The biomedical engineer works with the medical doctors, the nurses,the manufacturers and so on. In order to design new device for healthcare, basical understanding human body is prior. In order to find out the requirement of the special medical devices, therapy and so on, when we read the patents,journals, articles and so on and communicate with medical field people, it would be very helpful. In this chapter, fundamental anatomical terms and medical glossary would be introduced.
Anatomical Terms & Planes
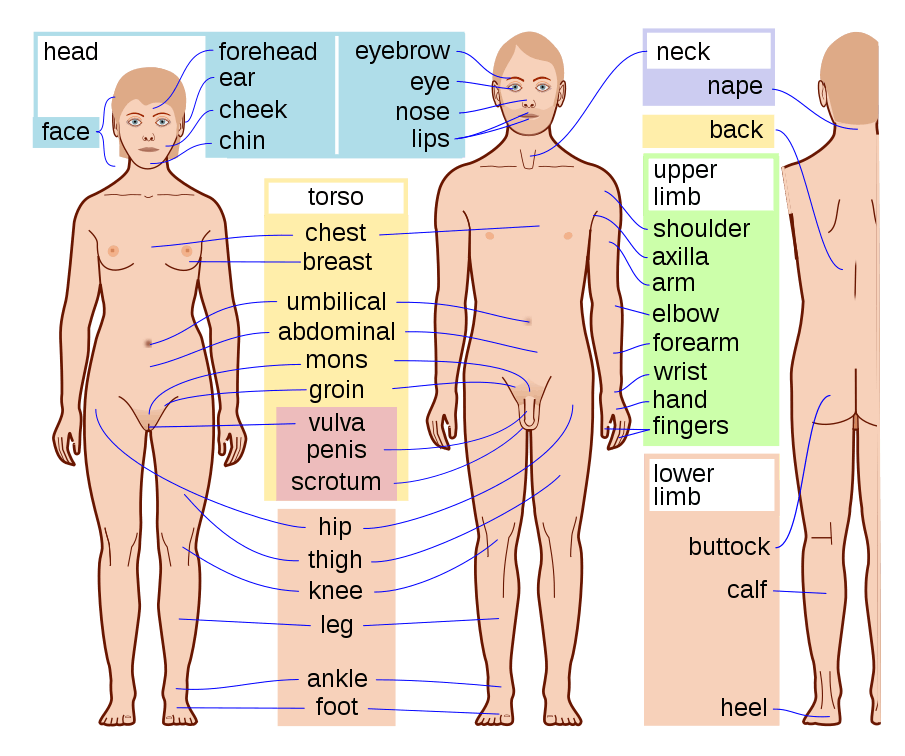 Anatomical Terms |
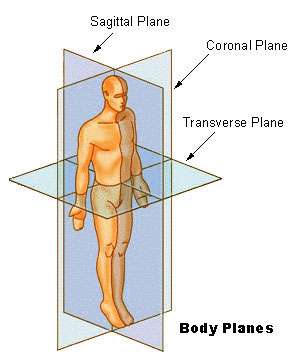 Anatomical planes in a human |
Anatomical Terms
- The body is composed of the head, trunk and limbs.
- The trunk consists of the neck, thorax(chest) and abdomen (belly). The lowest part of the trunk is the perineum. The central axis of the trunk is the vertebral column, and the upper part of it(cervical part) supports the head.
- The main parts of the upper limb are the arm, forearm and hand. Arm in anatomical form means the part between the shoulder and elbow. But, generally the arm means from the shoulder to before the hand.
- The main parts of the lower limb are the thigh, leg and foot. Here also leg in anatomical term point out the part from knee to foot.But, generally the leg means from thigh to before the foot.
Anatomical Planes
- For the positions of structure in human anatomy, the whole body should stand upright with the feet together and the head and eyes looking to the front with the arms straight by the side and the palms of the hands facing forwards.
- The ‘Median plane’ is an virtual vertical longitudinal line through the middle of the body from front to back, dividing the body into right and left halves.
- The ‘Coronal planes’ are imaginary planes at right angles to the median plane.
- The 'Transverse plane' divides the body into head and tail portions.
Anatomical Movement
'See also Wikipedia,Anatomical terms of motion.
