boolean overview
2D examples
 union ( or )
union ( or )
circle + square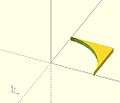 difference ( and not )
difference ( and not )
square - circle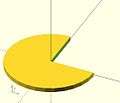 difference ( and not )
difference ( and not )
circle - square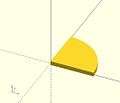 intersection ( and )
intersection ( and )
circle - (circle - square)
union() {square(10);circle(10);} // square or circle
difference() {square(10);circle(10);} // square and not circle
difference() {circle(10);square(10);} // circle and not square
intersection(){square(10);circle(10);} // square and circle
3D examples
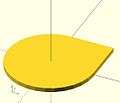
 union ( or )
union ( or )
sphere + cube difference ( and not )
difference ( and not )
cube - sphere difference ( and not )
difference ( and not )
sphere - cube intersection ( and )
intersection ( and )
sphere - (sphere - cube)
union() {cube(12, center=true); sphere(8);} // cube or sphere
difference() {cube(12, center=true); sphere(8);} // cube and not sphere
difference() {sphere(8); cube(12, center=true);} // sphere and not cube
intersection(){cube(12, center=true); sphere(8);} // cube and sphere
union
Creates a union of all its child nodes. This is the sum of all children (logical or).
May be used with either 2D or 3D objects, but don't mix them.

//Usage example:
union() {
cylinder (h = 4, r=1, center = true, $fn=100);
rotate ([90,0,0]) cylinder (h = 4, r=0.9, center = true, $fn=100);
}
Remark: union is implicit when not used. But it is mandatory, for example, in difference to group first child nodes into one.
difference
Subtracts the 2nd (and all further) child nodes from the first one (logical and not).
May be used with either 2D or 3D objects, but don't mix them.
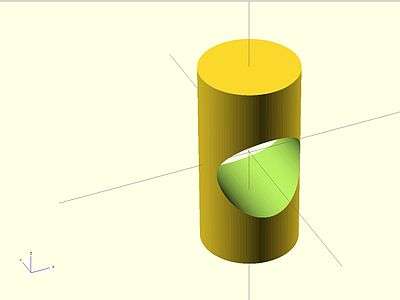
Usage example:
difference() {
cylinder (h = 4, r=1, center = true, $fn=100);
rotate ([90,0,0]) cylinder (h = 4, r=0.9, center = true, $fn=100);
}
difference with multiple children
Note, in the second instance, the result of adding a union of the 1st and 2nd children.
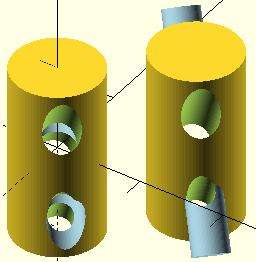
// Usage example for difference of multiple children:
$fn=90;
difference(){
cylinder(r=5,h=20,center=true);
rotate([00,140,-45]) color("LightBlue") cylinder(r=2,h=25,center=true);
rotate([00,40,-50]) cylinder(r=2,h=30,center=true);
translate([0,0,-10])rotate([00,40,-50]) cylinder(r=1.4,h=30,center=true);
}
// second instance with added union
translate([10,10,0]){
difference(){
union(){ // combine 1st and 2nd children
cylinder(r=5,h=20,center=true);
rotate([00,140,-45]) color("LightBlue") cylinder(r=2,h=25,center=true);
}
rotate([00,40,-50]) cylinder(r=2,h=30,center=true);
translate([0,0,-10])rotate([00,40,-50]) cylinder(r=1.4,h=30,center=true);
}
}
intersection
Creates the intersection of all child nodes. This keeps the overlapping portion (logical and).
Only the area which is common or shared by all children is retained.
May be used with either 2D or 3D objects, but don't mix them.
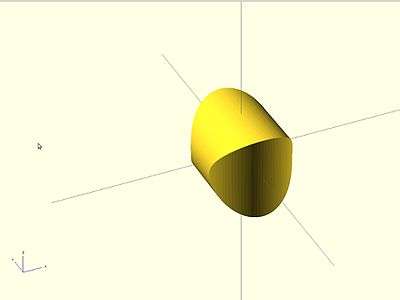
//Usage example:
intersection() {
cylinder (h = 4, r=1, center = true, $fn=100);
rotate ([90,0,0]) cylinder (h = 4, r=0.9, center = true, $fn=100);
}
render
Warning: Using render, always calculates the CSG model for this tree (even in OpenCSG preview mode). This can make previewing very slow and OpenSCAD to appear to hang/freeze.
Usage example:
render(convexity = 1) { ... }
| convexity | Integer. The convexity parameter specifies the maximum number of front and back sides a ray intersecting the object might penetrate. This parameter is only needed for correctly displaying the object in OpenCSG preview mode and has no effect on the polyhedron rendering. |
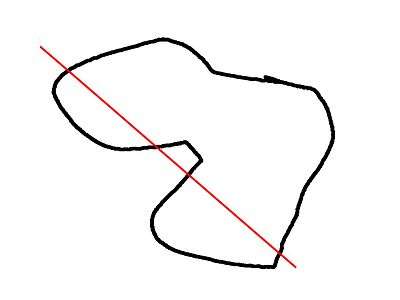
This image shows a 2D shape with a convexity of 4, as the ray indicated in red crosses the 2D shape a maximum of 4 times. The convexity of a 3D shape would be determined in a similar way. Setting it to 10 should work fine for most cases.