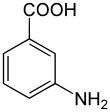
3-Aminobenzoic acid
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Aminobenzoic acid | |||
| Other names
meta-Aminobenzoic acid m-Aminobenzoic acid MABA 3-Carboxyaniline m-Carboxyaniline | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.477 | ||
| EC Number | 202-724-4 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C7H7NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 137.13598 | ||
| Appearance | White solid | ||
| Density | 1.51 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 178 to 80 °C (352 to 176 °F; 451 to 353 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |  | ||
| GHS signal word | Warning | ||
| H302, H315, H319, H335 | |||
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
3-Aminobenzoic acid (also known as meta-aminobenzoic acid or MABA) is an organic compound with the molecular formula H2NC6H4CO2H. MABA is a white solid, although commercial samples are often colored. It is only slightly soluble in water. It is soluble in acetone, boiling water, hot alcohol, hot chloroform and ether. It consists of a benzene ring substituted with an amino group and a carboxylic acid.
See also
References
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.