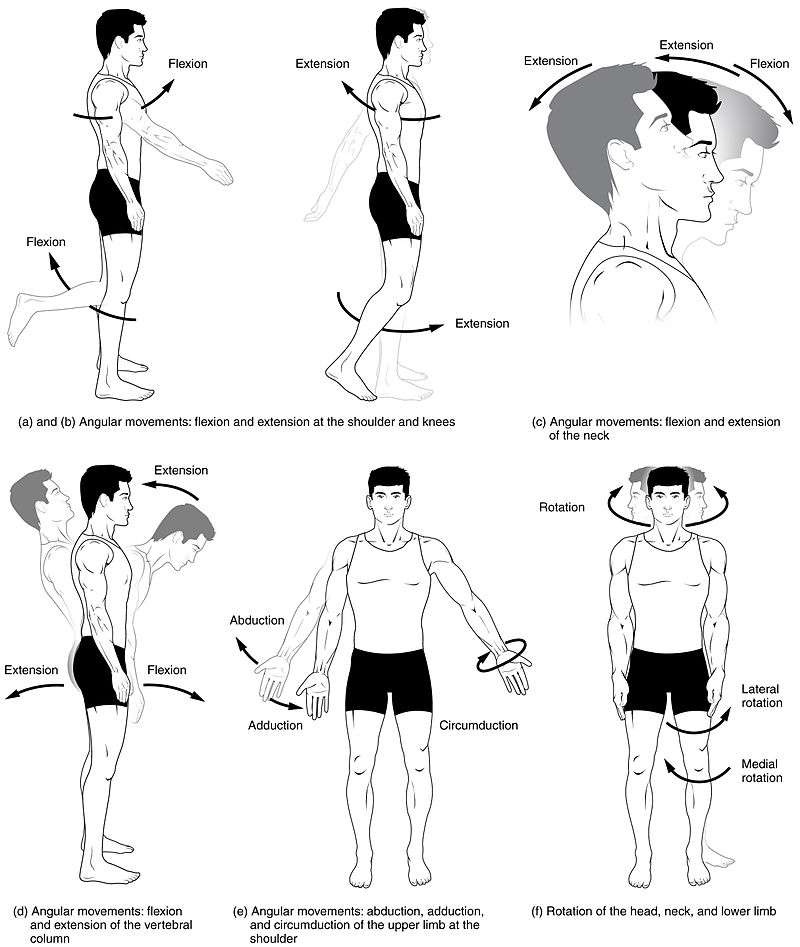
- 'Flexion' means a bending movement that decreases the angle between two parts like bending elbow, siting down and so on.
- 'Extension' is the opposite of flexion. It is a straightening movement that increases the angle between body parts.
- 'Abduction' is a motion that pulls a structure or part away from the midline of the body.
- 'Adduction' is a motion that pulls a structure or part toward the midline of the body, or towards the midline of a limb.
- 'Elevation' is the movement in a superior direction like raising the arm upwards.
- 'Depression' is the movement in an inferior direction, the opposite of elevation.
- 'Internal rotation' (or medial rotation) means rotation towards the axis of the body like the arms against the chest.
- 'External rotation' (or lateral rotation) means rotation away from the center of the body. For instance, the leg can rotate.
Medical Terminology
'See also Wikipedia,List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes
Table of Prefixes
| Prefix | Translation of Greek or Latin | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| A | Without, lack of | Apathy (lack of feeling); apnea (without breath); aphasia (without speech) |
| Ab | Away from | Abductor (leading away from); aboral (away from mouth) |
| Ad | To, toward, near to | Adductor (leading toward); adhesion (sticking to); adnexia (structures joined to); adrenal (near the kidney) |
| Ambi,Amphi,Ampho | Both | Ambidextrous (ability to use hands equally); ambilaterally (both sides), Amphibious (living on both land and water), Amphogenic (producing offspring of both sexes) |
| Ana | Up, back, again, excessive | Anatomy (a cutting up); anagenesis (reproduction of tissue) |
| Ante | Before, forward | Antecubital (before elbow); anteflexion (forward bending) |
| Anti | Against, reversed | Antiperistalsis (reversed peristalsis); antisepsis (against infection) |
| Apo | From, away from | Aponeurosis (away from tendon); apochromatic (abnormal color) |
| Bi | Twice, double | Biarticulate (double joint); bifocal (two foci); bifurcation (two branches) |
| Cata | Down, according to, complete | Catabolism (breaking down); catalepsia (complete seizure); catarrh (flowing down) |
| Circum | Around, about | circumarticular (around joint) |
| Com, Con | With, together | Commissure (sending or coming together),Conductor (leading together); concrescence (growing together); concentric (having a common center) |
| Contra | Against, opposite | Contralateral (opposite side); contraception (prevention of conception); contraindicated (not indicated) |
| De | Away from | Dehydrate (remove water from); dedentition (removal of teeth) |
| Di | Twice, double | Diplopia (double vision); dichromatic (two colors) |
| Dia | Through, apart, across, completely | Diaphragm (wall across); diapedesis (ooze through); diagnosis (complete knowledge) |
| Dis | Reversal, apart from, separation | Disinfection (apart from infection); disparity (apart from equality); dissect (cut apart) |
| Dys | Bad, difficult, disordered | Dyspepsia (bad digestion); dyspnea (difficult breathing); dystopia (disordered position) |
| E, ex | Out, away from | Enucleate (remove from); eviscerate (take out viscera or bowels); exostosis (outgrowth of bone) |
| Ec | Out from | Ectopic (out of place); eccentric (away from center); ectasia (stretching out or dilation) |
| Em, en. | In | Empyema (pus in); encephalon (in the head) |
| Endo | Within | Endocardium (within heart) |
| Epi | Upon, on | Epidural (upon dura); epidermis (on skin) |
| Exo | Outside, on outer side, outer layer | Exogenous (produce outside); exocolitis (inflammation of outer coat of colon) |
| Extra | Outside | Extracellular (outside cell); |
| Hemi | Half | Hemiplegia (partial paralysis); hemianesthesia (loss of feeling on one side of body) |
| Hyper | Over, above, excessive | Hyperemia (excessive blood); hypertrophy (overgrowth); hyperplasia (excessive formation) |
| Hypo | Under, below, deficient | Hypotension (low blood pressure); hypothyroidism (deficiency or underfunction of thyroid) |
| Im, in | In, Into | Infiltration (act of filtering in);immersion (act of dipping in); injection (act of forcing liquid into) |
| Im, in | Not | Involuntary (not voluntary);immature (not mature); inability (not able) |
| Infra | Below | Infraorbital (below eye); infraclavicular (below clavicle or collarbone) |
| Inter | Between | Intercostal (between ribs); intervene (come between) |
| Intra | Within | Intracerebral (within cerebrum); intraocular (within eyes); intraventricular (within ventricles ) |
| Intro | Into, within | Introversion (turning inward); introduce (lead into) |
| Meta | Beyond, after,change | Metamorphosis (change of form); metastasis change (beyond original position) |
