive from cores from Lakes Biwa and Suigetsu and they indicate an age of 29,430-30,150 years ago. Eruption of voluminous pyroclastic flows accompanied the formation of the 17 × 23 km-wide Aira caldera. Together with a large pumice fall, these amounted to approximately 400 km3 of tephra (VEI 7).
The major city of Kagoshima and the 16,000-year-old Sakurajima volcano lie within the caldera. Sakura-jima, one of Japan's most active volcanoes, is a post-caldera cone of the Aira caldera at the northern half of Kagoshima Bay.
References
- Smith, V.C. (2013). "Identification and correlation of visible tephras in the Lake Suigetsu SG06 sedimentary archive, Japan". Quaternary Science Reviews. 67: 121–137.
External links
- Aira - Smithsonian Institution: Global Volcanism Program
- Aira Caldera - Geological Survey of Japan
'