Links with Mathematics
- Harmonics
Natural & Artifical Systems
Representations of sound
Analogue
In analogue recordings, the machine is always recording any sound or noise that is coming through the microphones.
In digital recording, however, you don't have a constant recording of what's going on. Instead, you have a series of samples taken from the sound being recorded.
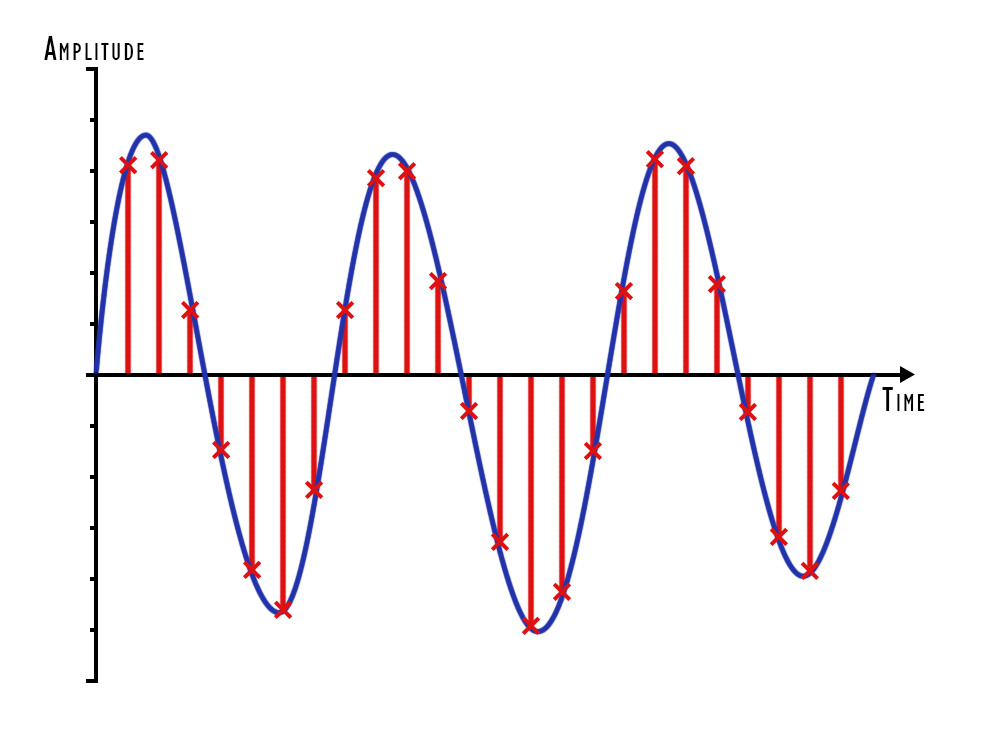
Think of it like a movie — a motion picture strings together a series of pictures to make it look like moving action. In this case, digital recording takes a series of "pictures" of what the sound is like and turns it into a digital recording. A standard compact disc contains sound that has been sampled at 44.1 kHz, or just over 44,000 times a second (that's a lot of pictures!). However, you may run into digital sound used by professional sound engineers in the music industry that's been recorded at 48 kHz, 96 kHz, or even higher. Just think of it as getting more detail from more pictures.
Digital
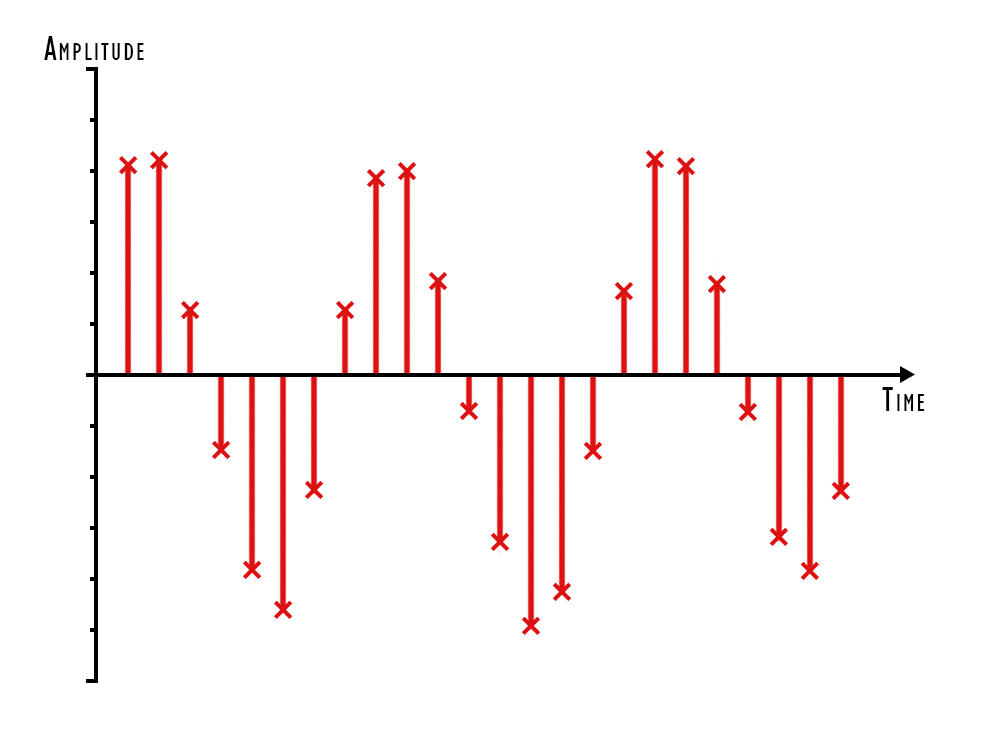
Conversion of Analog to Digital
Manipulation of sound
Digital Literacy
Q When you buy a CD how many songs are there on it?
A About 10 maybe 15...
So if an audio CD has approximately 600Mb of data then each song is maybe 70Mb
Q How large is the average MP3 that you download from iTunes or Amazon?
A About 4Mb maybe as much as 10Mb for a long one
Do the two files sound the same?
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a CD quality sound file over a MP3 one you might have on your mobile phone
Resources
Programming
- Sonic Pi
- Scheme of Work from Raspberry Pi Foundation under a Creative Commons CC BY-SA Attribution & Share-alike licence
Manipulation
Content
Copyright of audio