| Opistho | Behind, backward | Opisthotic (behind ears); opisthognathous (beyond jaws) |
| Para | Beside, beyond,near to | Paracardiac (beside the heart); paraurethral (near the urethra) |
| Per | Through,excessive | Permeate (pass through); perforate (bore through) |
| Peri | Around | Periosteum (around bone) |
| Post | After, behind | Postpartum (after childbirth); postocular (behind eye) |
| Pre,Pro | Before, in front of | Premaxillary (in front of maxilla),prognosis (foreknowledge); prophase (appear before) |
| Re | Back, again,contrary | Reflex (bend back); revert (turn again to); regurgitation (backward flowing, contrary to normal) |
| Retro | Backward,located behind | Retrocervical (located behind cervix); retrograde (going backward); retrolingual. (behind tongue) |
| Semi | Half | Semicartilaginous (half cartilage); semilunar(halfmoon); semiconscious (half conscious) |
| Sub | Under | Subcutaneous (under skin); subarachnoid (under arachnoid); subungual (under nail) |
| Super,Supra | Above, upper, excessive | Supercilia (upper brows);suprasternal (above sternum); suprascapular (on upper part of scapula) |
| Sym, syndrome | Together, with | Symphysis (growing together); synapsis (joining together); synarthrosis (articulation of joints together) |
| Trans | Across, through, beyond | Transection (cut across); transduodenal (through duodenum); transmit (send beyond) |
Table of Suffixes
| Suffix | Use | Example |
|---|---|---|
| al, c, ious | Add to nouns to make adjectives expressing relationship, concern, or pertaining to | Neural (referring to nerve); neoplastic (referring to neoplasm); cardiac (referring heart); delirious ( suffering from delirium) |
| ent | Add to verbs to make adjectives or nouns of agency | Recipient (one who receives); concurrent (happening at same time) |
| id | Add to verbs or nouns to make adjectives expressing state or condition | Flaccid (state of being weak or lax); fluid (state of being liquid) |
| ia, ity | Add to adjectives or nouns to make nouns expressing quality or condition | Septicemia (poisoning of blood); disparity (inequality); acidity (condition of excess acid) |
| ible, ile | Add to verbs to make adjectives expressing ability or capacity | Contractile (ability to contract); edible (capable of being eaten) |
| ium, olus, olum, culus, culum, cule, cle | Add to nouns to make diminutive nouns | Add to nouns to make diminutive nouns |
| ous | Add to nouns to make adjectives expressing material | Ferrous (composed of iron); serous (composed of serum); mucinous (composed of mucin) |
| oid, form | Add to nouns to make adjectives expressing resemblance | Polypoid (resembling polyp); plexiform (resembling a plexus); fusiform (resembling a fusion); epidermoid (resembling epidermis) |
Table of Basics Verbal Derivatives From Greek & Latin
| Root | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Algia | Pain | Cardialgia (heart); gastralgia (stomach); neuralgia (nerve) |
| Cau,caus | Burn | Caustic (suffix added to make adjective); cauterization; causalgia (burning pain); electrocautery |
| Centesis | Puncture, perforate | Thoracocentesis (chest); pneumocentesis (lung); arthrocentesis (joint); enterocentesis (intestine) |
| Clas, claz | Smash, break | Osteoclasis (bone); odontoclasis (tooth) |
| Duct | Draw | Ductal (suffix added to make adjective); oviduct (egguterine tube or fallopian tube); periductal (per means around); abduct (prefix meaning lead away from) |
| Dynia | Pain | Mastodynia (breast); pleurodynia (chest); esophagodynia (esophagus); coccygodynia (coccyx) |
| Ecta,ectas | Dilate | Venectasia(dilation of vein); cardioectasis (heart); ectatic (suffix added for adjective) |
| Edem | Swell | Myo edema (muscle); lymphedema (lymph);(a is a suffix added to make a noun) |
| Esthes | Feel | Esthesia (suffix added to make noun); anesthesia (an is prefix) |
| Fiss | split | Fissure; fission (suffixes added to make nouns) |
| Flex,flec | Bend | Flexion (suffix added to make noun); flexor (suffix added); anteflect, (prefix added meaning before bending forward) |
| Flu, Flux | Flow | Fluctuate; fluxion; affluent (abundant flowing) |
| Iatro, iatr | Treat, cure | Geriatrics (old age); pediatrics (children) |
| Kine,kino,kineto,kinesio | Move | Kinetogenic (producing movement); kinetic (suffix added to make adjective); kinesiology (study) |
| Liga | Bind | Ligament (suffix added to make noun) ligat ligature |
| Logy | Study | Parasitology (parasites); bacteriology (bacteria); histology (tissues) |
| Lysis | Breaking up, dissolving | Hemolysis (blood); glycolysis (sugar); autolysis (selfdestruction of cells) |
| Morph,morpho | Form | Amorphous (no definite form); pleomorphic (more occurring in various forms polymorphic (many) |
