1D neighborhood
Since in 1D there are no shapes, the definition of the neighborhood is usually very simple.
Radial neighborhood
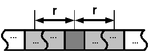
Usually the neighborhood in 1D is described by its radius , meaning the number of cell left and right from the central cell that are used for the neighborhood. The output cell is positioned at the center.
- Formal definition
Formally the radial neighborhood is the set of neighbors
or simply the neighborhood size with the output cell at the center .
- Symmetries
- reflection symmetry
Stephen Wolfram's notation
In Wolframs's texts and many others the number of available cell states and the radius are combined into a pair
- See also
- Stephen Wolfram, Statistical Mechanics of Cellular Automata (1983)
Brickwall neighborhood
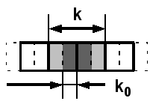
An unaligned neighborhood, usually the smallest possible . The output cell is positioned at between the two cells of the neighborhood. It is usually processed by alternatively shifting the output cell between and .
2D neighborhood
von Neumann neighborhood
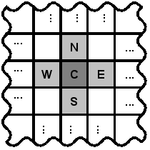
It is the smallest symmetric 2D aligned neighborhood usually described by directions on the compass sometimes the central cell is omitted.
- Formal definition
Formally the von Neumann neighborhood is the set of neighbors
or a subset of the rectangular neighborhood size with the output cell at the center .
- Symmetries
- reflection symmetry
- rotation symmetry 4-fold
- See also
Moore neighborhood
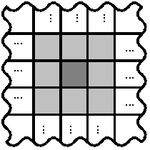
Is a simple square (usually 3×3 cells) with the output cell in the center. Usually cells in the neighborhood are described by directions on the compass sometimes the central cell is omitted.
- Formal definition
Formally the Moore neighborhood is the set of neighbors
or simply a square size with the output cell at the center .
- Symmetries
- reflection symmetry
- rotation symmetry 4-fold
- See also
- [mathworld] - [Moore Neighborhood]
Margolus neighborhood
reversible
Unaligned rectangular neighborhood
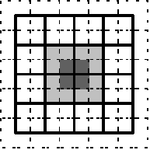
An unaligned (brickwall) rectangular neighborhood, usually the smallest possible . The output cell is positioned at between the four cells of the neighborhood. It is usually processed by alternatively shifting the output cell to and .
Hexagonal neighborhood
Hexagonal neighborhood
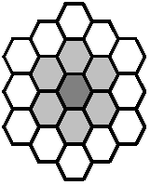
- Symmetries
- reflection symmetry
- rotation symmetry 6-fold
Small unaligned hexagonal neighborhood
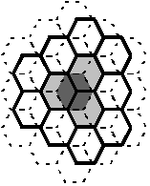
- Formal definition
Formally the small (3-cell) unaligned hexagonal neighborhood represented on a rectangular lattice is the set of neighbors
- Symmetries
- reflection symmetry
- rotation symmetry 3-fold
References
- [mathworld] - [Neighborhood]