Many electronic components are made of the functioning electronic part and a package to protect and support the working bit. There are hundreds of different packages, each with specific uses, advantages and disadvantages.
All packages have a "body", usually made of plastic or ceramic and occasionally metal, and "pins" to connect the internal workings to an external circuit.
This page lists packages by components type, with basic dimensions and links to more specific pages with package dimensions, PCB footprints, etc.
Passive Components
| Package | SMT/THM | Diagram | Dimensions (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length | Width | Height | |||
| 0805 | SMT | 2 | 1.25 | 1.2 | |
Semiconductor Devices
Semiconductor devices are labelled according to the JEDEC prefix convention:
- MO: microelectronic outline
- TO: transistor outline
- DO: discrete outline
Where applicable, the alternative names for the same package as given by JEITA or the common abbreviation (for example, DIL for dual in-line) will be noted, as well as the category of package (for example, "flange mounted, rectangular base").
Transistors
Transistors also have a column for the kind of lead. Axial leads are lead which follow the axis of the transistor, that is, perpendicular to the seating plane. Flat leads are parallel to the seating plane.
| Package | SMT/THM | Diagram | Pins | Lead Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JEDEC | JEITA | Abbrv. | ||||
| TO-92 | THM | 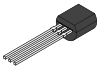 | 3 | Axial | ||
| TO-220 | THM | 2-3 | Axial | |||
ICs
| Package | SMT/THM | Diagram | Pins | Pitch | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbrv. | Name | mm | inches | |||
| CBGA | Ceramic Ball Grid Array | SMT |    | - | 1.27 | 0.05 |
| PDIP | Plastic Dual In-Line | THM | 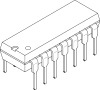 | 8-48 | 2.54 | 0.1 |