| Olfact | Smell | Olfactophobia (fear); olfactory (suffix added to make adjective) |
| Op,opto | See | Amblyopia (dull dimness of vision); presbyopia (old impairment of vision in old age); myopia (myein, meaning shut nearsighted);optic |
| Palpit | Flutter | Palpitation |
| Par,partus | Labor | Postpartum (after birth); parturition (act of giving birth); para i, ii, iii, iv, etc., are symbols of number of births |
| Pep | Digest | Dyspepsia (bad, difficult); peptic (suffix added to make adjective) |
| Pexy | Fix | Mastopexy (fixation of breast); nephrosplenopexy (surgical fixation of kidney and spleen |
| Phag,phago | Eat | Phagocytosis (eating of cells); phagomania (madness mad craving for food or eating); dysphagia (difficult eating or swallowing) |
| Phan,phas | Appear visible | Phanerosis (act of becoming visible); phantasia; phantasy; phasmophobia (fear of ghosts) |
| Phas | Speak | Aphasia (unable to speak); dysphasia (difficulty in speaking) |
| Phil | Love | Hemophilia (blood a hereditary disease characterized by delayed clotting of blood); acidophilia (acid stain liking or staining with acid stains); |
| Phobia | Fear | Hydrophobia (fear of water); photophobia (fear of light); claustrophobia (fear of close places |
| Phrax,phrag | Fence off, wall off | Diaphragm (across partition separating thorax from abdomen); phragmoplast (formed) |
| Plas | Form, grow | Choledochoplasty (common bile duct);neoplasm (new growth); rhinoplasty (nose operation for formation of nose); otoplasty (ear); |
| Plegia | Paralyze | Paraplegia (paralysis of lower limbs); ophthalmoplegia (eye); hemiplegia (partial paralysis) |
| Pne,pneo | Breathe | Dyspnea (difficult breathing); apnea (lack of breathing); hyperpnea. (overbreathing) |
| Poie | Make | Hematopoiesis (blood); erythropoiesis (red blood cells); leukopoiesis ( ' white blood cells) |
| Ptosis | Fall | Proctoptosis (anus prolapse of anus); splanchnoptosis (viscera) |
| Rrhagia | Burst forth, pour | Menorrhagia (abnormal bleeding during menstruation); menometrorrhagia (abnormal uterine bleeding); hemorrhage (blood) |
| Rrhaphy | Suture | Herniorrhaphy (suturing or repair of hernia); hepatorrhaphy (Jiver); nephrorrhaphy (kidney) |
| Rrhea | Flow, discharge | Leukorrhea (white discharge from vagina); galactorrhea (milk discharge); rhinorrhea (nasal discharge) |
| Rrhexis | Rupture | Enterorrhexis (intestines); metrorrhexis (uterus) |
| Schiz | Split, divide | Schizophrenia (mind split personality); schizonychia (nails); schizotrichia (hair) |
| Scope | Examine | Microscopic; cardioscope; endoscope (endo means within an instrument for examining the interior of a hollow viscus) |
| Stasis | Stop, stand still | Hematostatic (pertaining to stagnation of blood);epistasis (checking or stopping of any discharge) |
| Stazien | Drop | Epistaxis (nosebleed) |
| Teg,tect | Cover | Tegmen; tectum (rooflike structure); integument (skin covering) |
| Therap | Treat, cure | Therapy; neurotherapy (nerves); chemotherapy (chemicals); physiotherapy |
| Tomy | Cut, incise | Phlebotomy (incision of vein); arthrotomy (joint); appendectomy (ectomy, meaning cut out excision of appendix); oophorectomy (excision of ovary); ileocecostomy (ostomy, meaning creation of an artificial opening, and os, pertaining to opening or mouth thus, an anastomosis of ileum and cecum) |
| Tropho | Nourish | Hypertrophy (enlargement or overnourishment); atrophy (undernourishment) |
| Volv | Turn | Volvulus (twisting of an organ, intestinal obstruction with twisting of bowel, or twisting of the esophagus) |
Table of Combining Forms
| Form | Meaning | Form | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adeno – | gland | Adreno – | adrenal gland |
| Angio – | vessel | Ano – | anus |
| Arterio – | artery | Arthro – | joint |
| Balano – | glans penis | Blepharo – | eyelid |
| Broncho – | bronchus (windpipe) | Cantho – | canthus |
| Capit – | head | Cardi- or cardio – | heart |
| Carpo – | wrist | Cephalo – | head |
| Cerebello – | cerebellurn | Cerebro – | cerebrum |
| Cheilo – | lip | Chole – | bile |
| Chondro – | cartilage | Chordo – | cord or string |
| Cilia – | hair (Latin) | Cleido – | collarbone |
| Coccygo – | coccyx | Colpo – | vagina |
| Cordo – | cord | Coxa – | hip |
| Coccygo – | coccyx | Cranio – | head |
| Cysto – | sac, cyst, or bladder | Cyto – | cell |
| Dacryo – | tear | Dento- or donto – | tooth |
| Derma- | skin | Duodeno – | duodenum |
| Emia – | blood | Encephalo – | blood |
| Entero – | intestines | Fascia – | sheet or band of fibrous tissue |
| Fibro – | fibers | Gastro – | stomach |
| Genu – | knee | Gingivo – | gums |
| Glomerulo – | glomerulus | Glosso – | tongue |
| Gnatho – | jaw | Hallux – | great toe |
| Hem, hema,hemo, hemato – | blood | Hepato – | liver |
| Hilus – | pit or depression in an organ where vessels and nerves enter | Histio – | tissue |
| Hystero – | uterus | Ileo – | ileum (part of small intestine) |
| Ilio – | flank or ilium (bone of the pelvis) | Jejuno – | jejunum (part of small intestine) |
| Kerato – | cornea or horny layer of the skin | Labio – | lips |
| Lacrimo – | tears | Laparo – | loin or flank (also refers to abdomen) |
| Laryngo – | larynx | Linguo – | tongue |
| Lympho – | lymph | Masto – | breast |
| Meningo – | meninges (coverings of the brain and spinal cord) | Metra,metro – | uterus |
| Myelo – | bone marrow and also spinal cord | Myo – | muscle |
| Myringo – | eardrum | Naso – | nose |
| Nephro – | kidney | Neuro – | nerve |
| Oculo – | eye | Odonto – | tooth |
| Omphalo – | navel or umbilicus | Onycho – | nails |
| Oophoro – | ovary | Ophthalmo – | eye |
| Orchio,orchido – | testis | Oro – | mouth |
| Os –,Osteo- | mouth | Ovario – | ovary |
| Palato – | palate of mouth | Palpebro – | eyelid |
| Pectus – | breast, chest, or thorax | Pharyngo – | pharynx |
| Phlebo – | vein | Pilo – | hair |
| Pleuro – | pleura of lung | Pneumo or pneumono – | lungs |
| Procto – | rectum | Pyelo – | pelvis of kidney |
| Pyloro – | pylorus (part of stomach just be fore duodenum) | Rhino | nose |
| Sacro – | sacrum | Salpingo – | fallopian tube or oviduct |
| Sialo – | saliva | Splanchno – | viscera |
| Spleno – | spleen | Sterno – | sternum |
| Stoma – | mouth | Tarso – | instep of foot; ankle |
| Teno,tenonto – | tendon | Thoraco – | thorax or chest |
| Trachelo – | neck, particularly the neck of the uterus | Tracheo – | trachea |
| Unguis – | nail | Uretero – | ureter |
| Urethro – | urethra | Uro – | urine |
| Vaso – | vessel | Veno – | vein |
| Ventriculo – | ventricle | Viscero – | viscera |
Medical Glossary
'See also Wikipedia, Medical Dictionary
A
| Words | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Anatomy | A science of the structure of the body and the relationship of its constituent parts to each other. |
| Alveoli | Air sacs in the lungs formed at the terminals of a bronchiole.The thin membrance of the alveoli lets oxygen enter the blood stream. |
| Aorta | The largest artery in the body.It carries blood from heart to be distributed by branch arteries through the body. |
| Aortic valve | Outlet valve from left ventricle to the aorta. |
| Arrhythmia | An irregular heartbeat.The heart may beat too fast (tachycardia), too slowly (bradycardia) |
| Arteriole | A small diameter blood vessel in the microcirculation that extends and branches out from an artery and leads to capillaries. |
| Artery | A vessel through which the blood is pumped away from the heart. |
| Atrio ventricular | Located between an atrium and ventricle of the heart. |
| Atrium | A main chamber of the heart into which blood returns from circulation |
| Auscultation | The term for listening to the internal sounds of the body, usually using a stethoscope. |
| Axon | A nerve fibre in a neuron. |
B
| Words | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Bioelectricity | Electric potentials and currents produced by or occurring within living organisms. |
| Brachial | pertaining to the arm |
| Bradycardia | A slow heart rate. |
| Bronchus | A passage of airway in the respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. |
| Bundle of His | A small band of cardiac muscle fibers transmitting the wave of depolarization from the atria to the ventricles during cardiac contraction. |
| Bifurcation | The splitting of a main body into two parts. Branching as in blood vessel. |
C
| Words | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Capillaries | The smallest of a body's blood vessels system connecting arterioles with venules and forming or network throughout. |
| Cardiac | Having to do with the heart. |
| Cardiology | A medical special area dealing with disorders of the heart be it human or animal. |
| Cardiovascular | Relating to the circulatory system, which comprises the heart and blood vessels and carries nutrients and oxygen to the tissues of the body and removes carbon dioxide and other wastes from them. |
| Catheter | a thin tube device extruded from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. |
| Cell | The basic structural, functional and biological unit of all known living organisms. |
| Cerebellum | A region of the brain that plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions |
| Collagen | The major structural protein of the various connective tissues in animals. |
| Computerised Axial tomography (CAT) | Commonly known by its abbreviated name, CAT scan or CT scan. An x-ray procedure which combines many x-ray images with the aid of a computer to generate cross-sectional views |
| Cortex | The outermost layered structure of neural tissue of the cerebrum (brain), |
| Cranium | The part of the skull that encloses the brain. |
D
| Words | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Defibrillation | A common treatment for life-threatening cardiac dysrhythmias, ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia. Defibrillation is composed of delivering a therapeutic dose of electrical energy to the heart with a device called a defibrillator. |
| Diastole | The period of time when the heart refills with blood after systole (contraction). |
| Diastolic | Referring to the time when the heart is in a period of relaxation and expansion (dilatation). |
| Dicrotic | Relating or being to the second part of the arterial pulse occurring during diastole of the heart or of an arterial pressure recording made during the same period. |
E
| Words | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Electro cardiogram(ECG or EKG from Greek) | The recording of the electrical activity of the heart. |
| Embryo | An organism in the early stages of growth and differentiation, from fertilization to the beginning of the third month of pregnancy (in humans). |
| Enzyme | A protein secreted by cells that acts as a catalyst to induce chemical changes in other substances and itself remains unchanged
by the process. |
| Epilepsy | A disorder marked by disturbed electrical rhythms of the nervous system. |
F
| Words | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Fluoroscopy | A study of moving body structures—close to an X-ray |
H
| Words | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Hemorheology | The science of rheology of the blood, the relation of pressure,flow volume and resistance to blood vessels. |
| Heparin | A highly sulfated glycosaminoglycan which is used to prevent blood clots from forming in people who have certain medical conditions or who are undergoing certain medical procedures |
| Hormone | Our body's chemical messengers that is produced in all multicellular organisms by glands, and transported by the circulatory system to a distant target organ to control its physiology and behavior. |
| Hypoxia | A condition in which the body or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. |
I
| Words | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Inferior vena cava(IVC) | also referred to as the posterior vena cava. A vein that carries blood from the lower body to the heart. |
| In-vivo | Latin for "within the living".Often employed over in vitro because it is better suited for observing the overall effects of an experiment on a living subject. |
| Ischemic | also spelled as ischaemia or ischæmia.Supply to tissues, causing a shortage of oxygen and glucose needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). |
| Isometric | Comes from the Greek for "having equal measurement". |
| Isotonic | Having equal tension. Having the same concentration of solutes as the blood. Physiology Of or involving muscular contraction in which the muscle remains under relatively constant tension while its length changes. |
K
| Words | Meanings |
|---|---|
| Korotkoff sounds | The blood flow sound that medical personnel listen for when they are taking blood pressure using a non-invasive procedure. |
L
| Words | Meanings |
|---|---|
| Latency | The time required to locate the first bit or character in a storage location, expressed as access time minus word time. |
| Liver | A vital organ of the digestive system present in vertebrates and some other animals |
| Lung | The important respiration organ |
M
| Words | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Membrane | A very thin layer of tissue that covers a 'surface. |
| Metabolism | All the chemical processes inside your body. It depends on your age, gender, muscle-to-fat ratio, the food you eat and physical activity. Your hormones and nervous system control your body’s metabolism. |
| Mitral valve | One of the heart's four valves, opens to allow blood to flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle. |
| Motor | A muscle, nerve or centre that effects or producesmovement. |
| Myelin | An insulating layer, or sheath, that forms around nerves, including those in the brain and spinal cord. It is made up of protein and fatty substances. |
| Myocardium | The middle and thickest layer of the heart wall, composed of cardiac muscle. |
| Myograph | Any device used to measure the force produced by a muscle when under contraction. |
N
| Words | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Necrosis | The death of living cells or tissues. It occurs when there is not enough blood flowing to the tissue, whether from injury, radiation, or chemicals. |
| Nerve | Enclosed bundles of the long fibers or axons.The peripheral nervous system consists mainly of nerves. |
| Neuron | A neuron receives electrical input signals from sensory cells (called sensory neurons) and from other neurons and sends electrical output signals to muscle neurons (called motoneurons or motor neurons) and to other neurons. |
O
| Words | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Orthosis | An orthopedic appliance or apparatus used to support, align, prevent, or correct deformities or to improve function of movable parts of the body. |
| Oxyhaemoglobin | The combination of the red blood haemoglobin cells with the oxygen in the lungs. |
P
| Words | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Pathology | A field of medical science primarily concerning the examination of organs, tissues, and bodily fluids in order to make a diagnosis of disease. |
| Perfuse | To force a fluid through (an organ or tissue) especially by way of the blood vessels |
| Permeate | To spread or diffuse through |
| Pneumograph | Known as a pneumatograph or spirograph.A device for recording velocity and force of chest movements during respiration. |
| Prosthesis | An artificial device that replaces a missing body part, which may be lost through trauma, disease, or congenital conditions. |
| Protein | Macromolecules composed of one or more long chains of amino acid residues |
| Pulmonary | Relating to the lungs |
| Pulse pressure | The difference between the systolic and diastolic pressure readings. |
R
| Words | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Radioisotope | An atom that has an unstable nucleus and emits radiation during its decay to a stable form. |
| Radiology | a medical field that employs the use of imaging to both diagnose and treat disease visualized within the body. |
S
| Words | Meanings |
|---|---|
| (Semilunar) pulmonary valve | A semilunar valve between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery; prevents blood from flowing from the artery back into the heart |
| Sinoatrial | Involving, or being the sinus node. Sinoatrial node indicates the heart's natural pacemaker, one of the major elements in the cardiac conduction system, the system that controls the heart rate. |
| Sphygmomanometer | An apparatus for measuring blood pressure, composed of an inflatable cuff to restrict blood flow, and a mercury or mechanical manometer to measure the pressure. |
| Spirometer | A device for measuring the volume of air inspired and expired by the lungs. |
| Spleen | An organ located just below your rib cage on your left side. It acts primarily as a blood filter. |
| Stenusis | An abnormal narrowing in a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure. |
| Stroke volume | The amount of blood pumped out of the heart (left ventricle - to the body) during each contraction measured in mL/beat (millilitres per beat). It is calculated through measurements of ventricle volumes from an echocardiogram and subtracting the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of a beat (called end-systolic volume) from the volume of blood just prior to the beat (called end-diastolic volume). The stroke volume is not all the blood contained in the left ventricle; normally, only about two-thirds of the blood in the ventricle is expelled with each beat. |
| Superior vena cava | A large vein in the body that carries deoxygenated blood to the right atrium of the heart. It is also commonly referred to as the precava. |
| Systemic | Of or relating to an entire system. medical : Of, relating to, or affecting the entire body. |
| Systole | The time period when the heart is contracting. The period specifically during which the left ventricle of the heart contracts. |
T
| Words | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Tarso – | instep of foot; ankle (also edge of eyelid) |
| Teno,tenonto – | tendon |
| Thoraco – | thorax or chest |
| Thyro – | thyroid |
| Trachelo – | neck, particularly the neck of the uterus |
| Tracheo – | trachea |
U
| Words | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Unguis – | nail |
| Uretero – | ureter |
| Urethro – | urethra |
| Uro – | urine; urinary |
| Utero – | uterus |
V
| Words | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Vaso – | vessel |
| Veno – | vein |
| Ventriculo – | ventricle, either of heart or brain |
| Viscero – | viscera |
Y
Z
Histology
Histology is the study of the microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues. All organs of the body are formed of tissues. A tissue is a collection of similar type cells associated with some intercellular matrix (ground substance) controlled by some laws of growth and development. These cells perform the same functions. Tissues are usually divided into four categories:muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue.
Muscle tissue
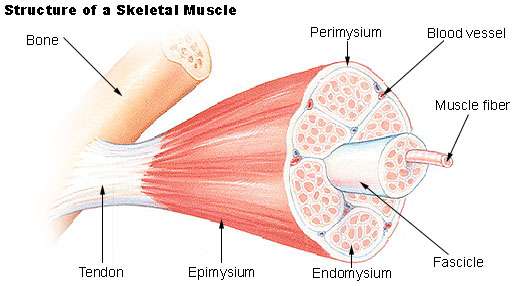
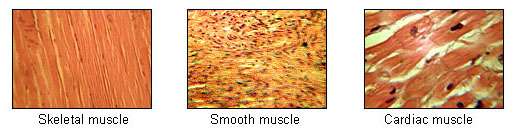
Muscle tissue is composed of "excitable" cells which can contract. Muscle tissue include a lot of microfilaments composed of actin and myosin, which are contractile proteins. There are three major types of muscle tissue:
- Skeletal Muscle:It is attached to bones by tendons and associated with the body's voluntary movements. Skeletal muscle is striated muscle. Unlike cardiac muscle, the cells are not branched.
- Visceral (Smooth) Muscle:It is found in many parts of the body such as the arteries, the bladder, the digestive tract and so on. Visceral muscle is also called smooth muscle as it doesn't have cross striations. Visceral muscle contracts slower than skeletal muscle, but the contraction can be continued for a longer period.
- Cardiac muscle:It is so named because it is found in the heart. Cells are joined to one another by intercalated discs which allow the synchronization of the heart beat. Cardiac muscle is branched, striated muscle.
Nervous tissue
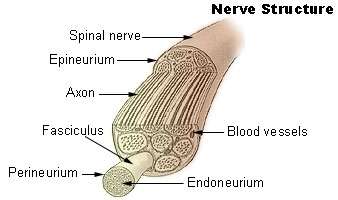
Nervous tissue is specialized to sense stimuli and transmit signals to and from different parts of an organism. The nervous system is split into two parts. One is the central nervous system which includes the brain and spinal cord while the peripheral nervous system contains the cranial and spinal nervous and provides the communication between the CNS and the rest of the body. Two main cell types are neurons and neuroglia. The neurons are the basic structural units of the nervous system. The neuroglia assist the propagation of the nerve impulse and provide nutrients to the neuron. Neurons transmit electricity through their plasma membrane and lose their ability to split once they commit to their roles (after birth). They last a life time and store memory. However, if they are destroyed they cannot be replaced. However with that said, you cannot avoid other parts of the brain to take over functions. Neurons also needs lots of oxygen and glucose and will die within 5 minutes without oxygen. Nervous tissue is composed of various types of nerve cells, all of which having an axon, the long stem-like part of the cell that sends action potential signals to the next cell. Nervous tissue is discussed more in Chapter 3.
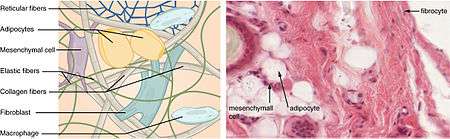
Connective tissue
Connective tissue (CT) supports, connects, or separates various tissues and organs of the body. It is one of the four major type tissues—the others of which are epithelial, muscle, and nervous tissues. Connective tissue can be found everywhere in the body except the central nervous system.
Epithelial tissue
It is one of the four major types tissues. It is related to secretion, selective absorption, protection, transcellular transport and detection of sensation. In Greek ἐπί (epi) means "on" or "upon", and θηλή (thēlē) means "nipple".
Further Reading
- Bronzino, Joseph D. (April 2006). The Biomedical Engineering Handbook, Third Edition. [CRC Press]. ISBN 978-0-8493-2124-5. http://crcpress.com/product/isbn/9780849321245.
- Villafane, Carlos, CBET. (June 2009). Biomed: From the Student's Perspective, First Edition. [Techniciansfriend.com]. ISBN 978-1-61539-663-4. http://www.biomedtechnicians.com.
Practise
Fill up the gaps
- The body consists of the head, ______and limbs. ((a) arms (b) trunks)
- Sagittal plane is parallel to _______ plane.((a)lateral (b) median)
- Nose is _______ to the ears. ((a) anterior (b) posterior)
- Rotation is the movement of a part of the body around its _______axis. ((a) central (b) long)
- All organs of the body are formed of ______.((a) flesh (b) tissue)
- Epithelium is ______ tissue. ((a) covering (b) connecting)
References
- Anatomy & Physiology Workbook For Dummies by Janet Rae-Dupree
- Wikipedia,Anatomical terms of motion.
- Wikipedia,List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes
- Wikipedia, Medical Dictionary
- Medical Terminology Database
- Dictionary of Medicines and Devices
- Medical Dictionary Database for the iPhone
- Medical Terminology Database iPhone
- Wikipedia,Histology